Class 9 SST: Sample Question Paper- 5 (With Solutions) PDF Download
Social Science
Time : 3 Hours
M.M.: 80
General Instructions:
1. Question paper comprises five Sections - A, B, C, D and E. There are 32 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
2. Section A : Question no. 1 to 16 are Objective Type Questions of 1 mark each.
3. Section B : Question no. 17 to 22 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
4. Section C : Question no. 23 to 26 are Source Based Questions, carrying 4 marks each.
5. Section D : Question no. 27 to 31 are Long Answer Type Questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
6. Section E : Question no. 32 is Map Based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 32.1 from History (2 marks) and 32.2 from Geography (3 marks).
7. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
8. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section - A
Q.1. Name the imaginary line in India along which time is taken as standard time. (1)
(a) Equator
(b) Standard Meridian
(c) Tropic of Cancer
(d) Tropic of Capricorn
Ans. b
Q.2. Fill in the blank : (1)
The longitudinal valley lying between the lesser Himalayas and the Shiwaliks are known as__________.
(a) Himadri
(b) Duns
(c) Himalayas
(d) Shiwaliks
Ans. b
Q.3. Correct and rewrite the sentences : (1 Mark)
Democracy is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the ministers.
Ans. Democracy is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people.
OR
In Bangladesh, General Pervez Musharraf led a military coup in October 1999.
Ans. In Pakistan, General Pervez Musharraf led a military coup in October 1999.
Q.4. Fill in the blank : (1)
According to ____________ any Indian citizen above 18 years of age has the right to vote, irrespective of caste, colour, status, religion, etc.
(a) Constitution
(b) Preamble
(c) Universal Adult Franchise
(d) Law
Ans. c
Q.5. Study the table and fill in the gaps: (1)
A farmer has grown wheat during different years. Each year the consumption of the farmer remains the same. The whole of surplus wheat after consumption is used as capital for next year’s production. Each year, the production is twice the capital used in production. Complete the table on the basis of the given information.
Choose the correct option:
(a) 120, 120
(b) 120, 80
(c) 100, 60
(d) 100, 90
Ans. a
Q.6. Which group opposed radicals and liberals? (1 Mark)
Ans. The Conservatives
OR
What was Gestapo?
Ans. The secret state police in Nazi Germany was called Gestapo.
Q.7. Choose the correct option from column A and B. (1 Mark)
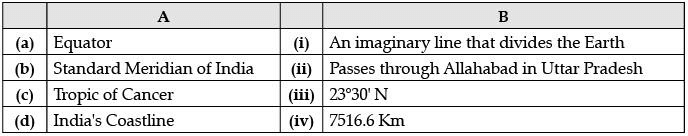
Ans. b
Q.8. Study the given picture carefully : (1 Mark)
 This picture is related to which of the following:
This picture is related to which of the following:
(a) 1956 election
(b) 1962 election
(c) 1967 election
(d) 1972 election
Ans. b
Q.9. Choose the correct option from column A and column B (1 Mark)
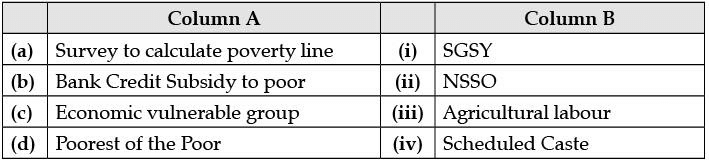
Ans. c
Q.10. Read the following information and write a single term for it : (1 Mark)
In a democratic election like in our country, the list of those who are eligible to vote is prepared much before the election and given to everyone. This list is officially called the Electoral Roll also.
(a) Ballot paper
(b) Manifesto
(c) Name List
(d) Voters' List
Ans. d
Q.11. How many people in Palampur village are engaged in non-farming activities? (1 Mark)
Ans. Around 25%.
Q.12. Correct and rewrite the statement : (1 Mark)
Rulers of other neighbouring countries too were worried by the developments in Prussia and made plans to send troops to put down the events that had been taking place there since the summer of 1791.
