Environmental Awareness In India | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
- Environmental awareness refers to understanding the natural world and making choices that either help or harm it.
- It involves recognizing the fragility of our environment and the need to protect it.
- Raising environmental awareness is a simple way to become a caretaker of the planet and work towards a better future for upcoming generations.
- People need to realize that the earth requires protection to survive.
- The term Environmentalism represents the idea that humans have a duty to respect, protect, and preserve nature from damage caused by human activities.
- On a larger scale, Environmentalism is one of the most effective approaches to address the serious consequences of human actions and improve the health of our planet.
- To effectively tackle current environmental problems, it helps to know some of the major issues that harm our environment. These include:
- Oil drilling: Society's dependence on fossil fuels is a major problem. Oil spills and offshore drilling harm marine life, pollute the earth, and contribute to increased carbon dioxide levels, which lead to global warming and ocean acidification.
- Deforestation: Cutting down trees for human use leads to the extinction of wildlife. As forests are cleared, many animals lose their homes, significantly reducing their chances of survival.
- Plastic goods production: A lot of waste comes from plastic products. Over 1 million plastic bottles are sold every minute, and 91% of them are not recycled, resulting in more than 8 million tons of plastic entering the ocean each year. Additionally, producing plastic increases air and water pollution due to the energy it requires.

Importance of Environmental Awareness
- The level of greenhouse gases is constantly rising, increasing by more than one-third since the industrial revolution.
- As greenhouse gases grow, global temperaturesalso increase, leading to various serious effects, including:
- Melting glaciers and severe droughts, which cause more water shortages and heighten the chance of wildfires.
- Rising sea levels that lead to coastal flooding, particularly affecting areas like Florida and the Gulf of Mexico.
- More pests, heat waves, and heavy rainfalls in forests, farms, and cities, which can harm or destroy agriculture and fisheries.
- An increasing rate of coral reef destruction, which contributes to the loss of plants and animals, leading to extinction.
- Higher rates of allergies, asthma, and infectious diseases due to more pollen from ragweed, increased air pollution, and better conditions for pathogens and mosquitoes to thrive.
- Without environmental awareness and active steps to protect our planet, everyone will breathe in poor air quality, leading to more serious health issues for people.
Air Pollution Challenges

- Air pollution accounts for 12.5% of all deathsin India and claims the lives ofapproximately 100,000 children under five years old annually.
- This issueis a significant concern due to its impactonpublic health.
Water Pollution Challenges
- 86% of water bodiesin India are classified as "critically polluted,"rendering them unsuitable for drinking or domestic use.
- TheGanges River is identified as the most polluted riverglobally, with the Yamuna River ranking as the 10th most polluted.
- Groundwateris extensively utilized, with over 94.5% of agricultural, irrigation, and other practices relying on it.
Waste Management Challenges

