Key Concepts - Electoral Politics | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
What are Elections and why are they Important?
- Elections: A mechanism by which people choose their representatives at regular intervals.
- Necessary in large democracies where direct decision-making by citizens is not feasible.
- Allow people to:
- Choose lawmakers and government.
- Express preferences on policies.
- Remove non-performing leaders.
 Election in India
Election in India
Assembly Election in Haryana
- In 1987, Haryana’s Congress government, in power since 1962, was defeated by Chaudhary Devi Lal’s Lok Dal, which won 60 of 90 assembly seats.
- Promising loan waivers for farmers and small businessmen, Devi Lal became Chief Minister and implemented these policies.
- This election shows how voters can change governments and influence policies, a pattern seen in recent elections like those in 2024, where voter choices reshaped leadership.
What Makes an Election Democratic?
Democratic elections must ensure:
- Universal Adult Franchise: All citizens above 18 can vote.
- One Vote, One Value: Every vote carries equal weight.
- Free and Fair Elections: No bias, bribery, or coercion.
- Real Choice: Multiple parties and candidates.
- Regular Elections: Held at fixed intervals.
- Secret Ballot: Maintains voter privacy.
Is it good to have Political Competition?
Political competition drives democratic elections but has both merits and demerits:
Merits:
- Forces parties to perform, as failure risks losing power (e.g., opposition parties critique government schemes to gain voter support).
- Ensures accountability, as voters reward or punish leaders every five years.
- Like shopkeepers competing for customers, parties compete for votes, ensuring better service to the people.
Demerits:
- Creates disunity and factionalism, as parties prioritize winning.
- Leads to allegations of unethical practices, like vote-buying or false promises.
- Discourages capable individuals from entering politics due to its competitive nature.
- Hinders long-term policy planning, as parties focus on short-term electoral gains.
Despite these drawbacks, competition ensures governments remain responsive, making it essential for democracy.
What is our System of Elections?
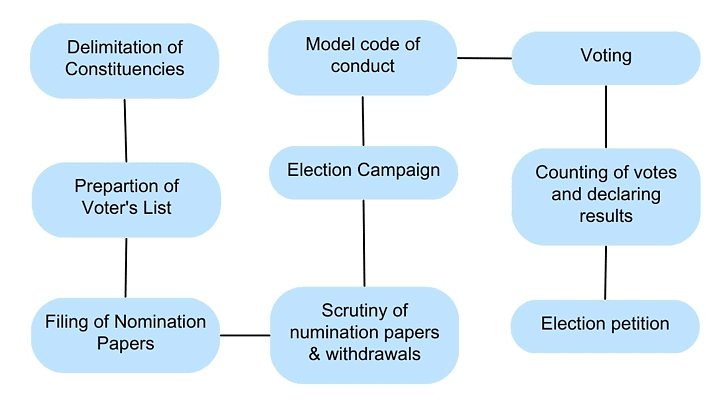 System of Elections
System of Elections
- Preparation and updating of the voters' list.
- Announcement of election date.
- Division of the country into constituencies for Lok Sabha and state assemblies.
- Election of Members of Parliament (MPs) from 543 Lok Sabha constituencies.
- Election of Members of Legislative Assembly (MLAs) within each state.
- Declaration of party manifestos and nomination lists.
- Apart from general elections, sometimes by-elections are held to fill vacant seats.
Electoral Constituencies
- India is divided into 543 Lok Sabha constituencies and state assembly constituencies, each electing one representative (MP or MLA).
- The Delimitation Commission redraws boundaries to ensure roughly equal voter populations, though challenges like population growth persist.
- Reserved constituencies (84 for Scheduled Castes, 47 for Scheduled Tribes, as of 2019) ensure representation for weaker sections.
- Local bodies also reserve seats for OBCs and one-third for women.
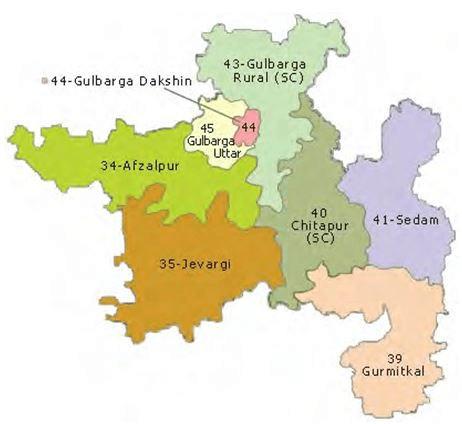 Gulbarga Lok Sabha Constituency
Gulbarga Lok Sabha Constituency
Reserved Constituencies
- True democracy aims for equal opportunity in elections and governance.
- Weaker sections (SCs, STs, OBCs, women) exist due to historical, social, cultural, and economic factors.
