Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 2
What are Microorganisms?
Living Organisms which are very minute and cannot be seen by naked (unaided) eyes are known as microorganisms or microbes.
 Microorganisms
Microorganisms
- Some multicellular microorganisms, such as fungus which grows on bread, can be seen with a magnifying glass. Others such as bacteria, cannot be seen without the help of a microscope, so they are called microorganisms or microbes.
- Viruses are also microscopic. They, however, reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant or animal.
- Microorganisms are classified into four major groups: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and some algae.
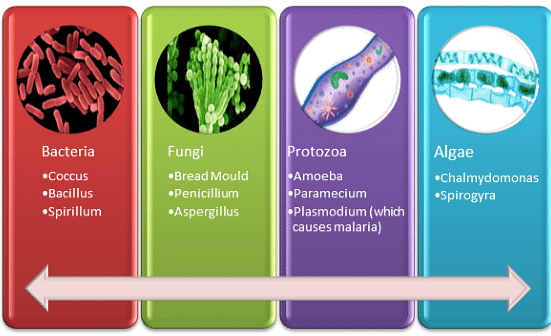 Four major groups of microorganisms
Four major groups of microorganisms
Where do Microorganisms Live?
- Microorganisms can be single-celled (bacteria, some algae, and protozoa) or multicellular (algae and fungi).
- They are capable of surviving in various environments, including ice-cold climates, hot springs, deserts, and marshy lands.
- Microorganisms can also be found living inside the bodies of other organisms, including humans.
Microorganisms and Us
Microorganisms play an important role in our lives. Some of them are beneficial in many ways whereas some others are harmful and cause diseases.
Making of Curd & Bread
- Bacteria are used in making curd, cheese, pickles, and many other food items.
- Specific bacteria, Lactobacillus, cause the formation of curd from milk. That is why a little quantity of curd (which includes Lactobacillus) is added to milk for making curd.
Bacteria and yeast aid in the fermentation of rice idlis and dosa batter.
Yeast reproduces quickly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. This process is used in the baking industry for making breads, pastries, and cakes.
Louis Pasteur discovered fermentation in 1857.
Commercial Use of Microorganisms
- Microorganisms are used to make a lot of alcohol, wine, and vinegar.
- Yeast is used to produce alcohol and wine on a large scale.
- To do this, yeast is grown using natural sugars found in grains like barley, wheat, rice, and in crushed fruit juices.
Medicinal Use of Microorganisms
- When we get sick, doctors may prescribe us antibiotic tablets, capsules, or injections like penicillin. These medicines are made from microorganisms.
- Nowadays, medicines made from bacteria and fungi are used to kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms. These medicines are called antibiotics.
- Some well-known antibiotics made from fungi and bacteria are streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin.
Vaccine
- When a disease-carrying microbe enters our body, the antibodies produced by our body fight with the invader. If microbes enter again, the body also remembers how to fight with the microbes.
- If dead or weakened microbes are injected into a healthy body, the body fights and kills them by producing suitable antibodies.
- The antibodies remain in the body for protection from the disease-causing microbes. This is how a vaccine works.
- Several diseases like cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox, and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination.
Increasing Soil Fertility
- Some bacteria and blue green algae are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility.
- These microbes are commonly called biological nitrogen fixers.

Cleaning the Environment
- Microbes, which are tiny organisms, help in breaking down plant waste and turning it into manure.
- When plants or animals die, they leave behind dead organic matter on the ground.
- Microorganisms decompose this organic waste and convert it into simpler substances.
- These substances are then used by other plants and animals for growth and nourishment.
- Microorganisms can also be used to break down harmful and smelly substances, helping to clean up the environment.
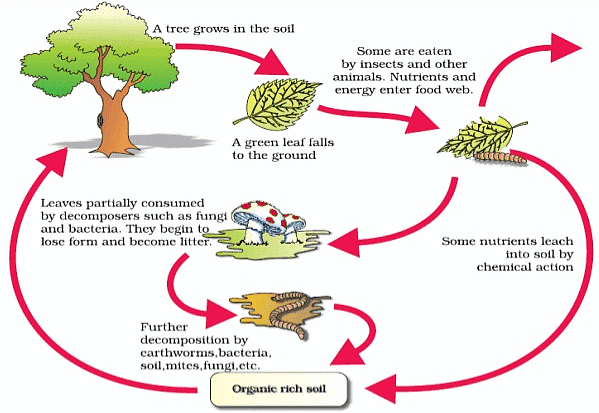 Diagrammatic representation of decomposition cycle in terrestrial ecosystem
Diagrammatic representation of decomposition cycle in terrestrial ecosystem
Harmful Microorganisms
- Microorganisms can be harmful in various ways.
- Certain microorganisms can cause diseases in humans, plants, and animals. These disease-causing microorganisms are called pathogens.
- Some microorganisms can also spoil food, clothing, and leather.
Disease-causing Microorganisms in Humans
- Microbial disease that can spread from an infected person to healthy person through any agency are called communicable disease. Examples of such diseases include cholera, common cold, chicken pox and tuberculosis.