- Urban areas in India produce a staggering62 million tonnes of waste annually, exceeding the weight of the Great Pyramid of Giza by more than tenfold.
- Only 70% of this waste is collected, 20% is treated, and the remaining half is deposited in landfills.
- Over the past decade, India has witnessed a 56% surge in industries generating hazardous waste, such as pesticides and heavy metals.
Deforestation Challenges
- Threats to Indian forests include illegal logging, mining, and land conversion for agriculture and urban development.
- These activities result in deforestation and land degradation, impacting both the environment and communities reliant on forests for their livelihoods.
- Biodiversity loss occurs due to deforestation, disrupting ecosystems and cultural practices tied to forest-dependent species.
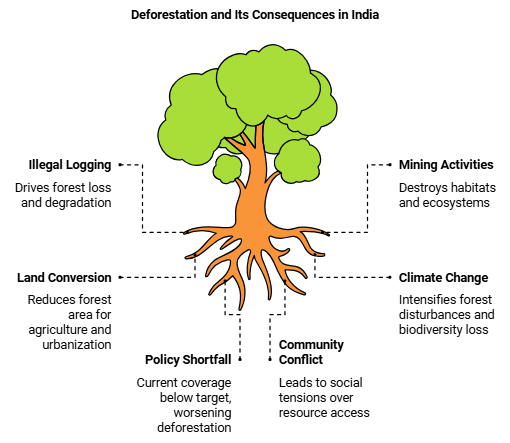
- Climate change exacerbates forest disturbances like insect outbreaks, wildfires, and storms, affecting forest productivity and species distribution.
- By 2030, 45-64% of India's forests will face the consequences of climate change.
- Despite a target of 33% forest cover outlined in the National Forest Policy, India currently only has 24.62% forest coverage, which is rapidly decreasing.
- Conflict arises between local communities and commercial interests like pharmaceutical or timber industries, leading to social tensions and violence over forest resource access.
Legislative Measures and Environmental Restoration Efforts
Future Projections
- By 2030, it is estimated that India's annual waste generation will escalate to 165 million tonnes, significantly exacerbating the existing waste management challenges.
Government Initiatives
- Recognizing the gravity of these environmental issues, the Indian government has enacted various laws and established committees to address the urgent need for environmental restoration.
Importance of Environmental Legislation
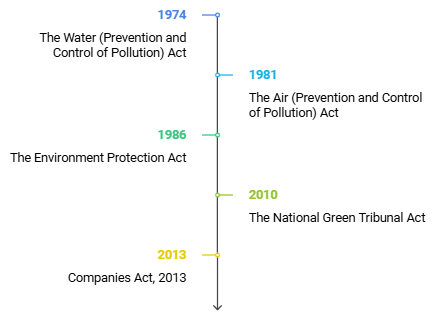
- Companies Act, 2013
- The National Green Tribunal Act, 2010
- The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- The Environment Protection Act, 1986
- The Hazardous Waste Management Regulations, etc.
Challenges in Environmental Sustainability
- Faulty plantation drives at Delhi
- Promotion of 'monoculture' plantation
- The disaster of converting Mangrove zones to Shrimp farms
- Frauds and loopholes under CSR
Despite the presence of crucial environmental laws such as the Companies Act, 2013, and the Environment Protection Act, 1986, there remains a significant gap between environmental ideals and practical implementation. This disparity has led to several environmental missteps in various sectors due to insufficient awareness and knowledge.

For Instance,
- Faulty Plantation Practices at Delhi
- In Delhi, over ₹137 million was expended on tree plantation efforts, yet the forest restoration endeavors failed. The failure stemmed from improper plantation techniques and the selection of high-maintenance tree species.
- Monoculture Plantation Issues
- Monoculture, characterized by the cultivation of a single type of crop or tree for commercial purposes, poses threats to biodiversity and the environment, earning the nickname 'biological desert.'
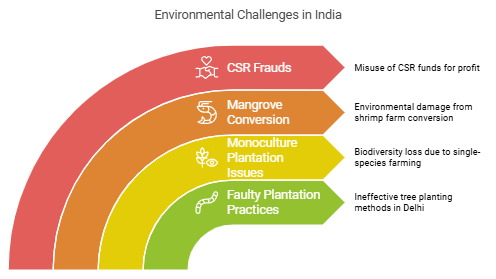
- Mangrove Conversion to Shrimp Farms
- Converting mangrove zones into shrimp farms, particularly in areas like Sundarbans and the Godavari Delta, has led to significant environmental repercussions. The acidic soil of mangrove forests is unsuitable for shrimp cultivation, resulting in ecological harm.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Frauds
- While CSR was mandated under the Companies Act, 2013, in India to integrate social and environmental values into business practices, some companies have exploited loopholes for profit, engaging in fraudulent activities like money laundering under the guise of charitable initiatives.
These instances underscore the critical need for comprehensive environmental education across sectors to bridge the existing knowledge gaps and promote sustainable practices.
Importance of Environmental Education
- Environmental Education is crucial for addressing issues and finding balanced solutions among Social, Environmental, and Economic dimensions.
- Education plays a significant role in fostering environmentally sustainable societies.
Reasons for Environmental Education in India
- For Nature and Conservation:Understanding ecosystems and biodiversity to protect natural resources.
- For the Community: Involving and empowering local communities in environmental initiatives.
- For Sustainable Development: Promoting practices that meet present needs without compromising future generations.
- For Research and Project Development:Enhancing research capabilities for environmental solutions and innovation.
How to Promote Environmental Awareness
While Earth Day is recognized on April 22nd each year, it is important for the health of our planet to develop a deeper understanding of how to care for it on all days of the year.
Some ways to raise environmental awareness include:
- Going paperless: Using online services is very friendly to the environment and can help cut down on the amount of paper needed for printing bills and reminders. So, choose paperless billing whenever possible.
- Educating your kids: A key way to protect the environment for the future begins at home. Teach your children the three R’s—Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle—and emphasize the importance of keeping the Earth clean. When kids learn and practice these habits early on, they are more likely to contribute to the planet's health in the future.
- Contributing to an environmental cause: Spending some of your time or money on a cause that supports a greener world not only benefits the planet but also gives you a sense of fulfilment from your contribution.
- Implementing green strategies: One of the best ways to help our planet survive is to start using more reusable items and recycling. Reducing your use of plastic water bottles significantly lowers your carbon footprint. Since plastic bottles can take hundreds of years to break down in landfills, choosing alternatives like aluminium or glass bottles can help reduce landfill waste and improve air quality.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Overview
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) involves companies incorporating social and environmental considerations into their business practices.
- CSR represents a company's commitment to improving the well-being of consumers, employees, stakeholders, and the community while also maintaining profitability.
- India stands out as the first and only country to enforce CSR requirements on a specific category of companies.