- A level playing field is needed for meaningful electoral competition.
- Reserved constituencies provide this level playing field for weaker sections.
 Reserved Parliamentary constituencies for SC-ST (2008)
Reserved Parliamentary constituencies for SC-ST (2008)
Voters' list
- All citizens aged 18 and above, regardless of caste, religion, or gender, can vote under universal adult franchise.
- The Election Commission updates the voter’s list regularly to add new voters and remove those who are deceased or ineligible.
- The Election Photo Identity Card (EPIC) verifies voters, though other IDs like ration cards are accepted.
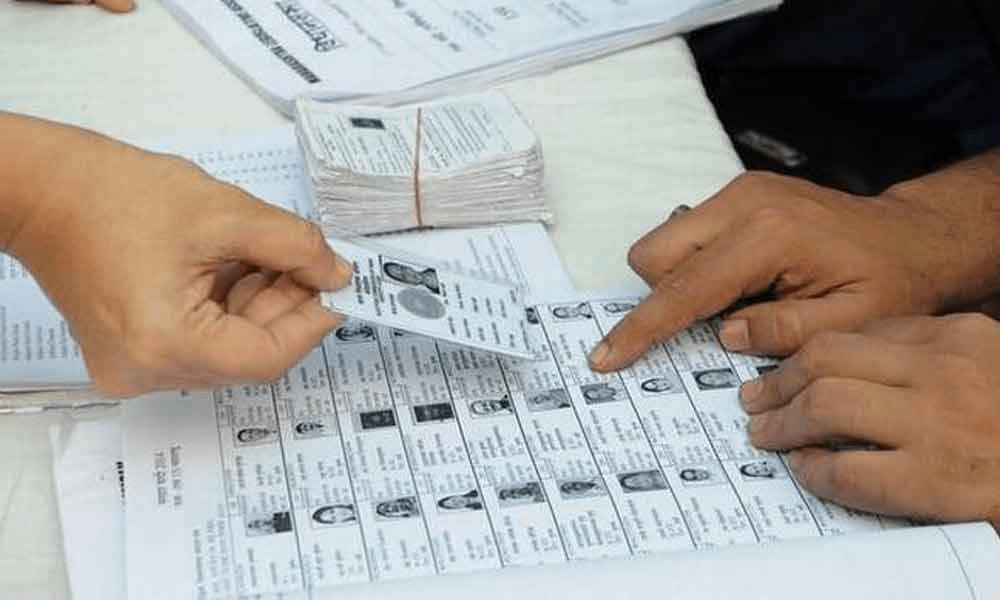 Voter's List at the time of the Election
Voter's List at the time of the Election
Nomination of Candidates
- Any citizen 25 years or older can contest.
- Must submit:
- Nomination form.
- Security deposit.
- Legal declaration:
a) Criminal record (if any)
b) Assets & liabilities
c) Educational qualifications - Ensures transparency and informed voting.
Election Campaign
- Conducted in the two weeks before polling.
- Parties present policies and criticize opponents.
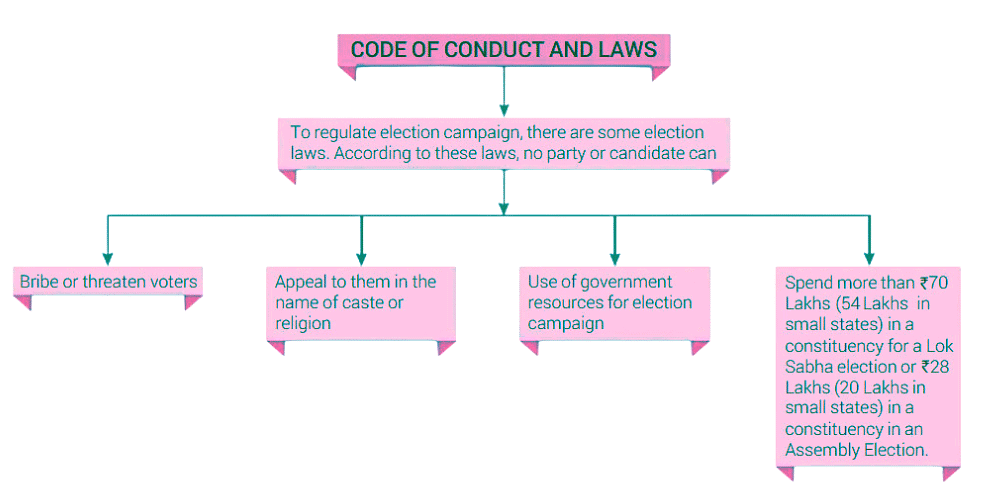
Restrictions (Model Code of Conduct):
- No use of caste/religion appeals.
- No bribes or threats.
