Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Question Answers - Matter in Our Surroundings
| Table of contents |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
| Value-Based Answer Type Questions |

|
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Define matter.
Ans. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called matter.
Q.2. State different states of matter with an example.
Ans. The matter has 3 different states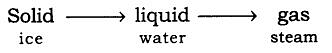
Q.3. What is diffusion?
Ans. The intermixing of molecules of one substance with that of the other is called diffusion.
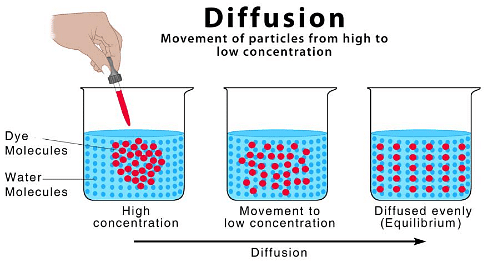 Diffusion
Diffusion
Q.4. What happens to the rate of diffusion if the temperature is increased?
Ans. With increased temperature, the rate of diffusion also increases as the particles gain energy and vibrate more.
Q.5. Name the state of matter that has the tendency to maintain its shape when subjected to outside force.
Ans. Solid.
Q.6. Define melting point.
Ans. The temperature at which a solid melts to become liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
Q.7. Define boiling point.
Ans. The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point.
Q.8. Define latent heat of vaporization.
Ans. Latent heat of vaporization is the heat energy required to change 1 kg of a liquid to gas at atmospheric pressure at its boiling point.
Q.9. Define latent heat of fusion.
Ans. Latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of solid into liquid at its melting point.
Q.10. Define sublimation.
Ans. Sublimation is the change of a gaseous state directly to a solid state without going through a liquid state and vice-versa.
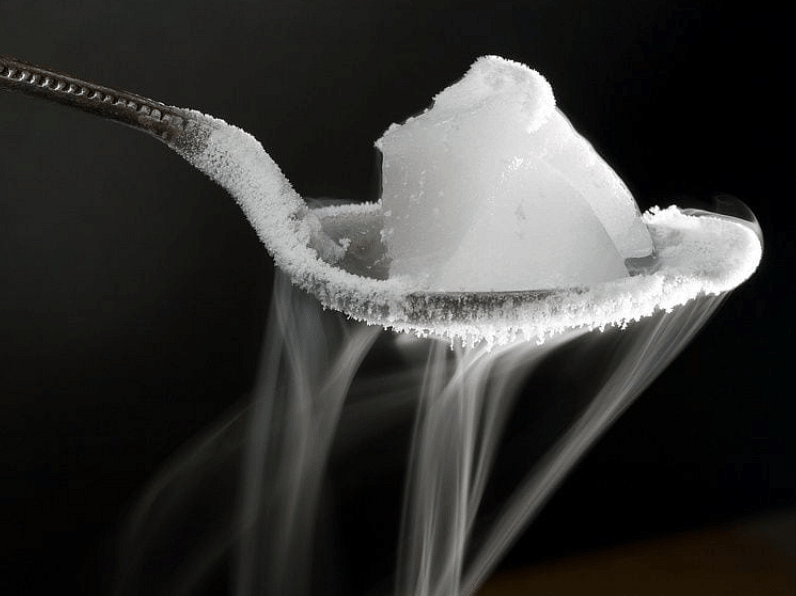 SublimationQ.11. What is dry ice?
SublimationQ.11. What is dry ice?
Ans. Solid carbon dioxide is obtained by cooling and applying pressure on carbon dioxide gas. It does not melt, so it is called dry ice.
Q.12. What is humidity?
Ans. The air holds water vapour, this air with water is called humid air and the phenomenon is called humidity.
Q.13. Give two properties of a solid.
Ans.
(i) Solids have fixed shapes and are rigid.
(ii) Solids cannot be compressed.
Q.14. What will happen if the pressure is reduced on solid carbon dioxide (dry ice)?
Ans. If the pressure is reduced on solid carbon dioxide, it will directly change into a gaseous state without melting.
Q.15. Name any three substances that show sublimation.
Ans. Ammonium chloride, camphor, and naphthalene balls.
Q.16. Sponge is solid, but we can still compress it. Why?
Ans. A sponge is a solid with minute pores in it. When we press the sponge the air present in these pores is released and hence we are able to compress it.
Q.17. What is normal atmospheric pressure?
