Thermodynamics
Definition:
Thermodynamics deals with energy interaction b/w two bodies & its effect on the properties of matter.
Scope of thermodynamics:
→ Feasibility of a process
→ Extent of a process
→ Efficiency of a process

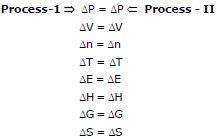
System Boundary Surrounding = Universe
System : The part of the universe under thermodynamical observation is called system.
surroundings : All the part of the universe excepting system is called surroundings.
Boundary : The part which separates system and surroundings is called boundary it may be rigid or flexible.
It may be diathermic (Heat can be exchanged) or adiabatic
Types of Systems

(Mass and energy both (Only energy can be (Neither mass nor energy
can be transfered) transfered) can be transfered)

State or condition of a system is described by certain measurable properties & these measurable properties are called state variables. e.g. mass, temperature, volume, pressure etc.


State function depends only on initial & final state of the system. If does not depend on the path or how process was carried out.
e.g. DU =  Where DU = uf - ui
Where DU = uf - ui
 = DT = Tf - Ti
= DT = Tf - Ti
Sol. The parameters which are required to completely define the state of the system are called state functions.
State functions are path independent function.

Path independent means the difference in state functions will be same for any path followed between two states.
Physical Properties


Path function depends on the initial as well as final state of a system & also depends on the path of the process.e.g. heat and work.
condition for a function to be state function
Euler's theorem f = f(T, V). If f is a state function then
 =
= 
PV = nRT ⇒ P = 
if pressure is a state function then
 =
= 


 =
= 

Hence P is a state function.
e.g. f(x,y) = yex + xy + xln y
Show that f(x,y) is a state function.
Sol.  = yex y ln y
= yex y ln y  = ex x x.
= ex x x. 
 =
=  = ex 1
= ex 1 
 =
= 
= ex + 1 + 
Hence f (x, y) is a state function.
Two other important result from differential calculus will be used frequently.
Consider a function. z = f(x, y). which can be rearranged x = g(y, z) or y = h(x, z)
For example, PV = nRT, P =  , T =
, T = 
in this case

The cyclic rule will also be used.
 = - 1
= - 1


(5) Cyclic Process: System undergoes series of changes & ultimately comes back to initial state.


(1) Quasi-Static(Reversible)Process: If system & surrounding can restore their original state by reversing the direction of the process then process is called reversible process. In reversible process, there is no loss of energy.
These are slow process as it takes infinite time. System & surrounding are always in equilibrium. Reversible process is a theoretical process. Reversible process is most efficient with respect to work.
In reversible process Pext = Pint
If all the above criteria are not fulfilled by any process, then it is known as irreversible process.
* irreversible process is a fast process. It takes definite time for completion
* In irreversible process Pext is not equal to Pint.
*It is an actual process. It is carried out in multiple stages and it tends towards reversible process.



Heat & work both are forms of energy. Both are boundary phenomena and take place at the interface of the system & surroundings.


Expansion  W = - ve
W = - ve
Compression → W =+ ve
Heat given to the system +ve
Heat loss (it released) = - ve
Types of equilibrium
(1) Thermal equilibrium  Equality of temperature
Equality of temperature
(2) Mechanical equilibrium  Equality of pressure
Equality of pressure
(3) Material equilibrium → no. of moles constant
When all the three equilibrium are established in a system, system is in true thermodynamics equilibrium


Internal energy : Internal energy of gaseous molecule present in a system or body is equal to sum of all possible kinds of energy.
Energy U = TE+ RE + VE + Chemical energy + nuclear energy + electron spin energy + PE


For ideal gas
Cp - Cv = R CP =  = (f/2 1) R f --> degree of freedom
= (f/2 1) R f --> degree of freedom
Cp/Cv = g Cv =  = f/2 R g --> Poisson's Ratio
= f/2 R g --> Poisson's Ratio

For Isobaric Process :
Q = nCpDT and Q = DH

For isochoric process
Q = nCvDT and Q = DE
DE = n Cv DT = 
For liquid and solids
U = 



Total degree of freedom = 3n
where n = no of atoms
for vibrational u = fnRT

Total 


Based on thermal equilibrium if A & B, & B & C are in thermal equilibrium then A & C must be in thermal equilibrium.

