Earth - Basics, Latitudes and Longitudes | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Longitudes and Latitudes |

|
| Rotation |

|
| Revolution |

|
| Time and Longitude |

|
| Standard Time |

|
| International Date Line |

|
| The Solar System |

|
| The Moon |

|
| Solstice |

|
| Equinox |

|
| Atmosphere |

|
Longitudes and Latitudes
- Longitude is an angular distance, measured in degrees along the equator east or west of the Prime (or First) Meridian.
- The prime meridian is at 0°, passing through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich near London, England
 Longitude and Latitude
Longitude and Latitude - They have one very important function, they determine local time in relation to G.M.T. or Greenwich Mean Time, which is sometimes referred to as World Time.
- Latitude of a place is defined as the arc, measured in degrees, north or south of the meridian between that place and equator. The Equator is given the value of 0°.
- The latitude thus ranges from 0° at the equator to 90° north or south at poles.
- As the earth is slightly flattened at the poles, the linear distance of a degree of latitude at the pole is a little longer than that at the equator.
For example at the equator (0°) it is 68.704 miles, at 45° it is 69.054 miles and at the poles, it is 69.407 miles. The average is taken as 69 miles (111km). (1 mile = 1.607 km)
Important parallels of latitude
- Besides the equator (0°), the north pole (90°N), and the south pole (90° S), there are four important parallels of latitudes:
(i) Tropic of Cancer (23½° N) in the northern hemisphere.
(ii) Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S) in the southern hemisphere.
(iii) Arctic circle at 66½° north of the equator.
(iv) Antarctic circle at 66½° south of the equator.
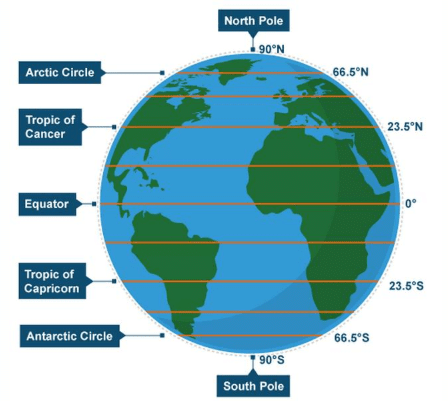 Parallels of latitude
Parallels of latitude
Important Meridians of Longitude
(i) The Prime Meridian is the reference line for measuring longitude. It is designated as 0 degrees, and all other longitudes are calculated as either east or west from this line. The most commonly recognized Prime Meridian today runs through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, near London, England.
(ii) The International Date Line is an imaginary boundary extending from the North Pole to the South Pole, primarily following the 180th meridian of longitude. It marks the division between two consecutive calendar days. Crossing the International Date Line from west to east results in losing a day, while traveling from east to west adds a day. This line helps manage time differences around the globe.

Rotation
- Earth rotates along its axis from west to east.
- It takes approximately 24 hrs to complete on rotation.
- Days and nights occur due to the rotation of the earth.
- The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called the circle of illumination.
- Earth rotates on a tilted axis. Earth’s rotational axis makes an angle of 23.5° with the normal i.e. it makes an angle of 66.5° with the orbital plane. The orbital plane is the plane of the earth’s orbit around the Sun.