Ans. The atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1 atmosphere and taken as the normal atmospheric pressure.
Q.18. What is Kelvin?
Ans. Kelvin is the SI unit of temperature (O°C = 273 K).
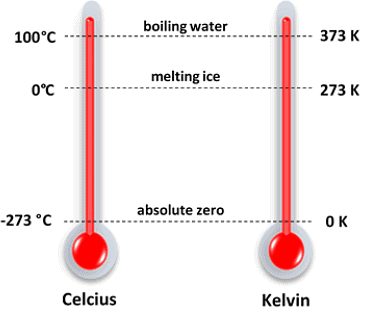 Temperature Scale in Degree and Kelvin
Temperature Scale in Degree and Kelvin
Q.19. Give two examples of diffusion.
Ans. Milk drops dissolved in water and perfume sprayed in a room.
Q.20. Give the temperature at which water exists in two different phases/states.
Ans.
(i) At 0°C, water can be in a solid or in liquid state.
(ii) At 100°C, water can be in liquid or in a gaseous state.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Why do we see water droplets collected on the outer surface of a glass container containing ice?
Ans. The water vapor present in the air comes in contact with the cold outer surface of the container, thereby condensing it to form water droplets.
Q.2. Explain why solids have a fixed shape but liquids and gases do not have a fixed shape.
Ans. Solids have fixed shapes due to strong intermolecular forces of attraction between them. The liquids and gases have molecules with less intermolecular force of attraction and hence, they can flow and take the shape of the container.
Q.3. Liquids and gases can be compressed but it is difficult to compress solids. Why?
Ans. Liquids and gases have intermolecular space, on applying pressure externally on them, the molecules can come closer, thereby minimizing the space between them. But in the case of solids, there is no intermolecular space to do so.
Q.4. A balloon, when kept in the sun, bursts after some time. Why?
Ans. The balloon has air filled in it. The balloon, when kept in the sun, gets heated, and the air inside it also gets heated. The molecules of air get energy and vibrate faster, thereby exerting a large force on the walls of the balloon, due to this expansion of gases, the balloon bursts.
Q.5. Why do people perspire a lot on a hot, humid day?
Ans. On a hot, humid day, due to the heat, our body starts sweating for the cooling mechanism i.e., by evaporation, and gets a cooling effect. But the air cannot hold any more water on a humid day and therefore, sweat or perspiration is seen.
Q.6. Distinguish between evaporation and boiling.
Ans.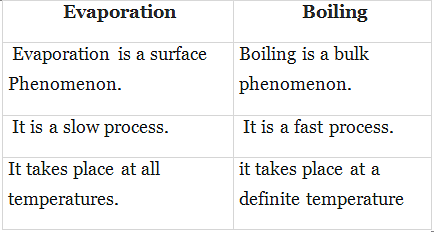
Q.7. Why is it advisable to use a pressure cooker at higher altitudes?
Ans. At higher altitudes, the atmospheric pressure is low, and the water boils very fast and evaporates at a faster rate therefore, the pressure is required to increase the cooking process, and this is done by using a pressure cooker, which increases the pressure inside the container and cooks food faster.
Q.8. What are fluids?
Ans. The states of matter that can flow due to less intermolecular force of attraction are liquids and gases and are called as fluids.

Q.9. One kg cotton and one kg sand, which is more denser? Why?
Ans. One kg of sand is denser than 1 kg of cotton because
Density = Mass/Volume
The volume required by cotton is more than the sand, and density and volume are inversely proportional.
Q.10. Why is water liquid at room temperature?
Ans. At room temperature, the molecules of water have some intermolecular force of attraction and the room temperature cannot provide sufficient heat for these molecules to overcome their force of attraction and, therefore, remain in a liquid phase.
Q.11. State the differences between solid, liquid and gas.
Ans.
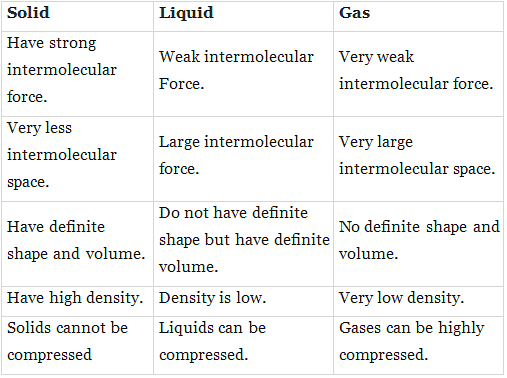
Q.12. Cotton is solid but it floats on water. Why?
