Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Worksheet Science Chapter 1
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Fill in the blanks:- |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Crossword Puzzle |

|

Given below are the Class 9 Science CBSE Important questions for matter in our Surroundings
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. According to ancient philosophers, matter consists of:
(a) Three constituents
(b) Four constituents
(c) Five constituents
(d) Six constituents
Q.2. Dry ice is:
(a) Solid ammonia
(b) Solid carbon dioxide
(c) Solid sulphur dioxide
(d) Normal ice. 
Q.3. Which of the following statements is not correct for liquid state?
(a) Particles are loosly packed in the liquid state
(b) Fluidity is the maximum in the liquid state
(c) Liquids can be compressed
(d) Liquids take up the shape of any container in which these are placed
Q.4. Which of the following will sublime?
(a) Common salt
(b) Sugar
(c) Camphor
(d) Potassium nitrate
Q.5. When the liquid starts boiling, the further heat energy which is supplied:
(a) Is lost to the surrounding as such
(b) Increases the temperature of the liquid
(c) Increases the kinetic energy of the particles in the liquid
(d) Is absorbed as latent heat of vaporisation by the liquid
Fill in the blanks:-
1. Matter is made up of small_________.2. The forces of attraction between the particles are _______ in solids, ______ in liquids and _________ in gases.
3. __________ is the change of gaseous state directly to solid state without going through liquid state, and vice versa.
4. Evaporation causes __________.
5. Latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of solid into liquid at its ________.
6. Solid, liquid and gas are called the three _______ of matter.
7. The smell of perfume gradually spreads across a room due to ______.
8. Rapid evaporation depends on the ______ area exposed to the atmosphere.
9. As the temperature of a system increases, the pressure of the gases ______.
10. As the volume of a specific amount of gas decreases, it’s pressure _______.
11. As the temperature of a gas decreases, I’s volume ______.
12. Gas molecules at higher temperatures have more _______ than at cooler temperatures.
13. A sponge has minute ________, in which ________ is trapped.
14. The pressure inside of a sealed tube if you raise the temperature go ______
15. Forces of attraction in liquids are _______ than in solid.
16. Latent heat of ________ is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of solid into liquid at its melting point.
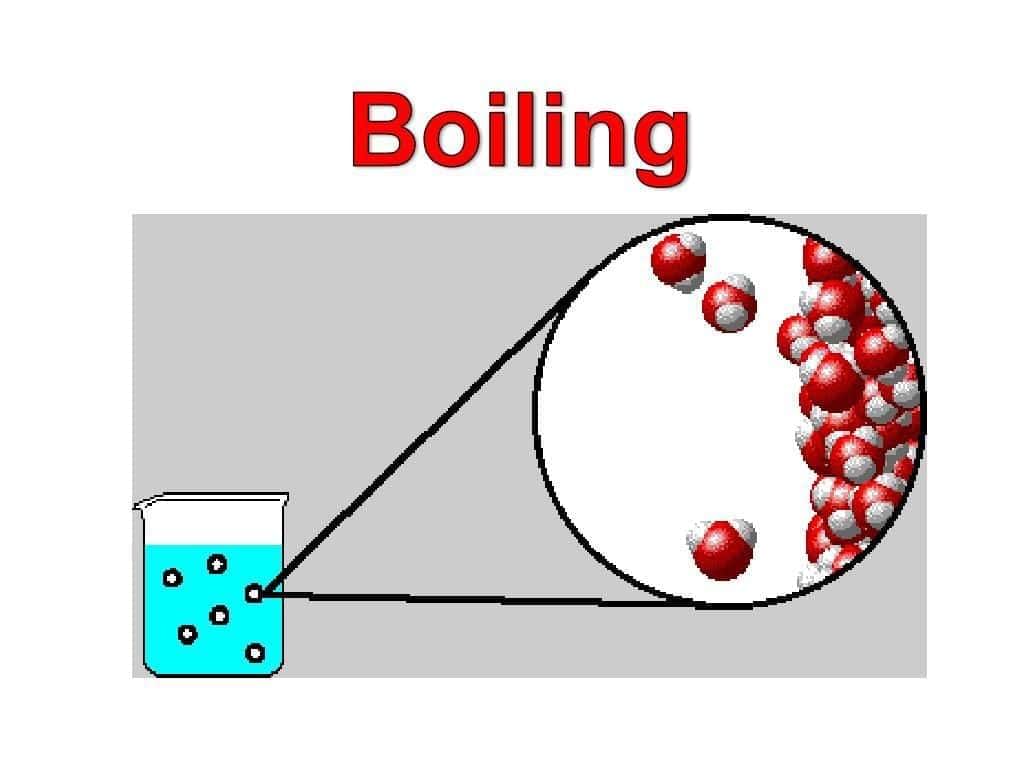
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Name one property which is shown by naphthalene and not by sodium chloride.
Q.2. A rubber band changes its shape when stretched. Can it be regarded as solid?
Q.3. Gases can be compressed but solids cannot. Explain.
Q.4. Kelvin scale of temperature is regarded better than the Celsius scale. Assign reason.
Q.5. What happens to the heat energy which is supplied to the solid once it has started melting?
Q.6. The freezing point of water is 0°C. What is the corresponding temperature on the Kelvin scale?
Q.7. Are the melting point temperature of the solid state and the freezing point temperature of the liquid state of a substance different?
Q.8. A substance is in liquid state at room temperature and changes into gas upon heating. What will you call its gaseous state?
Q.9. When a crystal of copper sulphate is placed at the bottom of a beaker containing water?
Q.10. The boiling point of ethyl alcohol is 78°C. What is the corresponding temperature on kelvin scale?

Crossword Puzzle
 Across
Across
1. BEC stands for Bose-Einstein-______
3. The state consists of super energetic and super excited particles
8. Conversion of solid to vapour is called ______
Down
2. This is the phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapours at any temperature below its boiling point
4. SI unit of Temperature
5. CNG stands ____ natural gas
6. It is the amount of water vapour present in air.
7. LPG stands for ______petroleum gas.
You can find Worksheet Solutions here: Worksheet Solutions: Matter in Our Surroundings
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Worksheet Science Chapter 1
| 1. What is matter and how is it classified? |  |
| 2. What are the properties of solids, liquids, and gases? |  |
| 3. How do changes in temperature affect the states of matter? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between physical and chemical changes in matter? |  |
| 5. Can matter change from one state to another? If so, how? |  |
