Benefits of CSR and Environmental Education
Cost Reduction for Businesses:- Sustainable practices can save money in the long run through operational efficiency and cost cutting.
- A survey shows 33% of businesses adopting sustainable practices do so to reduce expenses.
- Examples include using renewable energy sources and efficient appliances.
Enhanced Brand Value:
- 76% of Americans expect companies to act against climate change, favoring sustainable products and services.
- Sustainability improves brand image and offers a competitive advantage.
Environmental Impact:
- Urgent need for sustainable methods with UN Sustainable Development Goals deadline approaching.
- Single-use plastics represent a $120 billion annual waste, highlighting the potential for a circular economy.
- Over 140 million people could be displaced by 2050 due to environmental and social impacts of industries.
Sustainable Initiatives by Leading Companies
Infosys:- Partners with the United Nations to combat plastic pollution.
- Committed to eliminating single-use and non-recyclable plastics from campuses by 2020.
- Aims to reduce per capita plastic waste generation by 50%.
ITC:
- Strives to exceed Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016.
- Plans for 100% of its packaging to be reusable, recyclable, or compostable within the next decade.
LiFE(Lifestyle for Environment) Mission
- LiFE Movement, introduced by India at COP26 in 2021, promotes eco-conscious living over mindless consumption.
- It aims to shift from a "use-and-dispose" economy to a circular economy based on deliberate consumption.
- Objective:Encourage collective action for simple climate-friendly habits and influence social norms through social networks.
- The Movement seeks to establish a global community of "Pro-Planet People" (P3)committed to eco-friendly lifestyles.
- Through P3, the Mission aims to create a self-sustaining ecosystem reinforcing environmentally friendly behaviors.

India's Achievements in Environment Conservation
- Forest cover in India is increasing, leading to a rise in the populations of lions, tigers, leopards, elephants, and rhinos.
- The forest cover as a percentage of total geographical area slightly increased from 21.54% in 2017 to 21.71% in 2021.
- India has achieved its commitment to have 40% of installed electric capacity from non-fossil fuel sources, nine years ahead of schedule.
- The target of blending 10% ethanol in petrol was achieved five months before the November 2022 deadline, a significant accomplishment considering blending was only 1.5% in 2013-14 and 5% in 2019-20.
- Renewable energy is a top priority for the government, with installed capacity reaching 150.54 GW, including solar, wind, small hydro, bio-power, and large hydro as of November 30, 2021. Additionally, India holds the fourth-largest wind power capacity globally.
- Nuclear energy-based installed electricity capacity in India stands at 6.78 GW.
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Environmental Awareness In India - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main causes of air pollution in India? |  |
| 2. How does water pollution affect public health in India? |  |
| 3. What are the challenges of waste management in urban areas of India? |  |
| 4. What are some effective legislative measures taken in India to combat deforestation? |  |
| 5. How can corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives help in promoting environmental awareness? |  |






















