Motivation & Emotion Class 11 Psychology
Introduction
Motivation is the process that initiates and sustains activities aimed at achieving a specific goal. It is influenced by the expectancy-value theory, which suggests that motivation depends on the perceived likelihood of success and the value attached to that success.
Nature of Motivation
- The study of motivation seeks to understand the underlying reasons for human behaviour.
- The term 'motivation' is derived from the Latin word 'movere,' which means 'to move.'
- While motivation plays a crucial role in influencing behaviour, it is not the sole factor. Other components such as instincts, drives, needs, goals, and incentives also contribute to the motivational process.

The Motivation Cycle
- A need is recognized, indicating a deficiency of something important.
- This recognition triggers a state of arousal, referred to as a drive, which propels individuals to take action toward fulfilling their objectives.
- Upon reaching the goal, the drive diminishes, and the individual returns to a balanced state as their needs are met.

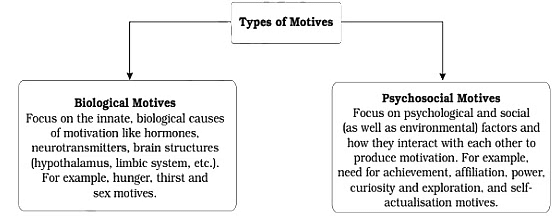
Types of Motive
There are two main types of motives: biological and social-psychological. Biological motives, also called physiological motives, are related to the body's needs and the desire to maintain homeostasis. Social-psychological motives, on the other hand, are influenced by a person's interactions with their environment and various social and psychological factors.
While these two types of motives are different, they are also connected. Sometimes, biological needs can lead to social-psychological motives, and vice versa. It's important to understand that most motives come from a mix of both biological and social-psychological factors, depending on the situation.
Biological Motives
The biological or physiological perspective is one of the earliest ways to understand motivation and behaviour. This view suggests that organisms experience internal physiological imbalances that create needs. These needs generate drives that motivate behaviour aimed at achieving specific goals to alleviate the drive.
- Early theories of motivation often relied on the idea of instinct.
- Instincts are innate patterns of behaviour that are biologically determined rather than learned.
- Common human instincts include curiosity, flight, repulsion, reproduction, and parental care.
- The term instinct refers to a drive to act, pushing the organism to reduce that drive.
- Basic biological needs like hunger, thirst, and sex are crucial for survival and are explained by this approach.
Hunger
- Changes in liver metabolism trigger feelings of hunger.
- The two regions linked to hunger are the Lateral Hypothalamus and the Ventromedial Hypothalamus; stimulating the first region causes hunger, while the second suppresses it.
Thirst
- Drinking water is essential to relieve a dry mouth, which, along with internal body functions, causes the sensation of thirst.
- The urge to drink is mainly triggered by conditions such as water loss from cells, decreased blood volume, and the presence of nerve cells called osmoreceptors in the anterior hypothalamus, which send signals when cells are dehydrated.
Sex
- Sexual motivation is influenced by biological factors and is essential for reproduction.
- Factors such as hormonal changes and social influences play a significant role in sexual behaviour.
Psychosocial Motives
Psychosocial motives are learned through interactions with social groups such as family, neighbours, friends, and relatives. These motives are complex and shaped by one’s social environment.
Need for Affiliation
- Companionship: Most people naturally seek companionship and prefer being with others rather than being alone.
- Group Formation: Individuals tend to form groups and connections with others when they find common interests or similarities.
- Importance of Relationships: Building connections and relationships is a fundamental part of human life.
- Affiliation: The motivation for social contact, known as affiliation, arises when individuals feel vulnerable, helpless, or even content.
- Active Seekers: People with a high need for affiliation actively seek out the company of others and work on nurturing friendly relationships.
Need for Power
- Desire for Influence: The need for power is about wanting to influence others and control resources.
- Goals of Power: This motivation includes goals like influencing, controlling, persuading, leading, and charming others, with the primary aim of enhancing one’s reputation in the eyes of others.
Need for Achievement
- Diligence and Competition: Some students are motivated to work hard and compete for good marks in exams.
- Opportunities: Good grades lead to better opportunities for advanced education and improved job prospects.
- Achievement Motivation: This drive for excellence, known as achievement motivation or n-Ach, guides behaviour and shapes perceptions.
- Development in Childhood: Children develop a sense of achievement motivation during their formative years by absorbing this drive from parents, role models, and cultural influences.
Curiosity and Exploration
- Goal-less Activities: People often engage in activities without a specific goal or purpose, finding pleasure in the activities themselves.
- Curiosity: This motivational tendency involves seeking novel experiences and gaining pleasure from obtaining information.
