Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > Facts that Matter - Light
Facts that Matter - Light | Science Class 8 PDF Download
- We can see an object only when light from an object enters our eyes. The light may have been emitted by the object or may have been reflected by the object.
- A mirror changes the direction of light that falls on it.
- Actually, a narrow beam of light is made of several rays. For simplicity, we use the term ray for a narrow beam of light.
- The mirror surface or a shiny surface scatters back a beam of light falling on it. This scattering back of light by mirror or shiny surface is known as reflection.
- The ray of light which falls on the mirror is called incident ray. The point at which an incident ray falls on the surface of a mirror is called point of incidence.
- The ray that comes back from the surface of a mirror after reflection is known as the reflected ray.
- A perpendicular (a line making an angle of 90º) at the point of incidence (where the incident ray strikes the mirror) is known as normal to the reflecting surface at point.
- The angle between the incident ray and the normal is called the angle of incidence (∠i).
- The angle between the normal and reflected ray is called the angle of reflection (∠r).
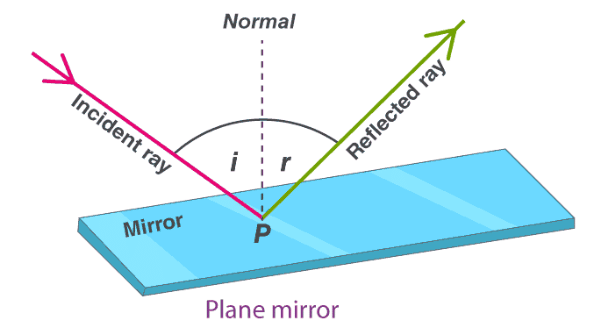 Angle of Incident and angle of reflection
Angle of Incident and angle of reflection
- Laws of reflection
(i) The a ngle of incidence (∠i) is always equal to the angle of reflection (∠r), i.e. ∠i = ∠r.
(ii) The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane. - The image formed by a plane mirror:
The image formed by a plane mirror is erect.
It is virtual (image cannot be obtained on screen) and is of the same size as the object.
The image is at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. - Lateral inversion: The left side of the object is seen on the right side in the image, and right side of the object appears to be on the left side in the image. This is known as lateral inversion.
- Irregular and regular reflection: When rays of light fall on uneven shiny surfaces, the reflected rays are scattered in all directions, as shown in Fig below. In this case reflected rays are not parallel. Such a reflection is known as diffused or irregular reflection. It is caused due to irregularities of the reflecting surface.
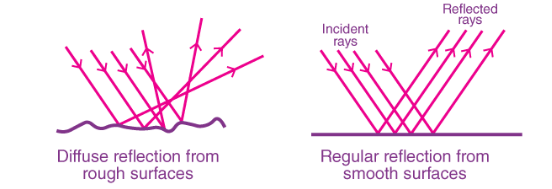 Reflection on Surface
Reflection on Surface
- When rays of light fall on a smooth shiny surface, they are reflected in a particular direction as shown in Fig above and are parallel. Such a reflection is called regular reflection. Images are formed by regular reflection.
- Nearly everything we see around is seen due to reflected light. The objects which shine in the light of other object are called illuminated objects.
- The objects which emit their own light are known as luminous objects.
 Luminous Object
Luminous Object - Periscope: The periscope makes use of two plane mirrors placed in ‘z’ shaped box at 45º angle as shown below.
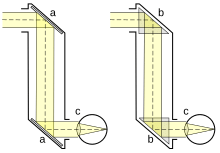 Periscope Due to reflection from mirror 1 and reflection from mirror 2 one is able to see objects which are not visible directly. Periscopes are used in submarines, tanks and also by soldiers in bunkers to see things outside.
Periscope Due to reflection from mirror 1 and reflection from mirror 2 one is able to see objects which are not visible directly. Periscopes are used in submarines, tanks and also by soldiers in bunkers to see things outside. - Kaleidoscope — It is based on the principle of multiple reflections. It consists of three plane mirror strips arranged at 60º angle to each other in a tube (hard cardboard tube).