First law of thermodynamics is based on energy conservation
E2 = E1 + q +w (E1 is the Ei)
E2 - E1 = q + w + (E1+ q + w is Ef)
(Ei = Ef)

or 
For an isolated system, q = 0, w = 0
DU = 0
or U = constant
For cyclic process.



Work done = -Fext.dx
= - P. A dx

for expansion --> dW = - ve
compression --> dW = ve
dq = CdT dqv = CvdT
Cv = 
For an isochoric process dv = 0
dU = qV 
dU = n CVdT

If CV is a function of temperature
DU = n 
We know that
U = f(T, V, P)
consider U = f(T, V)
du = 

For isochoric process dv = 0

for 1 mole of gas
CVdT =  dT
dT
CV = 

For an ideal gas U = f(T) only
 = 0
= 0
du = CVdT
DU = nCVDT = nCV(T2 - T1)


- H = U + PV
dH = dU + d(PV)
 =
=  +
+ 


From, Ist law of thermodynamics at constant pressure.
dU =  + dW
+ dW
dU =  - PdV
- PdV
 = dU + PdV
= dU + PdV
dH = dU + PdV
 ..........(1)
..........(1)


For an ideal gas expansion or compression

DH = nCVDT + nRDT
= nDT[CV + R]

We know that, H = f(T, P)
dH = 

At constant pressure
dP = 0
dH = 

**Calculation of Dng for any chemical reaction:
N2 3H2 2NH3
Dng = - 2
N2 + 3H2 --> 2NH3
10 30 0
0 0 20
Dng = 20 - (40) = -20

If reaction is 50% completed.
N2 + 3H2 --> 2NH3
10 30 0
5 15 10
Dng = 30 - 40 = -10

(1) Isochoric process:
V = constant
dV = 0

dU = dqV
DU = qV = nCVDT

(2) Isobaric process:
W = - Pext (V2-V1)
Reversible & isobaric process
W = - P (V2-V1)
= - nR (T2-T1)
Irreversible & isobaric process
P1 = P2 = Pext
For reversible & irreversible isobaric or isochoric process, workdone is same.
3. Isothermal process.
(a) Reversible Expansion or compression
W = 
= 
= 


In Expansion W = - ve
DE = 0

(b) Single stage irreversible expansion

W = - Pext(V2 - V1)
|Wrev| > |Wirr| (in case of expansion)
W = - Pext 

(c) Two Stage irreversible Expansion:
Stage I. P'ext = 3 atm Pi = 5 atm
Stage II. P"ext = 2 atm Pf = 2 atm
 Workdone in 2nd stage > Workdone in Ist stage
Workdone in 2nd stage > Workdone in Ist stage
(d) n- stage expansion

Compression - (One stage Compression )
| Wirr | = Pext DV
P1 = 1 atm , P2 = 5 atm , Pext = 5 atm
 | Wirr | > | Wrev | For compression
| Wirr | > | Wrev | For compression
Two stage Comp. n stage Comp


Ex.1 2 moles of an ideal gas initially present in a piston fitted cylinder at 300 K, and 10 atm are allowed to expand against 1 atm but the piston was stopped before it stablished the mechanical equilibrium. If temperature were maintained constant through out the change and system delivers 748.26 J of work, determine the final gas pressure and describe the process on PV diagram.
Sol. Wirrv = - 748.26
Wirr = - Pext [1/P2- 1/P1]nRT
P2 = 4atm
Ex.2 1150 Kcal heat is released when following reaction is carried out at constant volume.
C7H16(l) 11O2(g) --> 7CO2(g) 8H2O(l)
Find the heat change at constant pressure.
The pressure of liquid is a linear function of volume (P = a bV) and the internal energy of the liquid is U = 34 3PV find a, b, w, DE & DH for change in state from 100 Pa, 3m3 to 400 Pa, 6m3
Sol. 100 = a + bV
100 = a + 3b
Also, 400 = a + 6b