Revolution
- The second motion of the earth around the sun in its orbit is called revolution. It takes 365¼ days (one year) to revolve around the sun.
- Six hours saved every year are added to make one day (24 hours) over a span of four years. This surplus day is added to the month of February. Thus every fourth year, February is of 29 days instead of 28 days. Such a year with 366 days is called a leap year.
 Revolution of the Earth and Seasons
Revolution of the Earth and Seasons
Time and Longitude
- One hour of time is equivalent to 15° of longitude.
- This also means that 1° of longitude is covered every 4 minutes during the daily rotation of the earth.
- The earth rotates from west to east, so every 15° we go eastwards, local time is advanced by 1 hour. Conversely, if we go westwards, local time is retarded by 1 hour.
- We may thus conclude that places east of Greenwich see the sun earlier and gain time, whereas places west of Greenwich see the sun later and lose time.
- If we know G.M.T., to find the local time, we merely have to add or subtract the difference in the number of hours from the given longitude
Standard Time
- Most countries adopted a standard time following the International Meridian Conference of 1884, held in Washington.
- The standard time in India is the local time of a place at
 longitude near Allahabad.
longitude near Allahabad.
International Date Line
- The 180th meridian was designated the International Date Line by the IMC held in Washington D.C. in 1884.
- Counting from Greenwich Meridian, the date immediately east of this line is one day ahead or 12 hours faster than the west.
The Solar System
 Solar System
Solar System
- The Solar System consists of the Sun, eight planets, their moons, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids.
- The Sun, located at the center, is a massive ball of hot gases and provides light and heat to all celestial bodies.
- The planets revolve around the Sun in elliptical orbits, with Mercury being the closest and Neptune the farthest.
- Jupiter, the largest planet, has a diameter of approximately 143,000 km, while Mercury, the smallest planet, has a diameter of about 4,880 km.
- Earth, the third planet from the Sun, is the only planet known to support life due to its atmosphere, water, and temperature.
- Venus and Uranus rotate on their axes in a direction opposite to most other planets.
- The Solar System is held together by the Sun's gravitational force, maintaining the orbits of all celestial bodies.
The Moon
 View of moon
View of moon
- The moon is the earth’s only satellite with a diameter of about 3480 km and a mass of about 1/81 that of earth.
- The mean distance between the earth and the moon is about 385000 km.
- The time is taken by the moon to complete one revolution around the earth in 27 days, 7 hours, 43 minutes, and
 seconds.
seconds. - The moon at all times keeps the same side towards the earth. This means it rotates on its axis exactly once in each sidereal month.
- Like the earth, half of the moon’s surface is always illuminated by the sun’s rays.
Eclipses
- The total or partial obscuration of the light from a celestial body as it passes through the shadow of another body is known as an eclipse.
Geoids
- The geoid is the theoretical shape of the earth based on estimates of its mass, elasticity, and speed of rotation, ignoring its surface irregularities.
- On the basis of certain astronomical observation made by French astronomer, Jean Richer, it has been revealed that the true form of the earth is not a perfect sphere.
- Slightly compressed at the poles, its shape is known as an ‘oblate ellipsoid’, or ‘ellipsoid of revolution’.
Great circle
- It is a circle on the earth’s surface, the plane of which passes through the earth’s center, cutting it into two equal halves. The equator is a great circle.
Small circle
- It is made by a plane passing through the globe anywhere except through the center.
- The Tropic of Cancer at
 and the Tropic of Capricorn at
and the Tropic of Capricorn at  are small circles.
are small circles.
Solstice
- On 21st June, the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun. The rays of the sun fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer. As a result, these areas receive more heat.
- The areas near the poles receive less heat as the rays of the sun are slanting.
- The north pole is inclined towards the sun and the places beyond the Arctic Circle experience continuous daylight for about six months.
- Since a large portion of the northern hemisphere is getting light from the sun, it is summer in the regions north of the equator. The longest day and the shortest night at these places occur on 21st June.
- At this time in the southern hemisphere, all these conditions are reversed. It is winter season there. The nights are longer than the days. This position of the earth is called the summer solstice.
- On 22nd December, the Tropic of Capricorn receives direct rays of the sun as the south pole tilts towards it. As the sun’s rays fall vertically at the Tropic of Capricorn (23½° s), a larger portion of the southern hemisphere gets light. Therefore, it is summer in the southern hemisphere with longer days and shorter nights. The reverse happens in the northern hemisphere. This position of the earth is called the winter solstice.
Equinox
- On 21st March and September 23rd, direct rays of the sun fall on the equator. At this position, neither of the poles is tilted towards the sun; so, the whole earth experiences equal days and equal nights. This is called an equinox.
- On 23rd September, it is the autumn season (season after summer and before the beginning of winter) in the northern hemisphere and spring season (season after winter and before the beginning of summer) in the southern hemisphere. The opposite is the case on 21st March, when it is spring in the northern hemisphere and autumn in the southern hemisphere.
- Thus, you find that there are days and nights and changes in the seasons because of the rotation and revolution of the earth respectively.
- Rotation = Days and Nights.
- Revolution = Seasons.
Atmosphere
Troposphere:
- It is the lowermost atmospheric layer extending from about 8 km at the poles and 16 km at the equator. It is characterized by an almost uniform decrease of temperature with a rise in altitude (about 1°C per 165 meters)
Stratosphere
- The second layer of the atmosphere is called the stratosphere.
- The level at which the troposphere gives way to the stratosphere is called the tropopause.
- The upper limit of this layer is called stratopause.
- Within the stratosphere, temperature increases from about 60°C tropopauses to about 0°C at stratopause.
- Ozone is produced in tropical and mid-latitudes of the stratosphere.
- The stratosphere provides ideal conditions for flying airplanes.
Mesosphere
- The mesosphere is the atmospheric layer extending between the stratopause (at an altitude of about 50 km) and mesopause—the upper limit of the mesosphere (at about 80-90 km).
- Within the mesosphere, the temperature decreases with altitude from about 0°C at stratopause to about-100°C at mesopause.
Thermosphere and Exosphere
- The thermosphere is the uppermost layer of the atmosphere, extending from the mesosphere at an altitude of about 85 km. to 400 km. of the atmosphere.
- Within it, the temperature increases with altitude from about-100°C at the mesosphere to over 150°C.
- The exosphere is the boundary between the earth’s atmosphere and the interplanetary space.
- It extends from about 400 km above the earth’s surface.
- The magnetosphere is the area surrounding the earth extending to about 60,000 km on the side facing the sun and more on the opposite side.
 Layers of atmosphere
Layers of atmosphere
Isolation
- It is the radiant energy that reaches the surface of the earth from the sun. The sun emits a wide variety of energy waves from very short X-rays to longer infrared rays.
- Only about 1 part in 2,000 million of the total of sun’s radiation reaches the earth, it is essential for the sustenance of life here.
|
1366 videos|1313 docs|1016 tests
|
FAQs on Earth - Basics, Latitudes and Longitudes - SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year
| 1. What are the differences between latitude and longitude? |  |
| 2. How does the Earth's rotation affect time zones? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the International Date Line? |  |
| 4. What are solstices and equinoxes, and why are they important? |  |
| 5. How does the Moon influence Earth, and what are its phases? |  |
|
1366 videos|1313 docs|1016 tests
|















