Flow About a Cylinder without Circulation (Part - 3) | Additional Documents & Tests for Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
..contd...Analysis of Potential Flows through Complex Variables
Let us combine a source and sink now. Refer to Figure 21.4.The complex potential is given by
(22.24)
This follows
We know,
or ,
Therefore,
(22.25)
We also find
That results in
Under the limiting condition of 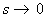 (the flow becomes a doublet)
(the flow becomes a doublet)
We also know,
The strength of the doublets given by
We get family of velocity potential from constant lines
or
(22.27)
This is the equation for constant lines (also see Figure 21.5)
Now from equation (22.25), for the limiting case of s → 0 , one can write
The streamlines associated with the doublet are
ψ = constant lines, which can be expressed as
(22.28)
This is the equation for ψ = constant lines (see Figure 21.5)
Therefore for the doublet
and,
It can also be written as
(22.30)
f s → 0 the F(z) represents a doublet.
Under the limiting conditions,
(22.31)
Thus, by using the elementary complex potential for source, sink, doublet, uniform flow, vortex flow etc more complicated fields can be constructed via the method of superposition. Especially, external flow past objects of various shapes can be simulated. However, for the first course, we shall follow simpler approach and construct various complex flows without using the route of complex potentials. We shall take up such exercises in the following lectures.
FAQs on Flow About a Cylinder without Circulation (Part - 3) - Additional Documents & Tests for Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the significance of flow without circulation around a cylinder in civil engineering? |  |
| 2. How does flow without circulation affect the stability of a cylinder in water? |  |
| 3. What factors influence the occurrence of flow without circulation around a cylinder? |  |
| 4. Can flow without circulation be achieved around any shape other than a cylinder? |  |
| 5. How can flow without circulation be utilized in civil engineering designs? |  |
















