Operating Principles Of DC Machines | Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
DC Machine: Introduction
Electrical machines, particularly rotating electrical machines, are basically electro-mechanical. That is, if you have an electrical machine, it can take electrical energy as input and gives mechanical energy as output , or we can reverse the direction of energy flow that is, mechanical energy can be input and electrical energy can be output.
 Electrical Machines
Electrical Machines
DC Machine: Construction & Its Working
- The DC machine can be classified into two types namely DC motors as well as DC generators.
- Most of the DC machines are equivalent to AC machines because they include AC currents as well as AC voltages in them.
- The output of the DC machine is DC output because they convert AC voltage to DC voltage.
- The conversion of this mechanism is known as the commutator, thus these machines are also named commutating machines.
- DC machine is most frequently used for a motor. The main benefits of this machine include torque regulation as well as easy speed. The applications of the DC machine is limited to trains, mills, and mines.
- For example, underground subway cars, as well as trolleys, may utilize DC motors. In the past, automobiles were designed with DC dynamos for charging their batteries.
Working Principle of DC Machine
- A DC machine is an electromechanical energy alteration device.
The working principle of a DC machine is when electric current flows through a coil within a magnetic field, and then the magnetic force generates a torque that rotates the dc motor. The DC machines are classified into two types such as DC generator as well as DC motor.
DC Machine
- The main function of the DC generator is to convert mechanical power to DC electrical power, whereas a DC motor converts DC electrical power to mechanical power.
- The AC motor is frequently used in industrial applications for altering electrical energy to mechanical energy.
- However, a DC motor is applicable where good speed regulation & an ample range of speeds are necessary like in electric-transaction systems.
Construction of DC Machine
- The construction of the DC machine can be done using some of the essential parts like Yoke, Pole core & pole shoes, Pole coil & field coil, Armature core, Armature winding otherwise conductor, commutator, brushes & bearings. Some of the parts of the DC machine is discussed below.
 Parts of D.C. Machine
Parts of D.C. Machine
1. Yoke
- Another name for a yoke is the frame.
- The main function of the yoke in the machine is to offer mechanical support intended for poles and protect the entire machine from moisture, dust, etc.
- Yoke provides the return path for magnetic flux.
- The materials used in the yoke are designed with cast iron, cast steel otherwise rolled steel.
2. Pole and Pole Core
- The pole of the DC machine is an electromagnet and the field winding is winding among pole.
- Whenever field winding is energized then the pole gives magnetic flux.
- The materials used for this are cast steel, cast iron otherwise pole core.
- It can be built with annealed steel laminations to reduce the power drop because of the eddy currents.
3. Pole Shoe
- Pole shoe in the DC machine is an extensive part as well as to enlarge the region of the pole. Because of this region, flux can be spread out within the air-gap as well as extra flux can be passed through the air space toward the armature.
- The main function of pole shoe is the uniform distribution of flux.
- The materials used to build pole shoe is cast iron otherwise cast steel, and also used annealed steel lamination to reduce the loss of power because of eddy currents.
4. Field Windings
- In this, the windings are wounded in the region of pole core & named as field coil.
- Whenever current is supplied through field winding than it electromagnetics the poles which generate required flux.
- The material used for field windings is copper.
5. Armature Core
- Armature core includes a huge number of slots within its edge.
- The armature conductor is located in these slots. It provides the low-reluctance path toward the flux generated with field winding.
- The materials used in this core are permeability low-reluctance materials like iron otherwise cast.
- The lamination is used to decrease the loss because of the eddy current.
6. Armature Winding
- The armature winding can be formed by interconnecting the armature conductor.
- Whenever an armature winding is turned with the help of prime mover then the voltage, as well as magnetic flux, gets induced within it. This winding is allied to an exterior circuit. The materials used for this winding are conducting material like copper.
7. Commutator
- The main function of the commutator in the DC machine is to collect the current from the armature conductor as well as supplies the current to the load using brushes. And also provides uni-directional torque for DC-motor.
- The commutator can be built with a huge number of segments in the edge form of hard drawn copper.
- The Segments in the commutator are protected from the thin mica layer.
8. Brushes
- Brushes in the DC machine gather the current from the commutator and supply it to the exterior load. Brushes wear with time to inspect frequently.
- The materials used in brushes are graphite otherwise carbon which is in rectangular form.
Types of DC Machines
- The excitation of the DC machine is classified into two types namely separate excitation, as well as self-excitation.
- In a separate excitation type of DC machine, the field coils are activated with a separate DC source.
- In the self-excitation type of DC machine, the flow of current throughout the field-winding is supplied by the machine.
The principal kinds of DC machines are classified into four types which include the following:
 Types of DC Machines
Types of DC Machines
1. Separately Excited
- In a Separately Excited DC Machine, a separate DC source is utilized for activating the field coils.
 Separately Excited DC Machine
Separately Excited DC Machine
2. Shunt Wound
- In Shunt wound DC Machines, the field coils are allied in parallel through the armature.
- As the shunt field gets the complete o/p voltage of a generator otherwise a motor supply voltage, it is normally made of a huge number of twists of fine wire with a small field current carrying.
 Shunt Wound DC Machine
Shunt Wound DC Machine
3. Series Wound
- In series-wound D.C. Machines, the field coils are allied in series through the armature.
- As series field winding gets the armature current, as well as the armature current is huge, due to this the series field winding includes few twists of wire of big cross-sectional region.