Ans. Cotton has a large number of pores in which air is trapped. Reducing its density and increasing its volume. Therefore, cotton floats on water. But when these pores get filled with water, it starts sinking.
Q.13. Why are solids generally denser than liquids and gases?
Ans. The density of a substance is given by a formula= Mass/Volume
In the case of solids, the molecules are tightly packed, and hence large mass is concentrated in a very small volume. Hence, their density is higher. But in the case of liquids and gases, their molecules have intermolecular space, and hence they don’t have large mass concentrated in small volume. So, the density of solids is generally more than that of liquids and gases.
Q.14. On a hot sunny day, why do people sprinkle water on the roof or open ground?
Ans. During hot sunny days, the surface of the roof or ground absorbs large amounts of heat and remains hot, on sprinkling water on these surfaces, the water absorbs large amounts of heat from the surface due to its large latent heat of vaporization, thereby allowing the hot surface to cool.
Q.15. On a hot sunny day, why do we feel pleasant sitting under a tree?
Ans. A tree has a lot of leaves that constantly show transpiration. Transpiration is the loss of water through small tiny pores of leaves called stomata. When this water comes to the surface of the leaf, the water evaporates thereby causing a cooling effect. Therefore, we feel pleasant sitting under the tree on a hot sunny day.
Q.16. The temperature at which liquids change into vapors is very high, for example, if water evaporates at 100°C, then how is water to evaporate at room temperature or at other temperatures?
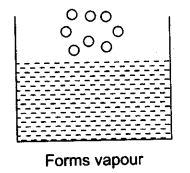
Ans. The molecules of water present on the surface of the exposed area, which are in very small fraction, gain the energy from the surroundings. With this higher kinetic energy, they are able to break the force of attraction between them and hence get converted into a vapor state.
This phenomenon of the change of a liquid into vapors that takes place at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.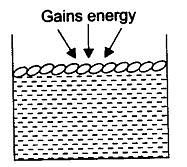
Q.17. Name the factors that affect evaporation.
Ans. The rate of evaporation will increase with
(a) an increase in surface area,
(b) an increase in temperature,
(c) a decrease in humidity,
(d) an increase in wind speed.
Q.18. The melting point of ice is 273.16 K. What does this mean? Explain in detail.
Ans. Ice is solid at 0°C i.e., 273° K. The molecules of ice are tightly packed. These molecules have to overcome the force of attraction with which they are held, and hence, they gain this heat from the surroundings but the temperature remains the same as their energy is used to overcome the force of attraction between the particles. The particles have their state and start vibrating freely, and a stage reaches when the solid ice melts and is converted to a liquid state at the same temperature i.e., 273 K.
Q.19. How is the high compressibility property of gas useful to us?
Ans. The gases have high compressibility. This property is used in the following situations:
(a) LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) is a fuel that is made up of petroleum gas. Compressing this petroleum gas forms a liquid.
(b) Oxygen cylinders in the hospitals have compressed gas filled in it.
(c) CNG (compressed natural gas) is a natural gas, methane, which is compressed and used as a fuel in vehicles and at home.
Q.20. With the help of an example, explain how diffusion of gases in water is essential.
Ans. The gases from the atmosphere diffuse and dissolve in water. Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in water and are essential for the survival of aquatic animals and plants.
Animals breathe in this oxygen dissolved in water for their survival, and plants can use carbon dioxide dissolved in water for photosynthesis.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Pressure and temperature determine the state of a substance. Explain this in detail.
Ans.
(a) Any matter i.e., solid, liquid, or gas, that experiences an increase in temperature and then changes its state.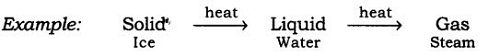
Take ice cubes in a beaker or heat them slowly. The temperature increases, and the ice melts to form a liquid. Heat this liquid further it will become steam.
(b) On lowering the temperature of any matter, show a change in their state.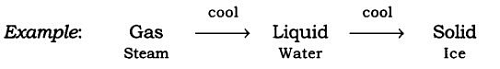
Take the steam that is coming out of boiling water and allow it to cool down; it condenses to form water and on further cooling of this water, we get ice.