DU = 34 3(P2V2 - P1V1)
= 6300 J
DH = DU P2V2 - P1V1
= 6300 2100 = 8400 J
P is a linear function
Pext =  = 250
= 250
W = - Pext(dV)
= - 250(6 - 3) = - 750 J
Ex.3 4 moles of an ideal gas (Cv = 15 J) is subjected to the following process represented on P - T graph. From the given data find out whether the process is isochoric or not ? also calculate q, w, DU, DH,
Sol. PV = nRT
4V = 4R × 400
V = 400 R ........(1)
3V = 4R × 300
V = 400 R ........(2)
i.e., V is constant
w = 0
DU = nCV DT 4 ×15 ×100 = 6000 J
DH = nCP DT n (CV R ) DT
4 ×(15 8.3)×100
9320 J

Ex.4 2 mole of a gas at 1 bar and 300 K are compressed at constant temperature by use of a constant pressure of 5 bar. How much work is done on the gas ?
Sol. w = - nRT ×Pext 
= 19953.6 J
Ex.5 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas (CV = 5/2 R) at 300 K, 5 atm expanded irreversibly and adiabatically to a final pressure of 2 atm against a constant pressure of 1 atm.
(1) Calculate final temperature q, w, DH & DU
(2) Calculate corresponding values if the above process is carried out reversibly.
Sol.. w = CV (T2 - T1) = - Pext R
Given 
Pext = 1,P2 = 2,P1 = 5
q = 0
w = DU = nCVDT
= -1247.1 J
DH = nCPDT
= 1745.94 J
If process is reversible Pvg = Constant
P1- gTg = Constant


dq = 0
dU = dW 

For an ideal gas CP - CV = R


nCVdT = - Pext dV
Pint = dP = Pext
Pint = Pgas = 


CV ln  = - Rln
= - Rln 
 ln
ln  = - R ln
= - R ln 
 ln
ln  = -ln
= -ln 
ln  = -(g -1) ln
= -(g -1) ln  ln
ln  = ln
= ln 

T2(V2)g - 1 = V1g - 1T1
TVg - 1 = Constant
 = Constant
= Constant


dU = dW
nCV(T2 - T1) = - Pext dV
nCV(T2 - T1) = - Pext [V2 - V1]
nCV(T2 - T1) = - Pext 
= - Pext nR


(1) If final volumes are same.
Isothermal process.
P1v1 = Piso V2

Adiabatic process.
P1v1g = Padia V2g

 > 1 >
> 1 > 
 >
> 

(2) If final pressures are same
Isothermal process.
P1V1 = P2 Viso
 =
=  .......(1)
.......(1)
P1V1γ = P2Vγadia
 =
= 
in ideal gas expansion, | Wiso | > | Wadia |
Hence 
Compression
(1) If final volumes are same

For isothermal process
P1V1 = PisoV2
 ..........(1)
..........(1)
Adiabatic process.
P1V1γ = PadiaV2γ
 ..........(2)
..........(2)


(2) If final pressures are same

P1V1 = P2 Viso ..........(1)
P1V1γ = P2 Vγadia ..........(2)


 <
< 



PVx = Const
W = 
= - 
= - k w =
w = 
= 


dU = dq + dW
nCVdT = nCmdT (-PdV)
Cm = CV  ..........(1)
..........(1)
PV = nRT
KV-x V = nRT
kV-x 1 = nRT
k(-x 1)V-x  = nR
= nR

Cm = Cv 

 x ¹ 1
x ¹ 1

1. First law of thermodynamics does not give information regarding the direction of propagation of a process
2. First law of thermodynamics does not tell us why an equilibrium is attained.
3. First law of thermodynamics does not tell us when an equilibrium will be attained.
4. First law of thermodynamics does not give information about why there can not be 100 percent conversion of heat into work

Statement(I) : Second law of thermodynamics states that heat can never be converted into work with 100% efficiency
Statement(II) : No engine in this world can be constructed which operates in cycles and converts all the heat from source to work.
Statement(III) : No refrigertator can be designed which operates in cycles and rejects heat from sink to source, perpetually (self - functioning).
Entropy : Entropy is the direct measurment of randomness or disorderness. Entropy is an extensive property & it is a state function
ds =  for reversible process. entropy is related with complexity of the molecule within the system.
for reversible process. entropy is related with complexity of the molecule within the system.
EtOH > MeOH
C2H6 (g) > C2H5(g)
N2O4 > NO2
O2 > N2 (molecular wt.)
Gas > Liq > Amorphous solid > crystalline solid
Entropy always increases in the following process
(1) s →  ,
,  → g, s → g,
→ g, s → g,
(2) Isothermal expansion of ideal gas.
(3) Mixing of two non reacting gases.
(4) In chemical reaction in which
Dng > 0
(5) Heating of any substance
Classification of process Based on spontaneity

Why Spontaneity


Points to ponder :
Why a system always moves towards disorderness ?
Answer : A system moves towards disorderness because the probability of moving towards disorderness is very high.

