Class 12 Economics Short Questions With Answers (Part - 2) - Introduction to Micro Economics
Q.11. What is a planned economy?
Ans. A planned economy is an economy in which the economic activities are planned by the central government to maximize social welfare.
Q.12. Why does the problem of what to produce arise? Explain
Ans. The problem of what to produce arises as the economy has limited resources. Because of the scarcity of resources producers are unable to produce everything in the desired quantity, but they will have to make a choice. This problem involves a twofold kind of decision, the kinds of goods to be produced and the quantity of goods to be produced.
Q.13. Why do problems related to the allocation of resources in an economy arise? Explain.
Ans. Problems related to the allocation of resources in an economy arise due to the following two basic features of resources:
(a) Resources are Limited: The resources used to produce goods and services that satisfy human wants are limited. Limited resources are incapable of satisfying unlimited human wants.
(b) Limited Resources have Alternative Uses: The resources used for producing goods and services are not only limited but they also have many competing usages. As a result, an individual has to face the problem of choosing among the available alternatives.
Q.14. Why is the Production Possibility Curve downward-sloping?
Ans. It is a curve which shows various production possibilities with the help of limited resources and technology. It is downward sloping from left to right because, in a situation of fuller utilization of the given resources, production of both goods cannot be increased together.
Example: More of good X can be produced only with less of good Y as resources are scarce.
Q.15. What does a leftward shift of a Production Possibility Curve indicate?
Ans. A leftward shift of a Production Possibility Curve indicates a reduction in the resources under which an economy has to produce less of both goods.
Q.16. What does a rightward shift of a Production Possibility Curve indicate?
Ans. A rightward shift of a Production Possibility Curve indicates the situation of growth of resources under which an economy is capable of producing more of both goods.
Q.17. When does the Production Possibility Curve shift outward to the right?
Ans. The Production Possibility Curve shifts outward to the right due to technological progress or increase in the supply of resources available to an economy or both.
Q.18. Why is the Production Possibility Curve concave to the origin?
Ans. The Production Possibility Curve is concave to the origin because of increasing marginal opportunity cost. 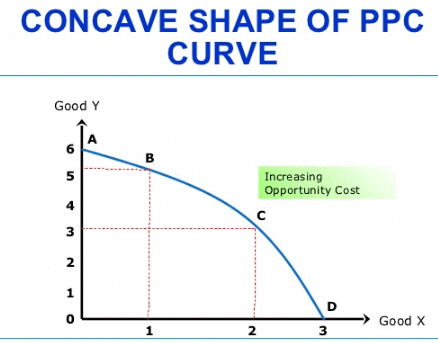
Q.19. Why Production Possibility Curve is also called the transformation curve?
Ans. The Production Possibility Curve is also called the transformation curve because it shows a trade-off between two goods. The movement along this curve indicates that one good is transformed into another, not physically, but by transferring resources from one use to the other.
Q.20. What is macroeconomics?
Ans. Macroeconomics is that branch of economics which studies the behaviour of the economy as a whole. Level of output and employment are the principal macroeconomic issues.
Q.21. Why is the study of consumer equilibrium a subject matter of microeconomics?
Ans. Consumer equilibrium is a subject matter of microeconomics because it is a study of individual consumer behaviour.
Q.22. Name any one variable of study in microeconomics.
Ans. In microeconomics, the price of a good or service is a key variable that influences how much consumers are willing to buy and how much producers are willing to sell.
For example, if the price of apples rises, consumers may buy fewer apples, while producers are encouraged to sell more. Price changes affect supply, demand, and overall market equilibrium.
Q.23. Is the study of the cotton textile industry a macroeconomic study or a microeconomic study?
Ans. The study of the cotton textile industry is a microeconomic study because it focuses on a specific industry rather than the economy as a whole. It examines aspects like production, costs, pricing, supply, demand, and competition within the cotton textile industry, which are all microeconomic concerns.
Q.24. What do you understand by macroeconomics?
Ans. Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that studies the overall functioning and performance of an economy. It focuses on economic factors such as national income, total employment, inflation, economic growth, and government policies that affect the economy as a whole, rather than individual businesses or markets.
Q.25. Write three points on the distinction between micro and macroeconomics.
Ans. The following points explain the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics: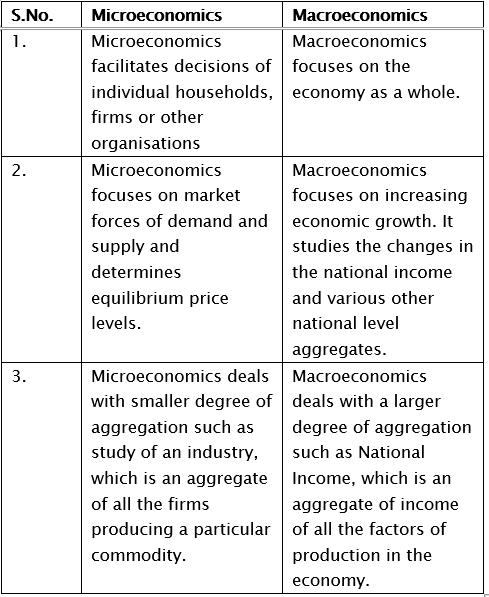
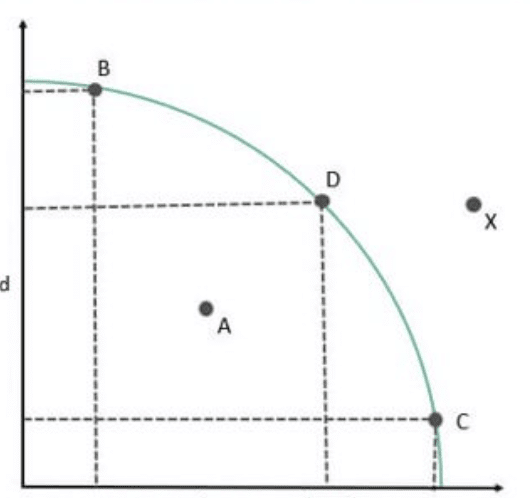
Q.26. The production in an economy is below its potential due to unemployment. The government starts employment generation schemes. Explain its effect using the Production Possibility Curve.
Ans. When an economy is operating below its potential due to unemployment, it means that resources are not fully utilized, and production is happening inside the Production Possibility Curve (PPC). When the government starts employment generation schemes, more people get jobs, leading to better utilization of resources. As a result, production increases, and the economy moves closer to the PPC.
However, the PPC itself does not shift because the total resources and technology remain unchanged. The economy simply moves from a point inside the curve to a point on or nearer to the curve, indicating efficient use of resources.
Thus, the economy moves from point ‘a’ inside the PPC to any point on the PPC as shown in the diagram.
|
59 videos|222 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Economics Short Questions With Answers (Part - 2) - Introduction to Micro Economics
| 1. What is microeconomics? |  |
| 2. How does microeconomics differ from macroeconomics? |  |
| 3. What are the main principles of microeconomics? |  |
| 4. How does microeconomics help in understanding market behavior? |  |
| 5. What are some practical applications of microeconomics? |  |

