Ans. Rulers of other neighbouring countries too were worried by the developments in France and made plans to send troops to put down the events that had been taking place there since the summer of 1789.
OR
Raja Ram Mohan Roy and Jawaharlal Nehru are the two examples of individuals who responded to the ideas coming from revolutionary France.
Ans. Tipu Sultan and Raja Ram Mohan Roy are the two examples of individuals who responded to the ideas coming from revolutionary France.
Q.13. Consider the following statements regarding the Philosophy of the Constitution : (1)
1. Values that inspired and guided the freedom struggle, and were, in turn, nurtured by it, formed the foundation for India’s democracy.
2. These values are embedded in the Preamble of the Indian Constitution.
3. Taking inspiration from American model, most countries in the contemporary world have chosen to begin their Constitutions with a Preamble.
Choose the right option from the following :
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1 and 3
(c) only 1
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. a
Q.14. Choose the incorrect option from the following : (1 Mark)
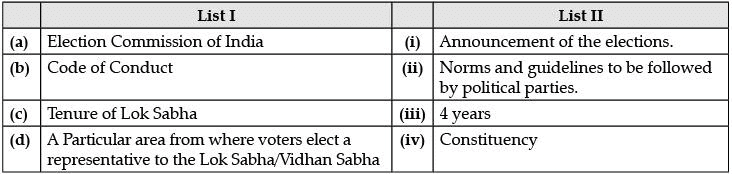
Ans. b
Q.15. Fill in the blank : (1)
Transportation is an example of_______________ activity.
(a) non-farming
(b) farming
(c) manufacturing
(d) mining
Ans. a
Q.16. Fill in the blank : (1 Mark)
______________is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people.
Ans. Democracy
OR
____________ allows every citizen the freedom of religion.
Ans. Secularism
Section - B
Q.17. Distinguish between folding and faulting. (3 Mark)
Ans.
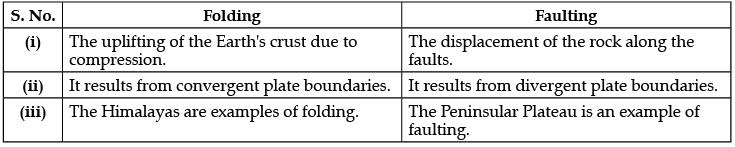
Q.18. ‘Major decisions in a democracy must be taken by elected leaders.’ Justify the statement by giving two reasons and a suitable example. (3 Mark)
Ans. In Pakistan, after passing a law, elections are held to national and state assemblies.(i) So now, elected representatives must have some powers, but final power vests with military officers.
(ii) Those who take final decisions are not elected by the people.
(iii) They have formally elected a parliament and government, but the real power is in the hands of those who are not elected.
OR
Explain the difficulties faced by the people in a non- democratic country.
Ans. Difficulties are:
(i) The people do not choose or change their rulers or representatives.
(ii) No freedom is in the hands of the people. They cannot nearly express their opinions.(iii) People cannot form political associations and organize protest and political actions.
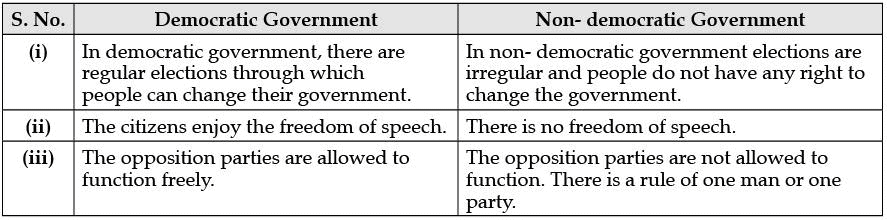
Q.19. Differentiate between a democratic government and a non-democratic government. (3 Mark)
Ans.
Q.20. How did the people of Palampur enhance their production? Explain the methods used for this. (3 Mark)
Ans. Introduction of the Green Revolution with the help of HYV seeds, the yield went up to 3200 kg per hectare, helped the people of Palampur.
Two ways of increasing production:
(i) Multiple cropping : To grow more than one crop on the same piece of land. Even a third crop like potato was also grown.
