Soil Classification & Particle Size Distribution | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Soil Classification
It is necessary to adopt a formal system of soil description and classification in order to describe the various materials found in ground investigation. Such a system must be meaningful and concise in an engineering context, so that engineers will be able to understand and interpret.
It is important to distinguish between description and classification:
Description of soil is a statement that describes the physical nature and state of the soil. It can be a description of a sample, or a soil in situ. It is arrived at by using visual examination, simple tests, observation of site conditions, geological history, etc.
Classification of soil is the separation of soil into classes or groups each having similar characteristics and potentially similar behaviour. A classification for engineering purposes should be based mainly on mechanical properties: permeability, stiffness, strength. The class to which a soil belongs can be used in its description.
The aim of a classification system is to establish a set of conditions which will allow useful comparisons to be made between different soils. The system must be simple. The relevant criteria for classifying soils are the size distribution of particles and the plasticity of the soil.
Particle Size Distribution
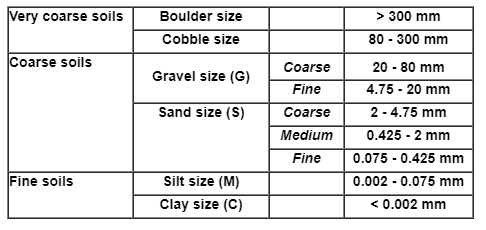
The grain-size range is used as the basis for grouping soil particles into boulder, cobble, gravel, sand, silt or clay.
For measuring the distribution of particle sizes in a soil sample, it is necessary to conduct different particle-size tests.
- Wet sieving is carried out for separating fine grains from coarse grains by washing the soil specimen on a 75 micron sieve mesh.
- Dry sieve analysis is carried out on particles coarser than 75 micron. Samples (with fines removed) are dried and shaken through a set of sieves of descending size. The weight retained in each sieve is measured. The cumulative percentage quantities finer than the sieve sizes (passing each given sieve size) are then determined.
- The resulting data is presented as a distribution curve with grain size along x-axis (log scale) and percentage passing along y-axis (arithmetic scale).
- Sedimentation analysis is used only for the soil fraction finer than 75 microns. Soil particles are allowed to settle from a suspension.
- The decreasing density of the suspension is measured at various time intervals. The procedure is based on the principle that in a suspension, the terminal velocity of a spherical particle is governed by the diameter of the particle and the properties of the suspension.
- In this method, the soil is placed as a suspension in a jar filled with distilled water to which a deflocculating agent is added. The soil particles are then allowed to settle down. The concentration of particles remaining in the suspension at a particular level can be determined by using a hydrometer. Specific gravity readings of the solution at that same level at different time intervals provide information about the size of particles that have settled down and the mass of soil remaining in solution.
The results are then plotted between % finer (passing) and log size.
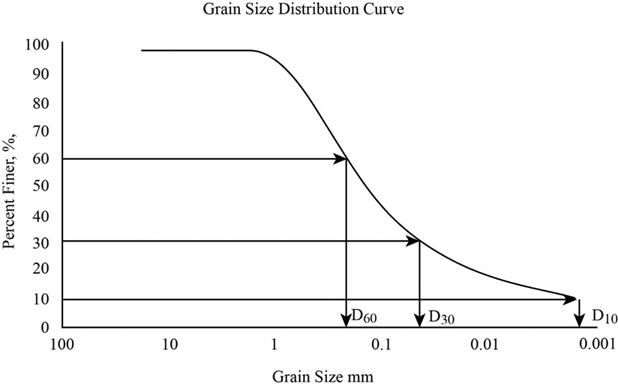
Grain-Size Distribution Curve
The size distribution curves, as obtained from coarse and fine grained portions, can be combined to form one complete grain-size distribution curve (also known as grading curve). A typical grading curve is shown.
From the complete grain-size distribution curve, useful information can be obtained such as:
1. Grading characteristics, which indicate the uniformity and range in grain-size distribution.
2. Percentages (or fractions) of gravel, sand, silt, and clay size.
|
30 videos|126 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Soil Classification & Particle Size Distribution - Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is soil classification and why is it important in civil engineering? |  |
| 2. How is soil classified based on particle size distribution? |  |
| 3. What are the different particle sizes considered in soil classification? |  |
| 4. How does soil classification affect construction projects? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of soil classification based on particle size distribution? |  |






















