Class 8 Civics Chapter 7 Notes - Understanding Marginalisation
| Table of contents |

|
| What Does it Mean to be Socially Marginalised? |

|
| Who are Adivasis? |

|
| Adivasis and Stereotyping |

|
| Adivasis and Development |

|
| Minorities and Marginalisation |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Marginalization is the social process of relegating individuals or groups to the periphery of society, limiting their access to resources and opportunities. It often results from systemic discrimination or unequal power dynamics, leading to exclusion and social disadvantages.
What Does it Mean to be Socially Marginalised?
Being marginalized means being pushed to the edges, away from the center of social activities. This is a common experience, such as in classrooms or playgrounds, where differences in music taste, accent, chattiness, sports preferences, or clothing can lead to exclusion. Feeling 'not with it' often arises when one's thoughts, feelings, and actions don't conform to the majority.  Marginalisation
Marginalisation
Who are Adivasis?
Adivasis, meaning 'original inhabitants,' closely associated with forests.
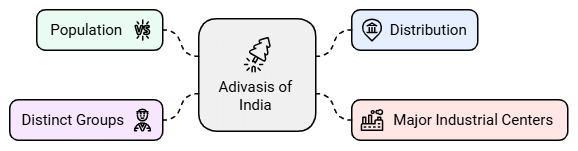
- They Constitute around 8% of India's population.
- Major industrial centers like Jamshedpur, Rourkela, Bokaro, and Bhilai are located in Adivasi areas.
- Over 500 distinct Adivasi groups in India.
- Predominant in states such as Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, and northeastern states.
- Odisha alone is home to over 60 tribal groups.
Diversity and Unique Societies
- Adivasi societies exhibit minimal hierarchy.
- Differ from societies organized around caste or monarchy principles.
- Diverse tribal religions involve ancestral, village, and nature spirit worship.
- Influenced by surrounding religions like Shakta, Buddhist, Vaishnav, Bhakti, and Christianity.
- Adivasi religions have impacted dominant regional faiths.
- Substantial Adivasis embraced Christianity in the nineteenth century.
Language and Influence
- Adivasis communicate in their own languages, possibly as ancient as Sanskrit.
- Santhali, with the largest number of speakers, has influenced mainstream Indian languages like Bengali.
Adivasis and Stereotyping
In India, Adivasi communities are often 'showcased' in specific ways, such as during school functions, official events, books, and movies. Portrayals are frequently stereotypical, featuring colorful costumes, headgear, and traditional dancing.
Misrepresentation and Lack of Understanding
- Despite such showcases, there is limited awareness about the realities of Adivasi lives.
- This misrepresentation can lead to misconceptions, viewing Adivasis as exotic, primitive, and backward.
False Assumptions and Blame
- False assumptions may attribute their perceived lack of advancement to resistance to change or new ideas.
- Adivasis are sometimes unfairly blamed for their supposed resistance, hindering their progress.
Adivasis and Development
 Adivasis
Adivasis
Forests in Indian History
- Forests played a crucial role in the development of Indian empires and settled civilizations.
- They provided essential resources like metal ores (iron, copper, gold, silver), coal, diamonds, timber, medicinal herbs, animal products, and animals such as elephants.
- Forests were vital for recharging rivers and maintaining air and water quality.
- Until the nineteenth century, forests covered a significant part of India, and Adivasis had deep knowledge, access, and control over these areas.
- Adivasis were crucial for providing access to forest resources, and empires heavily depended on them.
Changes in Adivasi Lives
- In the precolonial era, Adivasis were traditionally hunter-gatherers, nomads, and practitioners of shifting agriculture.
- Over the past 200 years, economic changes, forest policies, and political force have forced Adivasis into migration and changed their traditional ways of life.
- They have been compelled to work in plantations, construction sites, industries, and as domestic workers, losing direct access to forests.
 |
Download the notes
Short Notes - Understanding Marginalisation
|
Download as PDF |
Displacement and Loss
- Forest lands have been cleared for timber, agriculture, and industry, leading to Adivasi displacement.
- Mining and industrial projects take over areas rich in minerals, displacing Adivasis from their lands.
- Many displaced Adivasis face challenges in cities, working for low wages and experiencing poverty.
- Loss of lands and forest access results in the deprivation of livelihoods, food sources, and traditions.
Social and Economic Impact
- Adivasis, when displaced, not only lose income but also traditions and customs.
- The economic and social dimensions of tribal life are interconnected, and destruction in one sphere affects the other.
- Dispossession and displacement often lead to a painful and violent process for Adivasis.
Minorities and Marginalisation
We highlighted the Constitutional safeguards for religious and linguistic minorities, acknowledging the significance of protecting these communities from cultural domination, discrimination, and disadvantage.
Muslims and Marginalisation
 Muslims
Muslims
- The 2011 census indicates that Muslims constitute 14.2% of India's population, facing marginalization due to historical deprivation in socio-economic development.
- Tables presenting data on basic amenities, literacy, and public employment underscore the challenges faced by the Muslim community in comparison to other groups.
- Recognizing this disparity, a high-level committee chaired by Justice Rajindar Sachar in 2005 examined and reported on the social, economic, and educational status of Muslims, revealing parallels with the marginalization experienced by Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
Dimensions of Marginalization
- Economic and social marginalization among Muslims is evident in distinct customs and practices, leading to identification differences and unfair treatment.
- Social marginalization sometimes results in migration and ghettoization, while prejudice may escalate to hatred and violence.
Complex Nature of Marginalization
- The experiences of various marginalized groups, including Adivasis and women, emphasize the complexity of marginalization, requiring diverse strategies, measures, and safeguards for redressal.
- Protection of Constitutional rights and adherence to laws and policies are crucial for preserving India's unique diversity and fulfilling the State's commitment to equality for all.
Conclusion
- Explored marginalisation through the experiences of various communities.
- Different reasons for marginalisation exist, with each community experiencing it uniquely.
- Marginalisation linked to disadvantage, prejudice, and powerlessness.
- India has several marginalised communities, including Dalits, explored in the next chapter.
- Marginalisation results in low social status and unequal access to education and resources.
- Lives of marginalised individuals can change, and struggles for rights and opportunities persist.
- Marginalised communities aim to maintain cultural distinctiveness while pursuing development and rights.
|
69 videos|426 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Civics Chapter 7 Notes - Understanding Marginalisation
| 1. What does it mean to be socially marginalised? |  |
| 2. Who are Adivasis? |  |
| 3. How does stereotyping affect Adivasis? |  |
| 4. How do development initiatives impact Adivasis? |  |
| 5. What role do minorities play in the context of marginalisation? |  |





