- Agencies that can cause spread of communicable diseases may be air, contaminated food, water and other drinks, use of utensil and cloth of infected person and physical contact.
- Flies carry the disease‑causing microbes from excreta (faecal matter, spit etc.) of the diseased person to the foods or drinks of a healthy persons. In this way, flies and some other insects like cockroaches act as carriers of microbes. These carriers of disease-causing microbes are also called vectors.
 Housefly
Housefly - Mosquitoes are carriers of microbes of many various diseases. For example, female Anopheles mosquito is the carrier of parasite of malaria (Plasmodium). Female Aedes mosquito acts as carrier of dengue virus.
 Female Anopheles mosquito
Female Anopheles mosquito
Disease-causing Microorganisms in Animals
Several microorganisms not only cause diseases in humans and plants, but also in other animals. For example, anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium. Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by a virus.
Disease-causing Microorganisms in Plants
- Several microorganisms cause diseases in plants like wheat, rice, potato, sugarcane, orange, apple and others.
- The diseases reduce the yield of crops. They can be controlled by the use of certain chemicals which kill the microbes.

Food Poisoning
- Some microorganisms that grow on our food may produce toxic substances. The toxin make the food poisonous causing serious illness and even death.
Food Preservation
- Microbes such as bacteria and fungus spoil our raw or cooked food. To save the food from the attack of microorganisms we use some methods to preserve our food.
Common methods to preserve food in our Homes
(a) Chemical Method
- Salts and edible oils are the common chemicals generally used to check the growth of microorganisms.
- Therefore they are called preservatives. We add salt or acid preservatives to pickles to prevent the attack of microbes. Sodium benzoate and sodium meta-bisulphite are common preservatives.
(b) Preservation by Common Salt
- Common salt has been used to preserve meat and fish for ages.
- Meat and fish are covered with dry salt to check the growth of bacteria.
- Salting is also used to preserve amla, raw mangoes, tamarind, etc.
(c) Preservation by Sugar
- Jams, jellies and squashes are preserved by sugar. Sugar reduces the moisture content which inhibits the growth of bacteria which spoil food.
(d) Preservation by Oil and Vinegar
- Use of oil and vinegar prevents spoilage of pickles because bacteria cannot live in such an environment. Vegetables, fruits, fish and meat are often preserved by this method.
(e) Heat and Cold Treatments
- Boiling kills many microorganisms.
- Similarly, we keep our food in the refrigerator. Low temperature inhibits the growth of microbes.
- Pasteurised milk can be consumed without boiling as it is free from harmful microbes. The milk is heated to about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. By doing so, it prevents the growth of microbes.
- This process was discovered by Louis Pasteur. It is called pasteurisation.
(f) Storage and Packing
- These days dry fruits and even vegetables are sold in sealed air tight packets to prevent the attack of microbes.
Nitrogen Cycle
Rhizobium is involved in the fixation of nitrogen in leguminous plants (pulses).
- Sometimes nitrogen gets fixed through the action of lightning. But the amount of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains constant.
 Root of Legume Plants
Root of Legume Plants - Some bacteria and blue green algae present in the soil fix nitrogen gas from the atmosphere and convert it into nitrogenous compounds.
- On the other hand, certain bacteria convert compounds of nitrogen present in the soil into free nitrogen gas which is released to the atmosphere.
- Due to this nitrogen cycle, the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains more or less constant.
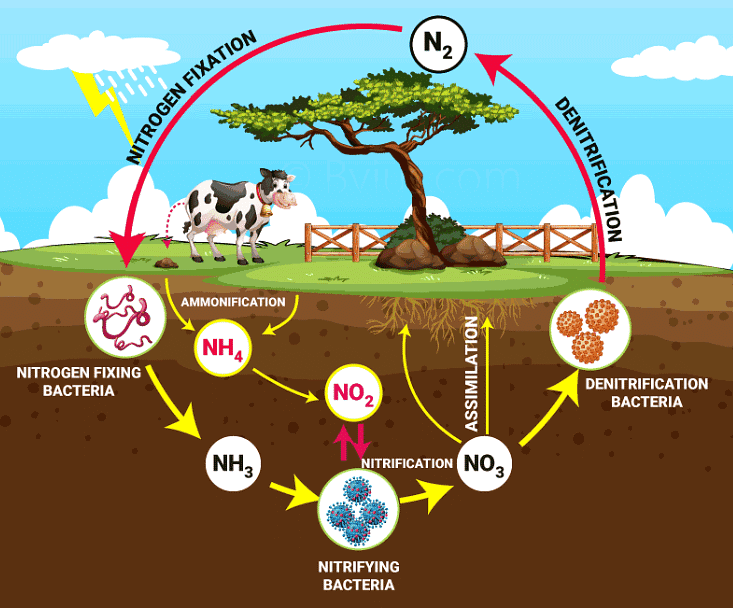 Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen Cycle
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 2
| 1. What are microorganisms and why are they important? |  |
| 2. Where do microorganisms typically live? |  |
| 3. How do microorganisms benefit humans? |  |
| 4. What are harmful microorganisms and how do they affect human health? |  |
| 5. How do microorganisms help in cleaning the environment? |  |

















