Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Mathematics for Class 5 > Mind Map: Symmetry
Mind Map: Symmetry | Mathematics for Class 5 PDF Download
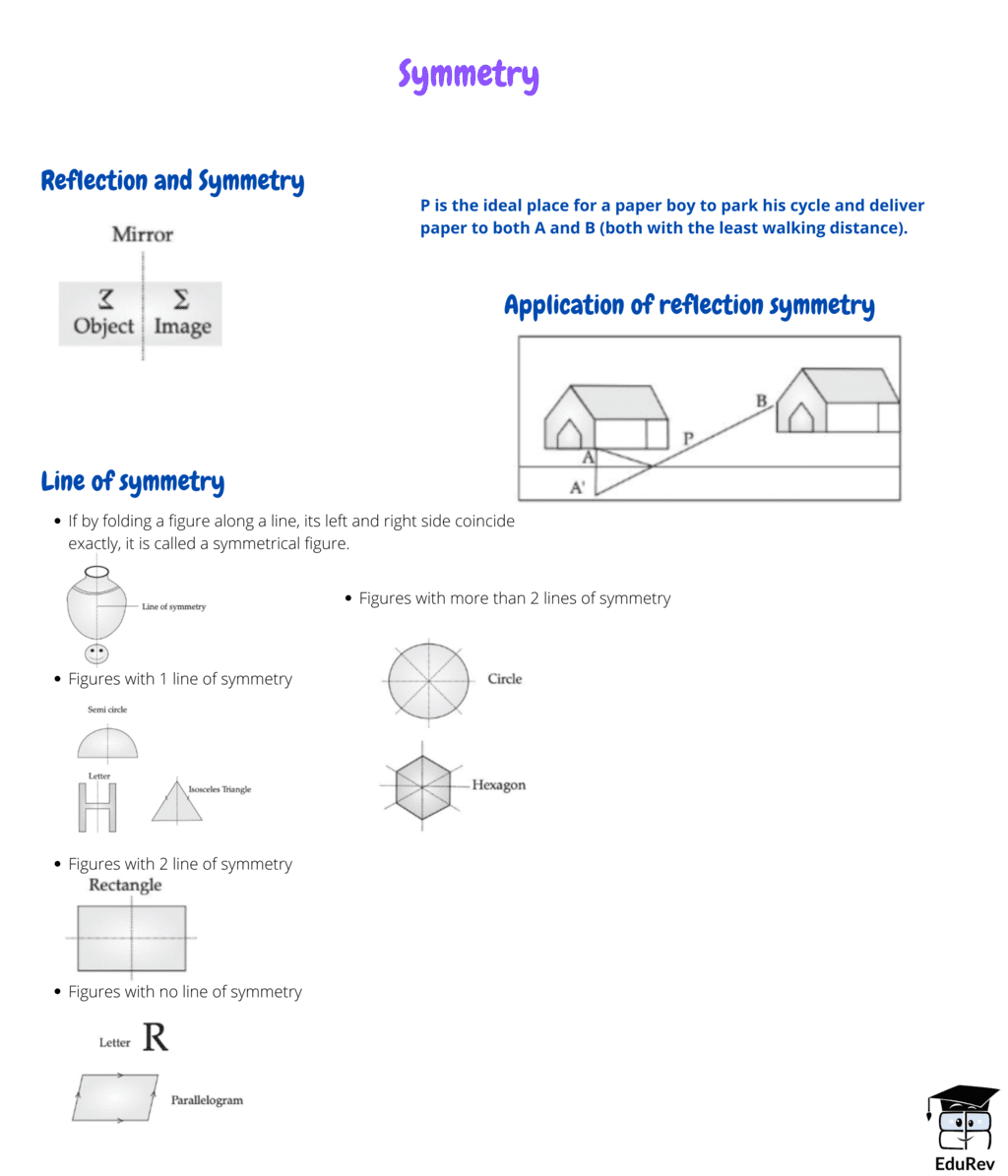
The document Mind Map: Symmetry | Mathematics for Class 5 is a part of the Class 5 Course Mathematics for Class 5.
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
56 videos|187 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Symmetry - Mathematics for Class 5
| 1. What is symmetry? |  |
Ans. Symmetry refers to a balanced arrangement of objects or elements that are the same on both sides of an axis or center. It is a property that describes the harmony and proportional arrangement of components in an object or design.
| 2. How many types of symmetry are there? |  |
Ans. There are three types of symmetry: reflectional symmetry, rotational symmetry, and translational symmetry. Reflectional symmetry occurs when an object is mirrored along a line. Rotational symmetry occurs when an object can be rotated around a fixed point and still maintain its original shape. Translational symmetry occurs when an object can be shifted or translated without changing its appearance.
| 3. What is reflectional symmetry? |  |
Ans. Reflectional symmetry, also known as line symmetry or mirror symmetry, occurs when an object can be divided into two parts that are mirror images of each other. In other words, if a line is drawn through the object, one side is a reflection of the other. Examples of reflectional symmetry can be found in nature, such as butterfly wings or human faces.
| 4. What is rotational symmetry? |  |
Ans. Rotational symmetry occurs when an object can be rotated around a fixed point and still maintain its original shape. The fixed point is called the center of rotation, and the angle of rotation is usually a multiple of 360 degrees. Objects with rotational symmetry can have multiple lines of symmetry or rotational axes. Examples include a perfect circle, a star shape, or a windmill.
| 5. What is translational symmetry? |  |
Ans. Translational symmetry refers to the property of an object or pattern that remains unchanged when it is shifted or translated in a certain direction. In other words, if an object can be moved along a straight line without changing its appearance, it exhibits translational symmetry. This type of symmetry is commonly observed in tessellations or repeating patterns, such as a tiled floor or a brick wall.
Related Searches





