(c) On applying pressure and reducing temperature, we can liquefy gases or change them into solids. Example: Take carbon dioxide gas, reduce its temperature, and apply a lot of pressure on it so that it changes into solid carbon dioxide, called dry ice, which is used as refrigerant for cooling. If the pressure on it is decreased it directly changes into gas.
In LPG cylinders, the petroleum gas is cooled and, with a lot of pressure, changes it into the liquid state.
While using this LPG, we release the pressure exerted on it and hence, it comes out in the form of gas.
Q.2. Explain, giving examples, the various factors on which the rate of evaporation depends.
Ans. The rate of evaporation depends on the following factors:
- Surface area: If the surface area is increased, the rate of evaporation also increases.
(a) To dry the clothes, we spread them to dry faster.
(b) Tea in a saucer cools faster than in a cup. - Temperature: If the temperature is increased, the rate of evaporation also increases. Due to an increase in temperature, the particles gain more kinetic energy and change their phase from liquid to gaseous. Water will evaporate faster in the sun than in the shade.
- Humidity: It is the amount of water vapor present in the air. The air can hold a definite amount of water vapor at a given temperature. If the amount of water vapor is high in the air, then the rate of evaporation decreases. On hot and humid days, desert coolers are not effective as the air cannot hold any more moisture to get the cooling effect.
- Wind speed: With the increase in wind speed, the rate of evaporation increases. The particles of water vapor move away with the wind, decreasing the amount of water vapor in the surroundings.
Value-Based Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Adil parked his bicycle on a sunny day in a parking stand on his school campus. When the school got over, Adil saw his burst cycle type. Thereafter, he kept less air in his cycle types and did not inflate them fully.
(a) Why did the type burst?
(b) Why is air compressible?
(c) What value of Adil is reflected in the above act?
Ans.
(a) The tyre burst because the air inside the tyre got heated and therefore exerted pressure on the walls of the tyre.
(b) Air is compressible because it has large intermolecular space.
(c) Adil showed the value of intelligence, awareness and self-responsibility.
Q.2. Akshay’s friend visited his house in Mumbai and he was surprised to see air conditioners installed in all of his rooms. His friend advised Akshay to use water coolers and save electricity. On this, Akshay told him that the water-cooler is not at all effective in coastal areas.
(a) Why are water-coolers not effective in coastal areas?
(b) What are the other two factors on which evaporation of water
depends?
(c) What value of Akshay’s friend is seen in this act?
Ans.
(a) Water coolers are not effective in coastal areas due to the high rate of humidity.
(b) The other two factors on which evaporation of water depends are temperature and surface area.
(c) Akshay’s friend showed the value of concerned citizens, morally responsible and friendly in nature.
Q.3. Sita lived in a village and could not afford a refrigerator in her house. She knew how to keep water cold and preserve all perishable items in her house. She kept an ivet cloth surrounding the earthen pot to keep water cool. She also kept vegetables fresh by keeping them in wet gunny bags and sprinkled water over them in a timely manner.
(a) Why did Sita keep wet cloth surrounding the earthen pot?
(b) Suggest one more method of keeping the house cool in summer.
(c) What value of Sita is reflected in the above case?
Ans.
(a) The wet cloth gave a cooling effect to the pot, as the water in the cloth evaporated and evaporation caused a cooling effect.
(b) By sprinkling some water on the lawn/veranda of the house can keep the house cool.
(c) Sita showed the value of responsible behavior.
Q.4. Shreya commutes in a CNG-fitted van to school every day along with many other students. She told the van driver to get the CNG connection certified and timely check it for any leakage or loose connection of pipes. She told the driver to be more careful during summer.
(a) What is CNG?
(b) Why should one be more careful with CNG cylinders during summer?
(c) What value of Shreya is seen in the above act?
Ans.
(a) CNG is Compressed Natural Gas used as fuel.
(b) During summers, the CNG connections and cylinder need to be checked because the gas expands due to heat and if there is any leakage, then it would cause a fire in the vehicle.
(c) Shreya showed the value of being a concerned citizen and morally responsible behavior.
|
88 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Question Answers - Matter in Our Surroundings
| 1. What are the different states of matter? |  |
| 2. How does matter change from one state to another? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between physical and chemical changes in matter? |  |
| 4. How does temperature affect the state of matter? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to study matter in our surroundings? |  |



