- No use of government vehicles or officials.
- No policy decisions after announcement.
Spending Limit:
₹25 lakh (Lok Sabha), ₹10 lakh (Assembly).
Polling and Counting of Votes
- Election day, when voters cast their votes, involves going to a nearby polling booth.
- Upon entering, officials identify voters, mark their fingers, and permit them to vote.
- Each candidate has an agent inside the booth to ensure fair voting procedures.
A ballot paper is a sheet of paper on which the names of the contesting candidates, along with party names and symbols, are listed.
The ballot paper was used earlier. Nowadays, electronic voting machines (EVM) are used to record votes.
- The machine shows the names of the candidates and the party symbols.
- The voter has to press the button against the name of the candidate she wants to give her vote to.
 Representation of EVMs
Representation of EVMs
- Once the polling is over, all the EVMs are sealed and taken to a secure place.
- A few days later, all the EVMs are opened and the votes secured by each candidate are counted.
- The candidate who secures the highest number of votes from a constituency is declared elected.
What Makes Election in India Democratic?
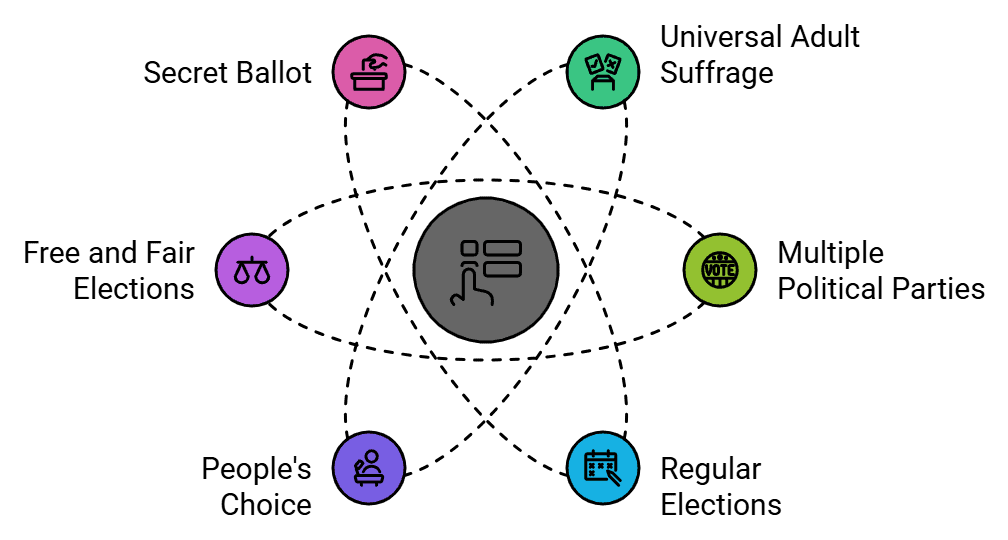 Factors which make election in India Democratic
Factors which make election in India Democratic
Indian elections meet the following conditions, distinguishing them from non-democratic elections:
Universal Adult Franchise: Every citizen above 18 has an equal right to vote, ensuring inclusive participation.
Real Choice: A multi-party system offers voters diverse parties and candidates.
Regular Elections: Held every five years for Lok Sabha and state assemblies, ensuring accountability.
People’s Choice: The candidate with the most votes wins, reflecting the majority’s will.
Free and Fair Elections: The Election Commission ensures transparency and impartiality, enforcing rules and penalizing violations (e.g., rescheduling polls for malpractices).
Secret Ballot: EVMs protect voter privacy, preventing coercion.
The Election Commission, led by the Chief Election Commissioner appointed by the President, oversees all election aspects, enforces the Model Code of Conduct, and controls government officials on election duty to prevent misuse of power.
Independent Election Commission
- Conducts all elections in India.
- Headed by Chief Election Commissioner (CEC).
- Appointed by the President, but independent.
Powers:
- Implement Model Code of Conduct.
- Order repolls.
- Punish candidates/parties for violations.
- Control election officials.
Popular Participation
In India, elections are conducted by the independent Election Commission (EC), led by the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) appointed by the President. Key aspects that make elections democratic in India include:
- EC's control over all aspects of elections, from announcement to declaration of results Implementation.
- Enforcement of the Code of Conduct Issuing guidelines for the government during elections ensuring government officials work under EC control while on election duty.
Acceptance of Election Outcome
 Sealed EVMs
Sealed EVMs
- EVMs from each area are opened on a fixed date, ensuring transparency.
- Election outcomes serve as a test of freedom and fairness.
- Ruling parties frequently lose elections at national and state levels.
- Incumbent representatives often lose elections, indicating competitiveness.
- Candidates spending excessive money or with criminal connections can lose elections.
