Forests - Our Lifeline Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 12
| Table of contents |

|
| Visit to a Forest |

|
| Forestry Structure |

|
| What is Food Chain? |

|
| Why are Forests called Green Lungs of the Planet? |

|
| What is Deforestation? |

|
| Conservation of Forests |

|
| Keywords |

|
Forests are vital ecosystems are interconnected systems. They provide habitats for various plants and animals, which rely on each other and their environment for sustenance. Trees form the backbone of the forest, with layers of vegetation providing food and shelter for different species. The diverse components of forests, including soil, water, and living organisms, interact dynamically, contributing to the ecosystem's stability and health.

What is a Forest?
A forest is a dense ecosystem rich in biodiversity, comprising various layers from the emergent layer to the forest floor. It requires specific temperature and rainfall conditions for its growth.
Forests act as natural green lungs and water purification systems to the world.
Visit to a Forest
Have you ever visited a forest? Do you wonder what it could be like if you visit one? Let's take you through this journey!- When you enter the forest, you'll see a thick green cover of treetops. The trees are so tall and close together that you might not see the ground below.
- The forest is peaceful with a cool breeze that feels refreshing.
- While you're exploring, you might hear birds chirping and rustling in the trees. Sometimes, monkeys in the trees make noises that can scare the birds, but this is normal in the forest.
- In the deeper parts of the forest, there are many animals like wild boar, bison, jackals, porcupines, and even elephants.
- It's important to stay on the paths and not go too far into the forest to stay safe.
- In the forest, the ground can be bumpy and covered with many trees. You might see different kinds of trees like sal, teak, neem, and bamboo. There are also shrubs, herbs, and grasses all around.
- The forest floor and the trees are often covered with vines and creepers. The sunlight doesn't shine through very brightly because the leaves of the trees make it quite dark inside the forest.

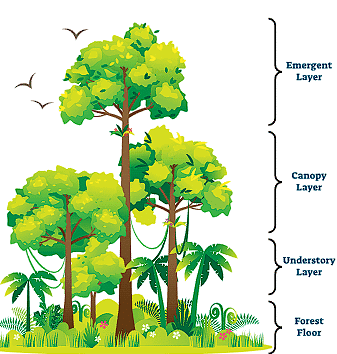
Forestry Structure
1. Layer of Emergence: This is the highest layer in the forest, with very tall trees that stand above the rest. These trees have crowns at their tops and are home to birds and lighter animals. They get a lot of sunlight and face stronger winds.
2. Canopy: The canopy is the thick layer of leaves and branches formed by the tops of trees in the forest. It blocks most of the sunlight from reaching the layers below, making it shady. Many animals live in this layer, using the abundant food and shelter it offers.
3. Understory: The understory is the layer just below the canopy, made up of smaller trees, bushes, and vines. It gets less sunlight because of the dense leaves above, leading to high humidity. This layer supports many different animals that thrive in these conditions.
4. Forest Floor: The forest floor is the bottom layer of the forest. It's covered with fallen leaves, branches, and other organic material. Microorganisms break down this material, releasing nutrients that help plants and other species grow. This layer is home to insects, fungi, and small animals.
What is Food Chain?
A food chain is a way to show how energy flows through an ecosystem by showing who eats whom. It starts with producers like plants, which make their own food. Next, consumers eat the producers, and then other consumers eat those consumers. This helps scientists understand how different living things depend on each other and how energy moves through the ecosystem.

A food chain shows how energy and nutrients flow from one living thing to another in an ecosystem. Here’s a simple example:
- Sunlight: The sun provides energy for plants.
- Plants: Plants use sunlight to make their own food through a process called photosynthesis. They are known as producers.
- Herbivores: Animals that eat plants are called herbivores. For example, a rabbit eats the plants.
- Carnivores: Animals that eat herbivores are called carnivores. For example, a fox eats the rabbit.
- Decomposers: When plants and animals die, decomposers like bacteria and fungi break them down and return nutrients to the soil.
Note: The organisms and micro-organisms that live under the soil consume dead plant and animal tissues and transform them into a dark substance known as humus. These organisms and micro-organisms are called decomposers. Humus helps release the nutrients from dead plants and animals into the soil. These nutrients are then absorbed by the roots of living plants.
Decomposers break down dead plants and animals into nutrients that enrich the soil. Some examples include:

These decomposers play a crucial role in recycling nutrients in ecosystems.
So, a simple food chain might look like this:
Sunlight → Plants → Rabbit → Fox → Decomposers.
This chain shows how energy moves from the sun to plants, then to animals that eat plants, and finally to animals that eat those animals, with decomposers helping to recycle nutrients.

What is Food Web?
A food web is a map of many food chains in an ecosystem. It shows how different plants and animals are connected through what they eat. It helps us see all the different ways living things depend on each other for food.