- Self-Contained Activities: Curiosity describes behavior where the primary motive is the activity itself, rather than an external goal.
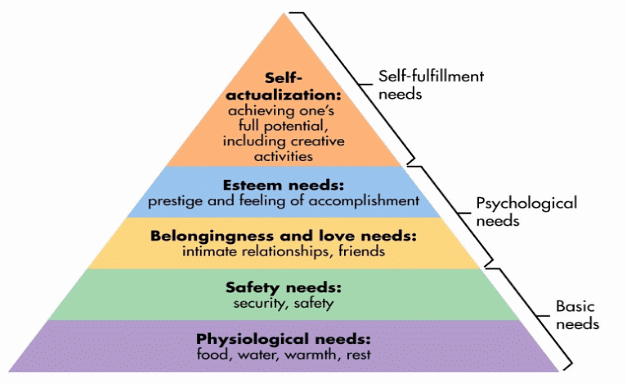
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- Physiological needs are the foundation of Maslow's hierarchy. These are the essential requirements for survival, such as food, water, and warmth.
- Safety needs constitute the second level. This includes the need for protection from harm and danger, as well as job security to ensure financial stability.
- Belongingness needs represent the third level, which involves the pursuit of positive and meaningful relationships and a sense of companionship.
- Esteem needs are part of the fourth level and focus on fostering a sense of self-worth, pride, and accomplishment. These needs contribute to enhanced self-confidence and self-esteem.
- The fifth and final level is self-actualization, which involves realizing one's full potential. A self-actualized individual is self-aware, socially responsive, and willing to embrace challenges.
Understanding Emotions
- Emotions refer to the feelings and moods that individuals experience. These involve a combination of arousal, personal feelings, and the way we interpret these feelings.
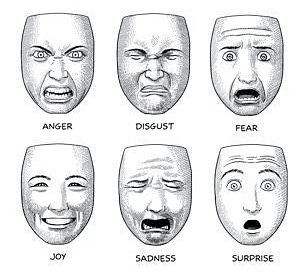
- Emotions can differ in their intensity (how strong they are) and quality (the type of emotion). Basic emotions include anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, and surprise.
- Various theorists have proposed different sets of basic emotions, with some suggesting there could be as many as ten basic emotions.
- Emotions are influenced by personal factors such as gender, personality, and psychological disorders, as well as by the specific situation one is in.
- Generally, women tend to feel emotions more intensely than men. However, men often experience and express anger more frequently and intensely.
- Emotions can also combine to create different emotional states. For example, joy and sadness are typically viewed as opposing feelings, but they can coexist in certain situations.

Culture and Emotional Expression
- Verbal communication involves spoken words and vocal features like pitch and loudness.
- Non-verbal communication includes facial expressions, body movements, and prosocial behaviours.
- Facial expressions are the most common way to convey emotions, indicating both intensity and pleasantness/unpleasantness.
- Research indicates that basic emotional facial expressions are innate and universal across cultures.
- Body movements, such as those seen in dance, also play a role in expressing emotions.
- Gestures and proximal behaviours are important aspects of non-verbal communication.
- Cultural differences can influence how emotions are expressed and gaze patterns during interactions.
- For example, Latin Americans and Southern Europeans tend to make direct eye contact with the person they are speaking to, while Asians, including Indians and Pakistanis, often prefer a more peripheral gaze.
Cultural and Emotional Labeling
- Different cultures have unique ways of describing and categorizing basic emotions.
- For instance, the Tahitian language has 46 different words for what English refers to as "anger."
- In North America, people may use 40 different terms to describe the facial expression of anger and 81 terms for contempt.
- Japanese individuals have various labels for emotions, such as 10 for happiness, 8 for anger, and 6 for disgust.
- Ancient Chinese literature identifies seven emotions: joy, anger, sadness, fear, love, dislike, and liking.
- In ancient Indian literature, eight emotions are recognized: love, mirth, energy, wonder, anger, grief, disgust, and fear.
- Western literature typically acknowledges basic emotions like happiness, sadness, fear, anger, and disgust, while emotions such as surprise, contempt, shame, and guilt are less commonly regarded as basic.
- Despite cultural variations, certain basic emotions are universally expressed and understood.
- Culture plays a significant role in shaping how emotions are expressed and experienced, with display rules influencing when and how emotions are shown.
Handling Negative Emotions
Managing negative emotions is crucial for reducing stress and enhancing our overall well-being. Here are some effective strategies to help manage negative emotions:
- Increase Self-Awareness: Develop a deeper understanding of your own emotions and feelings. This awareness is the first step in managing negative emotions effectively.