For Reversible process :
DS =  Qrevesible = constant
Qrevesible = constant
DS =  Qrevesible = Variable
Qrevesible = Variable
Note : Irreversible process
DSirreversible = 

The entropy change for an irreversible process can be calculated by substituting it with equivalent reversible process. Both will have same entropy change.

DSsystem = 
DSsurrounding = 
DSuniverse = DSsystem + DSsurrounding

1. DSuniverse > 0 Spontaneous
2. DSuniverse = 0 Equilibrium
3. DSuniverse < 0 Non-spontaneous.



(A) General heating or cooling
ds = 
DS =  =
= 
If C is temperature independent

If C is a function of Temperature
C = a + bT
DS = n 
DS = n
(B) In phase transformation
DSfus = 
*A(l)  A(g).
A(g).

*A(s)  A(g)
A(g)

(C) Entropy change during chemical reaction.
aA + bB --> cC + dD

For any chemical reaction


(D) Calculation of entropy change during expansion/compression of ideal gas from P1V1T1 to P2V2T2
From Ist law of thermodynamics
dE = dq + dW
dq = - dW + dE
TdS = PdV + nCVdT
dS =  dV + nCV
dV + nCV
dS =  dV +
dV + 
DS =  = nRln
= nRln +
+ 

For ideal gas
DS = nCVln  + nRln
+ nRln  .
. 
= nCVln  + nRln
+ nRln  + nRln
+ nRln 
= nRln  +(CV R)n ln
+(CV R)n ln

Conclusion

DS = n nRln
nRln
DS = n dT nRln
dT nRln
DS = n nR ln
nR ln 
Calculation of entropy change during isothermal Expansion;

because  =
= = -nRln
= -nRln
nRln =
= 
Wrev > Wirr
DStotal = + ve
Calculation of entropy change during isothermal compression.

qirr + wirr = 0
| wirr | > | wrev |
< 0 >0
| qirr | > | qrev |
Calculation of entropy change during for adiabatic expansion of ideal gas.

For reversible process

Where K is constant

For irreversible process

This means that the final temperature of irreversible process is greater than reversible process.
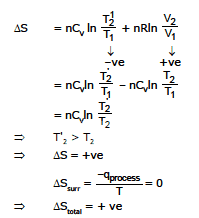
Calculation of entropy change in adiabatic compression.

dT = 110
For reversible
(T2 - T1) = 100K
T2 = T1 100 K
for irreversible  = T1 110 K
= T1 110 K

DSirr = nCVln  nRln
nRln
= nCVln  - nCVln
- nCVln
= nCvln  > 0
> 0

Carnot cycle is based on 4 reversible process.

(1) Reversible isothermal expansion from A to B.
DEAB = 0 ,
WAB = -nRT1ln
(2) Reversible adiabatic expansion from B to C
DEBC = nCV(T2 -T1)
WBC = DEBC
(3) Isothermal compression from C to D
DECD = 0,
WCD = -nRT2ln

(4) Adiabatic compression from D to A.
DEDA = nCV(T1 - T2)
WDA = DEDA
DECycle = 0
Wcycle = -nRT1ln nCV(T2- T1) - nRT2ln
nCV(T2- T1) - nRT2ln nCV(T1- T2)
nCV(T1- T2)
= 
For BC, 
For DA, 



