Drainage System Class 11 Geography
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Drainage Systems of India |

|
| The River Systems of the Himalayan Drainage |

|
| The Peninsular Drainage System |

|
| Extent of Usability of River Water |

|
Introduction
The flow of water through well-defined channels is known as ‘drainage’ and the network of such channels is called a ‘drainage system’.
- It is the outcome of the geological time period, nature and structure of rocks, topography, slope, amount of water flowing and the periodicity of the flow.
- It is perennial (always with water) or ephemeral (water during rainy season, and dry)
- A river drains the water collected from a specific area, which is called its ‘catchment area’.

- An area drained by a river and its tributaries is called a drainage basin.
- The boundary line separating one drainage basin from the other is known as the watershed.
- The catchments of large rivers are called river basins while those of small rivulets and rills are often referred to as watersheds.
- Watersheds are small in area while the basins cover larger areas.
- The drainage pattern resembling the branches of a tree is known as 'dendritic'. The examples of which are the rivers of northern plain.
- When the rivers originate from a hill and flow in all directions, the drainage pattern is known as ‘radial’. The rivers originating from the Amarkantak range present a good example of it.
- When the primary tributaries of rivers flow parallel to each other and secondary tributaries join them at right angles, the pattern is known as ‘trellis’.
- When the rivers discharge their waters from all directions in a lake or depression, the pattern is know as ‘centripetal’.
- On the basis of discharge of water (orientations to the sea), it may be grouped into:
- the Arabian Sea drainage;
- the Bay of Bengal drainage.
- They are separated from each other through the Delhi ridge, the Aravalis and the Sahyadris.
- Nearly 77 per cent of the drainage area consisting of the Ganga, the Brahmaputra, the Mahanadi, the Krishna, etc. is oriented towards the Bay of Bengal while 23 per cent comprising the Indus, the Narmada, the Tapi, the Mahi and the Periyar systems discharge their waters in the Arabian Sea.
- On the basis of the size of the watershed, the drainage basins of India are grouped into three categories:
- Major river basins with more than 20,000 sq. km of catchment area. It includes 14 drainage basins such as the Ganga, the Brahmaputra, the Krishna, the Tapi, the Narmada, the Mahi, the Pennar, the Sabarmati, the Barak, etc.
- Medium river basins with catchment area between 2,000-20,000 sq. km incorporating 44 river basins such as the Kalindi, the Periyar, the Meghna, etc.
- Minor river basins with catchment area of less than 2,000 sq. km include fairly good number of rivers flowing in the area of low rainfall
Drainage Systems of India
Indian drainage system consists of a large number of small and big rivers. It is the outcome of the evolutionary process of the three major physiographic units and the nature and characteristics of precipitation.
On the basis of the mode of origin, nature and characteristics, the Indian drainage may also be classified into:
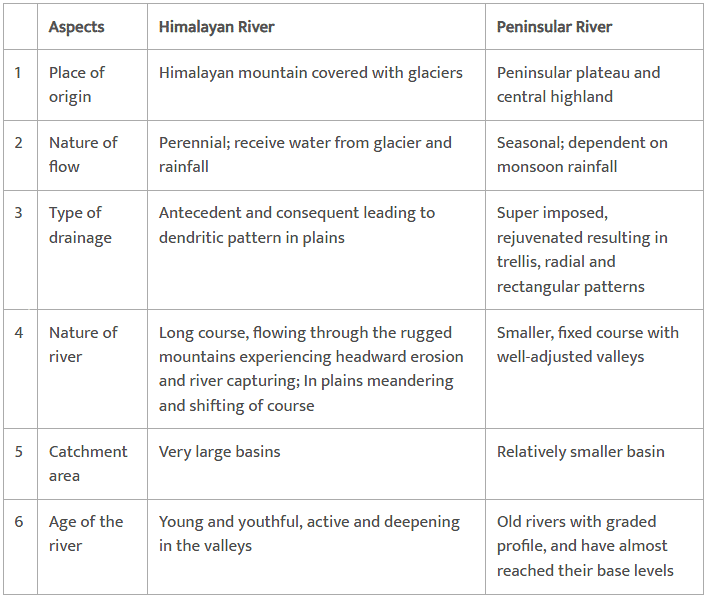
The Himalayan Drainage
- The Himalayan drainage system has evolved through a long geological history.
- Rivers form giant gorges V-shaped valleys, rapids and waterfalls in their mountainous course.
- While entering the plains, they form depositional features like flat valleys, ox-bow lakes, flood plains.
- The important rivers are Ganga, the Indus and the Brahmaputra rivers.
- Since these are fed both by melting of snow and precipitation, rivers of this system are perennial.
Evolution of the Himalayan Drainage
- Geologists believe that a mighty river called Shiwalik or Indo-Brahma traversed the entire longitudinal extent of the Himalaya from Assam to Punjab and onwards to Sind, and finally discharged into the Gulf of Sind near lower Punjab during the Miocene period some 5-24 million years ago.
- The remarkable continuity of the Shiwalik and its lacustrine origin and alluvial deposits consisting of sands, silt, clay, boulders and conglomerates support this viewpoint. in due course of time Indo- Brahma river was dismembered into three main drainage systems:
- The Stretch of the Brahmaputra in Assam and its Himalayan tributaries in the eastern part,
- The Ganga and its Himalayan tributaries in the central part; and
- The Indus and its five tributaries in the western part.
- The dismemberment was probably due to the Pleistocene upheaval in the western Himalayas, including the uplift of the Potwar Plateau (Delhi Ridge), which acted as the water divide between the Indus and Ganga drainage systems.
The River Systems of the Himalayan Drainage
The Himalayan drainage consists of several river systems but the following are the major river systems
The Indus System
- It is one of the largest river basins of the world, covering an area of 11,65,000 sq. km (in India it is 321, 289 sq. km and a total length of 2,880 km (in India 1,114 km).
- It enters into Pakistan near Chillar in the Dardistan region. Find out the area known as Dardistan.
- The Indus also known as the Sindhu, is the westernmost of the Himalayan rivers in India.
- Tributaries such as the Shyok, the Gilgit, the Zanskar, the Hunza, the Nubra, the Shigar, the Gasting and the Dras.