(ii) Use of modern farming methods : Use of HYV seeds and chemical fertilizers.
Q.21. Describe the incident known as the ‘Bloody Sunday ’. State any two events after the Bloody Sunday which led to the Revolution of 1905 in Russia. (3 Mark)
Ans. The incident of attack by police over protesting workers demanding improvement in working condition in Russia which left many workers killed and wounded, is known as the ‘Bloody Sunday’.
Events after that which led to the Revolution of 1905 in Russia:
(i) Strike took place all over the country, universities closed down.
(ii) Lawyers, doctors, engineers and other middle class workers established the Union of Unions and demanded a Constituent Assembly.
Q.22. Write a short note on Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yojana. (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) PMGY was introduced in 2000.
(ii) Its objective is to focus on village level development in five critical areas, that is, primary health, primary education, rural shelter, drinking water and roads. As a result of this, the quality of life of rural people will improve.
(iii) Rural electrification was added as an additional component from 2001-2002.
Section - C
Q.23. Read the source given below and answer the following questions : (4 Mark)
After February
In April 1917, the Bolshevik leader Vladimir Lenin returned to Russia from his exile. He and the Bolsheviks had opposed the war since 1914. Now he felt it was time for Soviets to take over power. He declared that the war be brought to a close, land be transferred to the peasants and banks be nationalised. These three demands were Lenin's April Theses'. He also argued that the Bolshevik Party rename itself the Communist Party to indicate its new radical aims. Most others in the Bolshevik Party were initially surprised by the April Theses. They thought that the time was not yet ripe for a socialist revolution and the Provisional Government needed to be supported. But the developments of the subsequent months changed their attitude.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
23.1. When did Bolshevik leader Vladmir Lenin returned to Russia from his exile?
(a) In April, 1918
(b) In April, 1915
(c) In April, 1916
(d) In April, 1917
Ans. d
23.2. How many demands were there in Lenin's 'April Theses'?
(a) Three
(b) Five
(c) Four
(d) Two
Ans. a
23.3. Lenin argued that the Bolshevik Party should rename itself as :
(a) Communist Party
(b) Socialist Party
(c) Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
(d) Socialist Revolutionary Party
Ans. a
23.4. Petrograd had led the February Revolution that brought down the :
(a) slavery in February 1917
(b) monarchy in February 1917
(c) clergy in February 1917
(d) nobility in February 1917
Ans. b
Q.24. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Rule of law and respect for rights
Zimbabwe attained independence from White minority rule in 1980. Since then the country has been ruled by ZANU-PF, the party that led the freedom struggle. Its leader, Robert Mugabe, ruled the country since independence. Elections were held regularly and always won by ZANU-PF. President Mugabe was popular but also used unfair practices in elections. Over the years his government changed the constitution several times to increase the powers of the President and make him less accountable. Opposition party workers were harassed and their meetings disrupted. Public protests and demonstrations against the government were declared illegal. There was a law that limited the right to criticise the President. Television and radio were controlled by the government and gave only the ruling party's version. There were independent newspapers but the government harassed those journalists who went against it. The government ignored some court judgments that went against it and pressurised judges. He was forced out of office in 2017.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
24.1. ZANU-PF was Zimbabwe's ____________________ Party. (1)
(a) Democratic Party
(b) Political Party
(c) Ruling Party
(d) Opposition Party
Ans. c
24.2. Who was Robert Mugabe? (1)
(a) Prime-Minister
(b) President
(c) Vice-President
(d) Governor general
Ans. b
24.3. Which nation justifies the example that 'popular governments can be undemocratic'? (1)
(a) China
(b) Saudi Arabia
(c) Zimbabwe
(d) Pakistan
Ans. c
24.4. Whom did the Zimbabwe Government harassed? (1)
(a) The Publishers
(b) The Reporters
(c) The Journalists
(d) The Editors
Ans. c
Q.25. Read the source given below and answer the following questions :
The French Revolution
On the morning of 14 July 1789, the city of Paris was in a state of alarm. The king had commanded troops to move into the city. Rumours spread that he would soon order the army to open fire upon the citizens. Some 7,000 men and women gathered in front of the town hall and decided to form a peoples militia. They broke into a number of government buildings in search of arms. Finally, a group of several hundred people marched towards the eastern part of the city and stormed the fortress-prison, the Bastille, where they hoped to find hoarded ammunition. In the armed fight that followed, the commander of the Bastille was killed and the prisoners released − though there were only seven of them. Yet the Bastille was hated by all, because it stood for the despotic power of the king. The fortress was demolished and its stone fragments were sold in the markets to all those who wished to keep a souvenir of its destruction.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
25.1. How many men and women gathered in front of the town hall? (1)
(a) 5,000
(b) 8,000
(c) 7,000
(d) 6,000
Ans. c
25.2. On 17th July, 1789 the city of Paris was in a state alarm because : (1)
(a) The King had ordered the army to open fire upon the citizens in reality.