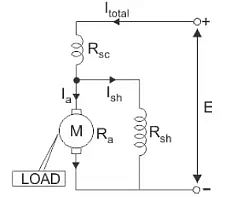
4. Compound Wound
- A compound machine includes both the series as well as shunt fields.
- The two windings are carried out with every machine pole.
- The series winding of the machine includes a few twists of a huge cross-sectional region, as well as the shunt windings, include several fine wire twists.
- The connection of the compound machine can be done in two ways.
1. If the shunt field is allied in parallel by the armature only, then the machine can be named as the ‘short shunt compound machine’.
2. If the shunt field is allied in parallel by both the armature as well as the series field, then the machine is named as the ‘long shunt compound machine’.
EMF Equation of DC Machine
- The DC machine e.m.f can be defined as when the armature in the dc machine rotates, the voltage can be generated within the coils.
- In a generator, the e.m.f of rotation can be called the generated emf, and Er = Eg.
- In the motor, the emf of rotation can be called as counter or back emf, and Er = Eb.

- As the flux for each pole is ‘Φ’, every conductor slashes a flux ‘PΦ’ within a single revolution.
The voltage produced for each conductor = flux slash for each revolution in WB / Time taken for a single revolution within seconds
As ‘n’ revolutions are completed within a single second, 1 revolution will be completed within 1/n second. Thus, the time for a single armature revolution is 1/n sec.
The standard value of produced voltage for each conductor:
P.Φ/1/n = n.P Φ volts
The voltage produced (E) can be decided with the number of armature conductors within series in any single lane among the brushes. Thus, the whole voltage produced:
E = standard voltage for each conductor x no. of conductors within series for each lane
E = n.P.Φ x Z/A
The above equation is the e.m.f. the equation of the DC machine
DC Machine Vs AC Machine
The difference between the AC motor and the DC motor includes the following points given in tables:
Table 1:

Table 2:

Table 3:

Losses in DC Machine
- We know that the main function of a DC machine is to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy.
- Throughout this conversion method, the whole input power cannot be changed into output power because of the power loss in different forms. The type of loss may change from one apparatus to another.
- These losses will decrease the apparatus efficiency as well as the temperature will be increased.
- The DC machine energy losses can be classified into Electrical otherwise Copper losses, Core losses otherwise Iron losses, Mechanical losses, Brush losses, and Stray load losses.
DC Machine Advantages
- DC machines like DC motors have various advantages like starting torque is high, reversing, fast-starting & stopping, and changeable speeds through voltage input
- These are very easily controlled as well as cheaper when compared with AC.
- Speed control is good
- The torque is high.
- Operation is Seamless
- Free from harmonics
- Installation and maintenance is easy
Applications of DC Machine
- At present, the generation of electrical energy can be done in bulk in the form of AC (an alternating current).
- Therefore, the utilization of DC machines like motors and generators DC generators is extremely limited because they are utilized mainly for providing excitation of tiny & middle-range of alternators.
- In industries, DC machines are used for different processes like welding, electrolysis, etc.
- Generally, the AC is generated and after that, it is changed into DC with the help of rectifiers. Therefore DC generator is suppressed through an AC supply which is rectified to use in several applications.
- DC motors are frequently used like variable speed drives.
|
19 videos|90 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Operating Principles Of DC Machines - Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is a DC machine? |  |
| 2. What are the types of DC machines? |  |
| 3. What is the EMF equation of a DC machine? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of DC machines? |  |
| 5. What are the applications of DC machines? |  |




