Wcycle = -nR(T1 - T2)ln V2/V1
Efficiency of any engine may be given as

 =
= 


DEcycle = qcyc wcycle
wcycle = - qcycle = 

1 
 =
= 


This means DS is a state function
Gibb's Free Energy (G)
Gsystem = Hsystem - TSsystem
W = Wexpansion Wnon-expansion
Wnon - expansion = wuseful (useful work)
DG = Wnon expansion = Wuseful
All those energy which is available with the system which is utilized in doing useful work is called Gibb's free energy :
Rx :
1. DGsystem = DHsystem - TDSsystem = - TDSuniverse = Wnon expansion = Wuseful
2. DGsystem = - TDSuniverse
3. (a) DSuniverse > 0 or DGsystem < 0 Spontaneous
(b) DSuniverse = 0 or DGsystem = 0 Equilirbium
(c) DSuniverse < 0 or DGsystem > 0 Non-Spontaneous


Rx :
(1) aA bB  cC dD
cC dD
DG° = Standard Gibb's free energy change (P = 1 atm, 298 K)
DG = Gibb's free energy change at any condition.

DG = DG° 2.303 RT log Q ; Q = Reaction Quotient

At equilibrium, DG = 0 and Q = Keq. 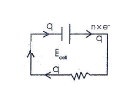
0 = DG° 2.303 RT log keq
DG° = -2.303 RT log keq
å G°(product) - å G° (Reactant) = - 2.303 RT log keq
DH° - TDS° = -2.303 RT log keq
(2) Wcell = q × E
DG = - Wcell
DG = - q × Ecell
Now, one mole e- have charge 96500 coulomb = 1 Faraday (F)
n mole of e- will have charge = n × F or q = n × F
DG = - nFEcell
DG° = -nFE°cell


Third law of thermodynamics states that as the temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of perfectly crystalline substance also approaches zero.


Taking T2 = T and T1 = 0°k.
ST - 0 =  ST =
ST =  For perfectly crystalline substance
For perfectly crystalline substance
The entropy of perfectly crystalline substance can be determined using third law of thermodynamics.
or
With the help of third law of thermodynamics we can calculate the exact value of entropy.

(DG)T,P is a measure of useful work a non PV work (non expansion work) that can be produced by a chemical transformation.e.g.electrical work .
For reversible reaction at constant T & P
dU = dq +dWtotal
dU = dq + dWP, V + dWnon P,V
dU = T.dS - P. dV + dWnon P,V
dU P.dV = T. dS + dWnon P,V
dH = T.dS + dWnon P,V
(dGsys)T,P = dWnon P,V

Useful work done on the system = increase in Gibb's energy of system at constant T & P.
- (DGsys)T,P= - Wnon P,V
- (DGsys)T,P= - Wby, non P,V
Useful work done by the system = decrease in Gibb's energy of system at constant T & P .
If (DGsys)T,P = 0, then system is unable to deliver useful work.

For reversible process in which non expansion work is not possible
dU = dq dW

H = U + PV
dH = dU + P.dV + VdP
dH = T.dS - PdV + PdV + V.dP
dH = T.dS +V.dP
G = H -TS
dG = dH - T.dS -S.dT
dG = T.dS V.dP - T.dS - S.dT
 For a particular system (s/
For a particular system (s/ /g)
/g)
(1) At constant temperature dG = V.dP or  = V
= V
(A) For a system is s/ phase
phase


(B) For an ideal gas, expansion/compression :-
 =
=

(2) At constant pressure : dG =-S.dT or  = - S
= - S
* For phase transformation/chemical reaction
d(DG) = DV.dP - DS dT
H2O(s) --> H2O(l)
DV = VM(H2O,l) - Vm(H2O,s)
DS = SM(H2O,l) - Sm(H2O,s)
A(s) --> B(g) 2C(g)
DrS = SM(B,g ) 2Sm(C,g) - Sm(A,s)
C (s, graphite) --> C(s, diamond)
DV = Vm(C, diamond) - Vm(C-graphite)
At constant temperature:-
d(DG) = DV. dP

At constant pressure

DrGT2 - DrGT1 = - DrS(T2 - T1)
FAQs on Thermodynamics, Chapter Notes, Class 11, Chemistry (IIT-JEE & AIPMT)
| 1. What is thermodynamics? |  |
| 2. What are the laws of thermodynamics? |  |
| 3. What is enthalpy? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions? |  |
| 5. How is thermodynamics related to engineering? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|


