- It originates from a glacier near Bokhar Chu (31 °15' N latitude and 81 °40' E longitude) in the Tibetan region at an altitude of 4,164 m in the Kailash Mountain range.
- In Tibet, it is known as ‘Singi Khamban; or Lion’s mouth. After flowing in the northwest direction between the Ladakh and Zaskar ranges, it passes through Ladakh and Baltistan.
- It cuts across the Ladakh range, forming a spectacular gorge near Gilgit in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The other important tributaries joining the right bank of the Indus are the Khurram, the Tochi, the Gomal, the Viboa and the Sangar. They all originate in the Sulaiman ranges.
The Ganga System
- The Ganga river system is the largest in India having a number of perennial and nonperennial rivers originating in the Himalayas in the north and the Peninsula in the south, respectively.
- The Ganga is the most important river of India both from the point of view of its basin and cultural significance. It rises in the Gangotri glacier near Gaumukh (3,900 m) in the Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand. Here, it is known as the Bhagirathi.
- It cuts through the Central and the Lesser Himalayas in narrow gorges.

- At Devprayag, the Bhagirathi meets the Alaknanda, hereafter, it is known as the Ganga.
- The other tributaries of Alaknanda such as the Pindar joins it at Karna Prayag while Mandakini or Kali Ganga meets it at Rudra Prayag.
- The Ganga enters the plains at Haridwar. From here, it flows first to the south, then to the south-east and east before splitting into two distributaries, namely the Bhagirathi and the Hugli. The river has a length of 2,525 km. It is shared by Uttarakhand (110 km) and Uttar Pradesh (1,450 km), Bihar (445 km) and West Bengal (520 km).
- The Ganga basin covers about 8.6 lakh sq. km area in India alone.
- The river finally discharges itself into the Bay of Bengal near the Sagar Island.
The Brahmaputra System
- The Brahmaputra, one of the largest rivers of the world, has its origin in the Chemayungdung glacier of the Kailash range near the Mansarovar lake.
- The Rango Tsangpo is the major right bank tributary of this river in Tibet. It emerges as a turbulent and dynamic river after carving out a deep gorge in the Central Himalayas near Namcha Barwa (7,755 m). The river emerges from the foothills under the name of Siang or Dihang.
- In Bangladesh, the Tista joins it on its right bank from where the river is known as the Yamuna. It finally merges with the river Padma, which falls in the Bay of Bengal.