(b) Rumours spread that the King would soon order the army to open fire upon the citizens.
(c) There was a foreign attack on the citizens.
(d) The earthquake struck Paris that moment.
Ans. b
25.3. In armed fight who was killed in the 'Fortress of Bastille? (1)
(a) The King
(b) The Minister
(c) The Commander
(d) The Prisoner
Ans. c
25.4. Why did people hate 'Bastille'? (1)
(a) Because it stood for the despotic power.
(b) Because it stood for the armed power.
(c) Because it stood for the man power.
(d) Because it stood for the money power.
Ans. a
Q.26. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow : (4 Mark)
The Cold Weather Season (Winter)
The cold weather season begins from mid-November in northern India and stays till February. December and January are the coldest months in the northern part of India. The temperature decreases from south to the north. The average temperature of Chennai on the eastern coast, is between 24° C - 25° Celsius, while in the northern plains, it ranges between 10°C and 15° Celsius. Days are warm and nights are cold. Frost is common in the north and the higher slopes of the Himalayas experience snowfall.
During this season, the northeast trade winds prevail over the country. They blow from land to sea and hence, for most part of the country, it is a dry season. Some amount of rainfall occurs on the Tamil Nadu coast from these winds as, here they blow from sea to land.
In the northern part of the country, a feeble high-pressure region develops, with light winds moving outwards from this area. Influenced by the relief, these winds blow through the Ganga valley from the west and the northwest. The weather is normally marked by clear sky, low temperatures and low humidity and feeble, variable winds. A characteristic feature of the cold weather season over the northern plains is the inflow of cyclonic disturbances from the west and the northwest. These low-pressure systems, originate over the Mediterranean Sea and western Asia and move into India, along with the westerly flow. They cause the much-needed winter rains over the plains and snowfall in the mountains. Although the total amount of winter rainfall locally known as 'mahawat' is small, they are of immense importance for the cultivation of 'rabi' crops.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
26.1. In cold weather season of winter, the temperature decreases from : (1)
(a) South to the North
(b) East to the West
(c) South to the Earth
(d) North to the West
Ans. a
26.2. Which one of the following characterizes the cold weather season in India? (1)
(a) Warm days and warm nights
(b) Warm days and cold nights
(c) Cold days and cold nights
(d) Cold days and warm night
Ans. b
26.3. Some amount of rainfall occurs on the ________ coast from these winds, as they blow sea to land. (1)
(a) Coromandel
(b) Malabar
(c) Kerala
(d) Tamil Nadu
Ans. d
26.4. Winter rainfall called _________ is of immense importance for the cultivation of __________ crops. (1)
(a) Monsoon Showers, Rabi Crops
(b) Mango Showers, Kharif Crops
(c) Mahawat, Rabi Crops
(d) Kaal Baisakhi, Kharif Crops
Ans. c
Section - D
Q.27. State any five causes for the empty treasury of France under Louis XVI. (5 Mark)
Ans. Five causes for the empty treasury of France under Louis XVI are:
(i) Long years of war had drained the financial resources of France.
(ii) The high cost of maintenance of the immense palace of Versailles and Court.