- Assess Situations Objectively: Take a step back and evaluate whether a situation is genuinely upsetting or if it's just a temporary reaction. This helps in gaining perspective.
- Practice Self-Monitoring: Regularly review your past achievements, feelings, and experiences. This practice can help you stay grounded and remind you of your capabilities.
- Engage in Modelling: Look at your past successes and use them as motivation. Reminding yourself of what you have accomplished can boost your confidence.
- Use Cognitive Restructuring: Challenge negative thoughts and try to see events from a different, more positive angle. This technique helps in eliminating harmful thought patterns.
- Develop Joyful Interests: Find and nurture hobbies or interests that bring you genuine joy. Engaging in activities you love can significantly improve your mood.
- Choose Positive Friends: Surround yourself with happy and positive individuals. Their positivity can rub off on you and enhance your own happiness.
- Show Empathy: Practice empathy by understanding and acknowledging others' feelings. This can strengthen your relationships and create a supportive environment.
- Build Meaningful Relationships: Focus on developing deep and meaningful connections with others. Mutual support in relationships can help during tough times.
- Get Involved in Community Service: Participating in community service can provide a new perspective on your own challenges while making a positive impact on others' lives.
Managing Your Anger
- Recognizing the Role of Thoughts: Understand that anger is often triggered by our thoughts and perceptions. Being aware of this can help you manage your reactions better.
- Taking Control: Realize that you have the power to control your emotions and reactions. Avoid blaming external factors for your anger.
- Avoiding Negative Self-Talk: Negative self-talk can escalate feelings of anger. Replace negative thoughts with more positive and constructive ones.
- Not Assuming Others' Intentions: Avoid jumping to conclusions about others' intentions. Misinterpretations can lead to unnecessary anger.
- Resisting Irrational Beliefs: Challenge irrational beliefs that fuel your anger. Replace them with more rational and balanced thoughts.
- Finding Constructive Outlets: Look for healthy ways to express your anger, such as talking it out, writing, or engaging in physical activity.
- Introspection: Look inward to identify the root causes of your anger. Understanding the underlying issues can help you manage your reactions better.
- Allowing Time for Change: Change takes time and effort. Be patient with yourself as you work on managing your anger more effectively.
Enhancing Positive Emotions
- Emotions are vital for our adaptation and survival. Negative emotions such as fear, anger, and disgust prepare us to respond swiftly to threats. However, when negative emotions are excessive or inappropriate, they can harm our health and immune system.
- On the contrary, positive emotions like hope, joy, and gratitude energize us and enhance our emotional health. These positive feelings boost our resilience and help us solve problems more effectively.
- Research shows that films triggering positive emotions inspire more ideas and actions compared to those that incite anger and fear.
Ways to Enhance Positive Emotions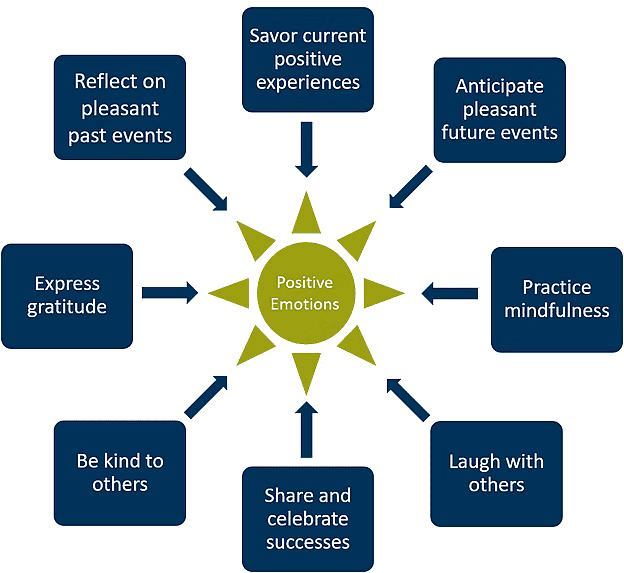
- Cultivating positive personality traits.
- Finding meaning in challenges.
- Maintaining supportive relationships.
- Engaging in fulfilling work.
- Cultivating faith.
- Making positive interpretations of everyday events.
|
43 videos|88 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Motivation & Emotion Class 11 Psychology
| 1. What is the nature of motivation and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of motives according to motivation theories? |  |
| 3. How does Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs explain human motivation? |  |
| 4. How do culture and emotional expression influence our emotional experiences? |  |
| 5. What are effective strategies for handling negative emotions and enhancing positive emotions? |  |






