- The Brahmaputra is well-known for floods, channel shifting and bank erosion. This is due to the fact that most of its tributaries are large, and bring a large quantity of sediments owing to heavy rainfall in its catchment area. It enters India west of Sadiya town in Arunachal Pradesh.
- The Brahmaputra receives numerous tributaries in its 750 km long journey through the Assam valley. Its major left bank tributaries are the Burhi Dihing and Dhansari (South) whereas the important right bank tributaries are the Subansiri, Kameng, Manas and Sankosh. The Brahmaputra enters into Bangladesh near Dhubri and flows southward.
The Peninsular Drainage System
The Peninsular Drainage System
- The Peninsular drainage system is older than the Himalayan one. This is evident from the broad, largely-graded shallow valleys, and the maturity of the rivers.
- The Western Ghats running close to the western coast act as the water divide between the major Peninsular rivers, discharging their water in the Bay of Bengal and as small rivulets joining the Arabian Sea.
- Most of the major Peninsular rivers except Narmada and Tapi flow from west to east. The Chambal, the Sind, the Betwa, the Ken, the Son, originating in the northern part of the Peninsula belong to the Ganga river system.
- Peninsular rivers are characterised by fixed course, absence of meanders and non-perennial flow of water. The Narmada and the Tapi which flow through the rift valley are, however, exceptions.
The Evolution of Peninsular Drainage System
Three major geological events in the distant past have shaped the present drainage systems of Peninsular India:
- Subsidence of the western flank of the Peninsula leading to its submergence below the sea during the early tertiary period. Generally, it has disturbed the symmetrical plan of the river on either side of the original watershed.
- Slight tilting of the Peninsular block from northwest to the southeastern direction gave orientation to the entire drainage system towards the Bay of Bengal during the same period.
- The upheaval of the Himalayas when the northern flank of the Peninsular block was subjected to subsidence and the consequent trough faulting. The Narmada and The Tapi flow in trough faults and fill the original cracks with their detritus materials. Hence, there is a lack of alluvial and deltaic deposits in these rivers.
River Systems of the Peninsular Drainage
- The Mahanadi rises near Sihawa in Raipur district of Chhattisgarh and runs through Odisha to discharge its water into the Bay of Bengal.
- It is 851 km long and its catchment area spreads over 1.42 lakh sq. km.
- Some navigation is carried on in the lower course of this river. Fifty three per cent of the drainage basin of this river lies in Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh, while 47 per cent lies in Odisha.
- The Godavari is the largest Peninsular river system. It is also called the Dakshin Ganga.
- It rises in the Nasik district of Maharashtra and discharges its water into the Bay of Bengal. Its tributaries run through the states of Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh. It is 1,465 km long with a catchment area spreading over 3.13 lakh sq. km 49 per cent of this, lies in Maharashtra, 20 per cent in Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh, and the rest in Andhra Pradesh.
- The Penganga, the Indravati, the Pranhita, and the Manjra are its principal tributaries. The Godavari is subjected to heavy floods in its lower reaches to the south of Polavaram, where it forms a picturesque gorge. It is navigable only in the deltaic stretch. The river after Rajamundri splits into several branches forming a large delta.
- The Krishna is the second largest east- flowing Peninsular river which rises near Mahabaleshwar in Sahyadri. Its total length is 1,401 km. The Koyna, the Tungbhadra and the Bhima are its major tributaries. Of the total catchment area of the Krishna, 27 per cent lies in Maharashtra, 44 per cent in Karnataka and 29 per cent in Andhra Pradesh.
- The Kaveri rises in Brahmagiri hills (1,341m) of Kogadu district in Karnataka. Its length is 800 km and it drains an area of 81,155 sq. km. Since the upper catchment area receives rainfall during the southwest monsoon season (summer) and the lower part during the northeast monsoon season (winter), the river carries water throughout the year with comparatively less fluctuation than the other Peninsular rivers. About 3 per cent of the Kaveri basin falls in Kerala, 41 per cent in Karnataka and 56 per cent in Tamil Nadu.
- Its important tributaries are the Kabini, the Bhavani and the Amravati. The Narmada originates on the western flank of the Amarkantak plateau at a height of about 1,057 m.
- Flowing in a rift valley between the Satpura in the south and the Vindhyan range ,,...Dhuandhar waterfall near Jabalpur. After flowing a distance of about 1,312 km, it meets the Arabian sea south of Bharuch, forming a broad 27 km long estuary. Its catchment area is about 98,796 sq. km. The Sardar Sarovar Project has been constructed on this rive.
- The Tapi is the other important westward flowing river. It originates from Multai in the Betul district of Madhya Pradesh. It is 724 km long and drains an area of 65,145 sq. km. Nearly 79 per cent of its basin lies in Maharashtra, 15 per cent in Madhya Pradesh and the remaining 6 per cent in Gujarat.
- The pattern of flow of water in a river channel over a year is known as its regime.
- The Ganga has its minimum flow during the January-June period. The maximum flow is attained either in August or in September. After September, there is a steady fall in the flow. The river, thus, has a monsoon regime during the rainy season.
- The Narmada has a very low volume of discharge from January to July but it suddenly rises in August when the maximum flow is attained The Godavari has the minimum discharge in May, and the maximum in July- August. After August, there is a sharp fall in water flow although the volume of flow in October and November is higher than that in any of the months from January to May.
Extent of Usability of River Water
Variability in Water Distribution: Perennial rivers flow year-round, while non-perennial rivers lack water in dry seasons. Excess water during the rainy season often causes floods.
Management Issues: Problems stem more from poor water management than from water scarcity, affecting how floods and droughts are addressed simultaneously.
Inter-Basin Water Transfer: Suggests transferring water from surplus basins to deficit ones and explores existing schemes for inter-basin linkage.
Challenges of River Linking: Highlights logistical challenges, including terrain unevenness, and questions the availability of surplus water for consistent transfer.
Pollution and Usage Problems: Discusses river water pollution from urban, industrial, and ritual sources, and ranks issues like water quantity, pollution, silt, and uneven flow.
Clean-up Initiatives: References major efforts like the Ganga Action Plan and suggests organizing a debate and creating a write-up on river cleanliness initiatives.
|
47 videos|183 docs|155 tests
|
FAQs on Drainage System Class 11 Geography
| 1. What is the significance of the Peninsular Drainage System? |  |
| 2. How does the Peninsular Drainage System contribute to agriculture in India? |  |
| 3. What are some of the major rivers in the Peninsular Drainage System? |  |
| 4. How does the Peninsular Drainage System influence the landscape of southern India? |  |
| 5. What are some of the challenges faced by the Peninsular Drainage System? |  |
|
47 videos|183 docs|155 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|