(iii) Under Louis XVI, France helped the thirteen American colonies to gain independence from Britain.
(iv) War added more than a billion livres to a debt that had already risen to more than 2 billion livres.
(v) Lenders who gave the state credit began to charge high interest on loans.
OR
Why was Nazi propaganda effective in creating a hatred for the Jews? Explain any five reasons.
Ans: Reasons:
(i) The Nazi regime used language and media with care.
(ii) They used chilling terms. They never used the words ‘kill’ or ‘murder’.
(iii) Mass killing was termed as special treatment leading towards the final solution (for the Jews).
(iv) Nazi ideas were spread through visual images, films, radio, posters, etc.
(v) Propaganda films were made to create hatred for Jews.
(vi) They were referred to as vermin, rats, pests. Nazism worked on minds of the people.
Q.28. How is the Arabian Sea branch of Southwest Monsoons responsible for good rainfall in the Northern Plains of India? Why doesn’t it give rain in the Central Peninsula? (5 Mark)
Ans. (i) The part of South west monsoons which blow over the Arabian Sea is responsible for high rainfall on the western coast of India.
(ii) These winds enter through Saurashtra and enter the Northern plains. These winds strike the Himalayas and give fairly good rainfall and they have abandoned moisture.
(iii) South west monsoons are perpendicular to the direction of the Western Ghat thus, they give heavy rainfall on the windward side of the Western Ghat.
(iv) Central Peninsula lies on the leeward side of the Western Ghat. This Arabian Sea branch of South west Monsoon does not reach the region.
OR
Why is biodiversity necessary? Why should it be conserved?
Ans. Biodiversity in a region typically refers to its flora and fauna :
(i) We have selected our crops from a bio- diverse environment of edible plants.
(ii) Animals from large stock provided by nature as milch animal.
(iii) Animals and birds also provided us draught power, transportation, meat, eggs.
(iv) First it provides nutritive food and insects help in pollination of crops and fruit trees and exert biological control on such insects which are harmful.
(v) Every species has a role to play in the ecosystem. Hence, conservation is essential.
(vi) Excessive exploitation of plants and animal resources by humans has disturbed ecosystem endangering many species.
Q.29. Write any three arguments in favour and two against democracy as a form of government. (5 Mark)
Ans. Arguments in favour of democracy:
(i) Democratic form of government is more accountable.
(ii) It improves the quality of decision making.
(iii) It provides a method to deal with differences and conflicts.
(iv) It enhances the dignity of citizens.
(v) It allows us to correct our mistakes.
Arguments against democracy:
(i) Change of leaders leads to instability.
(ii) It involves only political competition with no scope for morality.
(iii) Consulting more people leads to delays.
(iv) It leads to corruption.
(v) Ordinary people don’t know that what is good for them.
Q.30. During 1980s, 80% of Indian population was dependent on agriculture sector but gradually it decreased. Analyse the reasons behind the newly developed trend. (5 Mark)
Ans. (i) In recent years, there has been a decline in the dependence of population on agriculture partly because of the disadvantages caused by disguised unemployment prevalent there.
(ii) Some of the surplus labour in agriculture has moved to either the secondary or the tertiary sector.
(iii) In the secondary sector, small-scale manufacturing is the most labour-absorbing.
(iv) In case of the tertiary sector, various new services are now appearing, like biotechnology, information technology and so on.
(v) With the increase in the number of jobs, dependence on agriculture has reduced to a great extent.
OR
What is the aim of production? Explain labour and human capital as the requirements for production of goods and services.
Ans. The aim of production is to produce the goods and services that satisfy our needs.
(i) Labour: Some production activities require highly educated workers to perform the necessary task. Other activities require manual work. Each worker provides the labour necessary for production.
(ii) Human Capital: We need knowledge and enterprise to be able to put together with land, labour and physical capital and produce an output. This is called human capital.
Q.31. “Legal Framework Order of August 2002 in Pakistan was non-democratic in nature.” Justify by giving five reasons. (5 Mark)
Ans. Reasons are:
(i) President can dismiss the National/Provincial Assemblies.