Why are Forests called Green Lungs of the Planet?
Forests are known as green lungs for various reasons like:
Oxygen Production: Plants use photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into oxygen. This oxygen is essential for animals and humans to breathe.
Support for Respiration: By releasing oxygen, plants help animals and humans breathe. Animals rely on this oxygen for survival.
Atmospheric Balance: Plants play a key role in regulating the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. They absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, helping to maintain a stable atmosphere.
Due to their crucial role in producing oxygen and maintaining atmospheric balance, forests are often called the "lungs" of the Earth.
 Forests as Lungs of the Planet
Forests as Lungs of the Planet
Why are Forests called Dynamic Living Entity?
Let's understand why forests are called a dynamic living entity:
Diverse Plant Life: Forests host a wide variety of plants, offering more food and habitats for herbivores.
Support for Herbivores: A larger number of herbivores creates more food sources for various carnivores.
Animal Diversity: The variety of animals in the forest contributes to its regeneration and growth.
Nutrient Recycling: Decomposers play a crucial role in recycling nutrients, which supports the growth of new plants.
Because of its vibrant plant and animal life, the forest is considered a "dynamic living entity," teeming with vitality and activity.
How do Forests Protect us against Floods?
Forests play an important role in regulating water levels and protecting soil.
Rainwater Absorption: Forests act as natural absorbers of rainwater, allowing it to seep into the ground and helping to maintain the water table throughout the year.
Flood Control: Forests help control floods by absorbing excess rainwater and reducing runoff, which prevents water from accumulating in large quantities.
Stream Flow Maintenance: Forests help maintain a steady flow of water in streams by regulating the amount of water that reaches them.
- Soil Protection: Tree roots bind the soil together, preventing erosion. Without trees, rain can wash away or erode the soil, leading to damage and loss of land.
Importance of Forests
- Forests provide essential resources for human survival, including timber, food, medicines, and industrial raw materials.
- They also play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by regulating rainfall, reducing noise pollution, preventing soil erosion, and supporting biodiversity.
What is Deforestation?
Deforestation is the process of cutting down or removing trees from a forest. This can happen to make space for farming, building, or other activities. When trees are removed, it can harm animals and plants that live in the forest and can lead to problems like soil erosion and loss of habitats.
Effects of Deforestation
- Deforestation leads to an increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, contributing to climate change by raising Earth's temperature.
- Wildlife will suffer from lack of habitat and food sources.
- Deforestation can disrupt the natural water cycle, leading to soil erosion and increased flooding risks. This poses risks to both human lives and the environment.
Conservation of Forests
Forests can be conserved in a variety of ways:
Sustainable Logging: Cut trees in a way that lets the forest grow back.
Reforestation: Plant new trees where forests were cut down.
Protected Areas: Create parks and reserves to keep animals and plants safe.
Community Involvement: Get local people involved in taking care of forests.
Legal Frameworks: Make and follow rules to stop illegal logging.
International Cooperation: Work with other countries to protect forests.
Keywords
1. Canopy: The canopy is the thick layer of leaves and branches formed by the tops of trees in the forest. It blocks most of the sunlight from reaching the layers below, making it shady. Many animals live in this layer, using the abundant food and shelter it offers.
2. Crown: The crown of a tree is the upper part, including the branches and leaves or needles. It forms the topmost layer of the tree and is responsible for providing shade. Canopies consist of tree crowns.
3. Decomposers: Decomposers break down dead plants and animals into nutrients that enrich the soil.
4. Deforestation: Deforestation is the process of cutting down or removing trees from a forest. This can happen to make space for farming, building, or other activities.
5. Humus: Humus is a dark substance that forms in the soil when organisms and micro-organisms break down dead plant and animal material.
6. Regeneration: Regeneration of a forest is the process of a forest recovering and growing back after disturbances. Animals help this process in various ways - by decomposing and enriching the soil, as well as by seed dispersal.
7. Seed dispersal: Seed dispersal in a forest is the way seeds are spread from one location to another where they can grow. This can happen through various methods, such as being carried by wind, water, or animals. Animals disperse seeds by eating and dropping them, carrying them to new places, or having seeds stick to their fur or feathers.
8. Soil erosion: Soil erosion is the process where wind or water carries away the top layer of soil. This can lead to the loss of fertile soil, which is important for growing plants, and can cause problems like land degradation and reduced crop yields.
9. Understory: The understory is the layer just below the canopy, made up of smaller trees, bushes, and vines. It gets less sunlight because of the dense leaves above, leading to high humidity. This layer supports many different animals that thrive in these conditions.
|
111 videos|246 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Forests - Our Lifeline Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 12
| 1. What is the importance of forests in maintaining ecological balance? |  |
| 2. How does deforestation affect the environment? |  |
| 3. What steps can be taken for the conservation of forests? |  |
| 4. Why are forests referred to as the "Green Lungs of the Planet"? |  |
| 5. What is the concept of a food chain in forests? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|


















