Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Question Answers - Light
Q. 1. What is reflection of light? State the laws of reflection.
Ans. Reflection is a phenomenon in which a beam of light falls on some surface and returns back in different directions. It may be regular or irregular.
Following are the laws of reflection:
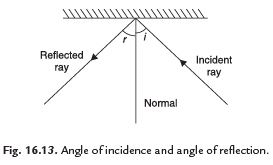
(i) When a ray of light falls on a reflecting surface it is reflected back in such a way that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, i.e. ∠i = ∠r.
(ii) The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane.
Q. 2. What are the characteristics of image formed by plane mirror?
Ans. Characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror are:
(i) Plane mirror forms virtual images.
(ii) Plane mirror forms erect images.
(iii) Image is laterally inverted.
(iv) Image formed is of the same size as the object.
(v) The distance of image from the mirror is equal to the distance of object from the mirror.
Q. 3. How will you prove that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Ans. Draw lines showing the position of the plane mirror, the incident ray and the reflected ray on the paper with the help of your friends. Remove the mirror. Draw a line making an angle of 90º to the line representing the mirror at the point where the incident ray strikes the mirror. This line is known as the normal. The angle between the normal and incident ray is called the angle of incidence (∠i). The angle between the normal and the reflected ray is known as the angle of reflection (∠r). Measure the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. Repeat the activity several times by changing the angle of incidence. You will see that at every time the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. This proves that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Q. 4. Explain the structure and working of a human eye.
Ans. The eye has a roughly spherical shape. The outer coat of the eye is white. It is tough so that it can protect the interior of the eye from accident. Its transparent front part is called cornea. Behind the cornea, we find a dark muscular structure called iris. In the iris, there is a small opening called pupil. The size of the pupil is controlled by the iris. The iris controls the amount of light entering into the eye. Behind the pupil of the eye is a lens which is thicker at the centre. The lens focuses light on the retina. The retina contains several nerve cells. Sensations felt by the nerve cells are then transmitted to the brain through the optic nerves. There are two kinds of cells; cones and rods.
Q. 5. What is Braille system? Explain.
Ans. Braille is a method of writing for visually challenged person. This system was invented by Louis Braille in 1821 and adopted in 1932. He was also a blind person. In this method text is written on a thick paper using special symbols representing the letters of alphabet. Groups of dots are employed to write letters. There is Braille code for common languages, Mathematics and Scientific notation. Braille system has 63 dots patterns. Each pattern represents a letter, a combination of letters, a common word or a grammatical sign. Dots are arranged in cells of two vertical rows of three dots each. Codes of music and mathematics are different. Any language can be read through the codes of Braille.

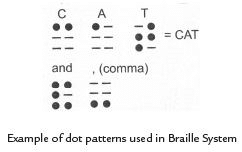
Fig. 16.15
|
92 videos|419 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Question Answers - Light
| 1. What is light and how does it travel? |  |
| 2. What is the speed of light and how was it determined? |  |
| 3. How does light interact with matter? |  |
| 4. What are the different colors of light and how are they produced? |  |
| 5. How does light affect our daily lives? |  |

