(ii) Work of civilian cabinet was supervised by military officers.
(iii) National Security Council was dominated by military officers.
(iv) In spite of having elected representatives, final power vests with military officers.(v) Final decisions were taken by those not elected by people.
Section - E
Map Skill based Questions
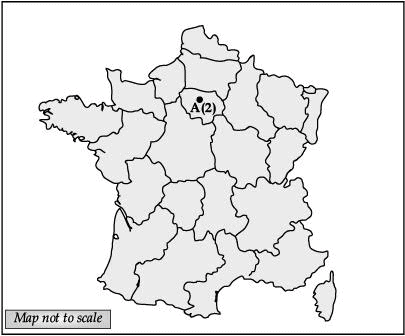
Q.32. (A) 1. On the given political map of France, locate and label: Marseilles
2. Identify the place where the French Revolution occurred: (2 Mark)
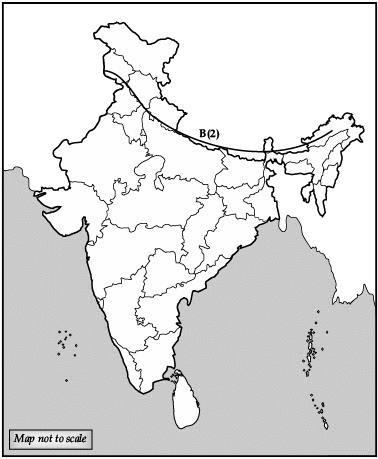
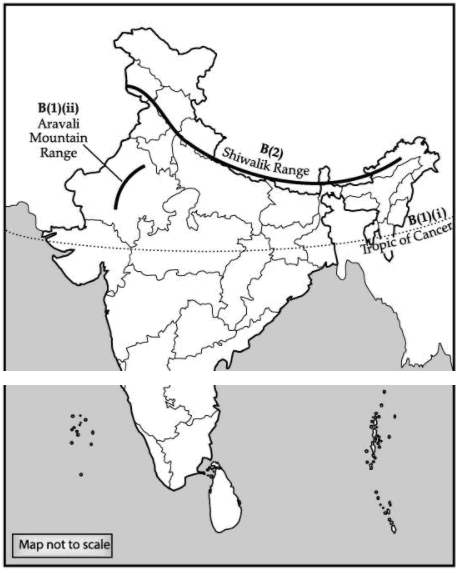
 (B) 1. On the given political map of India, locate and label the following :
(B) 1. On the given political map of India, locate and label the following :
(i) Tropic of Cancer
(ii) Aravalli Mountain Range
2. A feature is marked on the political map. Identify the feature and write its name : Outermost Range of the Himalayas. (3 Mark)
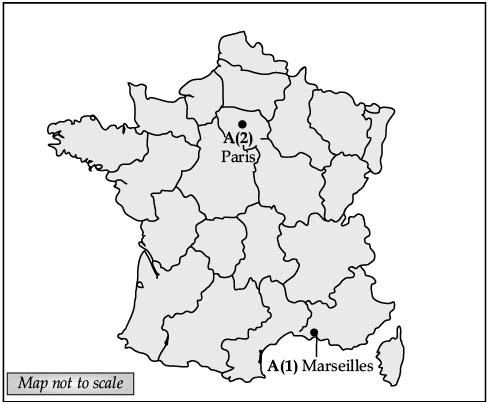
 Ans. (A) 1. Ref. to map work
Ans. (A) 1. Ref. to map work
2. Paris
 (B) 1. Ref. to map work
(B) 1. Ref. to map work
2. Shiwalik Range.
FAQs on Class 9 SST: Sample Question Paper- 5 (With Solutions)
| 1. What is the format of the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 5? |  |
| 2. How many questions are there in the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 5? |  |
| 3. Are solutions provided for the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 5? |  |
| 4. How can the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 5 help in exam preparation? |  |
| 5. Can the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 5 be used for self-study? |  |




