- Electoral outcomes are generally accepted as the 'people's verdict' by defeated parties.
Challenges to Free and Fair Elections
Indian elections are largely free and fair, as evidenced by:
Ruling parties losing elections (e.g., two out of three elections in the last 25 years).
About half of incumbent MPs/MLAs losing re-election.
Acceptance of results as the “people’s verdict” by defeated parties.
High voter turnout (60–70%), especially among the poor and underprivileged.
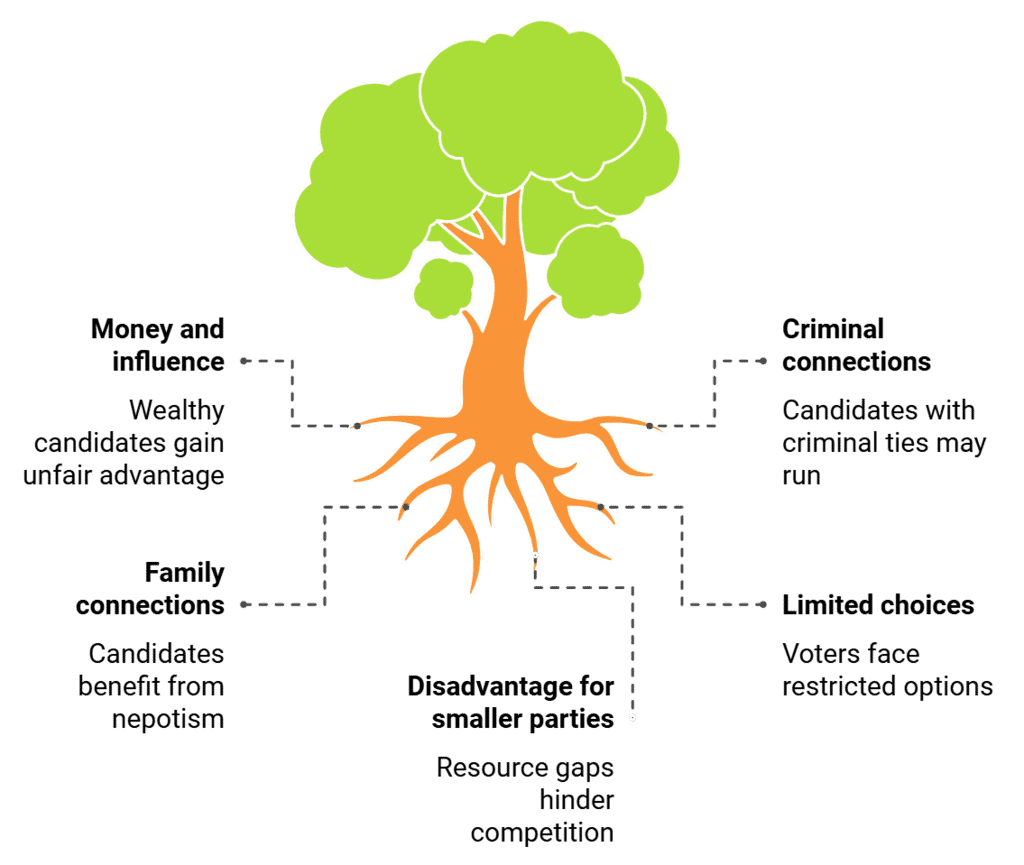 Challenges to Free and Fair Elections
Challenges to Free and Fair Elections
- Money and influence: Wealthy candidates hold an advantage, but it doesn't determine election outcomes.
- Criminal connections: Candidates with criminal backgrounds may secure party tickets but aren't guaranteed victory.
- Family connections: Some candidates receive tickets due to family ties, yet voters ultimately decide their fate.
- Limited choices: Major parties may align, but voters can opt for smaller parties or independents.
- Disadvantage for smaller parties: Despite resource disparities, smaller parties and independents contribute to the democratic process.
The Election Commission addresses these through expenditure monitoring, voter education, and strict enforcement. Citizens and activists advocate for reforms to ensure a level playing field.
Conclusion
Elections in India ensure citizen participation and government accountability. Despite certain flaws and challenges, they are largely free and fair, upheld by an independent Election Commission, active voter participation, and a strong rule of law. The observance of National Voters' Day on 25 January promotes awareness about the electoral process and encourages citizens to vote.
Pledge: "We, the citizens of India, pledge to uphold democracy and vote in every election without fear or bias."
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts - Electoral Politics - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What is the significance of elections in a democratic country like India? |  |
| 2. How are electoral constituencies determined in India? |  |
| 3. What are the key steps involved in the election process in India? |  |
| 4. What challenges do free and fair elections face in India? |  |
| 5. What role does an election campaign play in the electoral process? |  |






