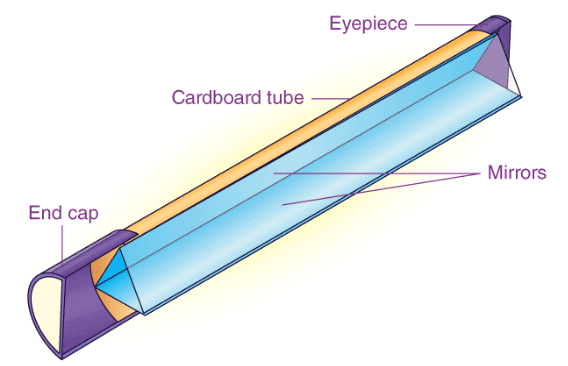 Kaleidoscope
Kaleidoscope
- Dispersion: The splitting of light into its constituent colours is called dispersion. The sunlight is referred to as white light which consists of seven colours.
- Structure of the eye :
Cornea: The outer coat of the eye is white. Its transparent front part is called cornea.
Iris: A dark muscular structure present behind cornea is called iris. The colour of the iris determines the colour of the eye.
Pupil: It is a small opening in the iris. The size of the pupil is controlled by the iris. Thus, iris controls the amount of light entering into the eye.
Eye Lens: It is a double convex lens situated behind the iris. The eye lens has the capacity to change its focal length. So that it can focus the images of objects at different distances on the retina of the eye.
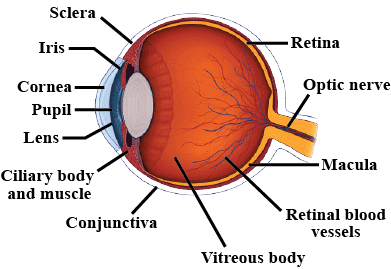 Structure of Human Eye
Structure of Human Eye
Understanding the Eye
- Retina: It is the innermost layer of the eyeball on which the eye lens focuses the image.
- Retina consists of :
Nerve cells: These cells detect visual sensations.
Cone cells: They respond to bright light and can detect colours.
Rod cells: These cells are sensitive to low light conditions. - Optic Nerves: Sensations felt by the nerve cells of the retina are transmitted to the brain through the optic nerves.
- Blind Spot and Yellow Spot: At the point where the optic nerve meets the retina, there are no rods or cones, which means vision is not possible there. This area is known as the blind spot. In contrast, the yellow spot is found in the centre of the retina and has the highest number of light-sensitive cells.
- The impression of at image persists for about 1/16 of a second on the retina even after we have stopped seeing the object. If still images of a moving object are flashed on the eye at a rate faster than 16 second, then the eye perceives this object as moving.
- Range of normal vision: The distance between infinity and 25 cm is called the range of normal vision. The most comfortable distance at which one can read with a normal eye is about 25 cm.
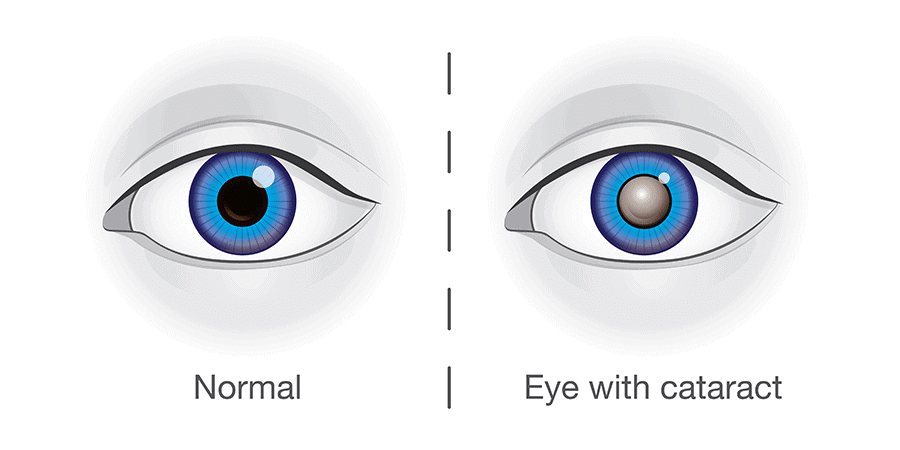
- Cataract: It is the eye disease in which eye lens becomes opaque and eye sight becomes foggy. The disease is treated by removing the opaque lens and inserting a new artificial lens.
- Lack of vitamin A: Insufficient vitamin A in the diet can lead to various eye issues, including night blindness. Foods rich in vitamin A include raw carrots, broccoli, spinach, cod liver oil, eggs, milk, cheese, butter, and fruits like papaya and mango.
- Braille: Louis Braille developed a system for visually challenged persons and published it in 1821. Braille system has 63 dot patterns or characters. These patterns when embossed on Braille sheets help visually challenged persons to recognise words by touching.
- Owl can see very well in the night. It has a large cornea and a large pupil to allow more light in its eyes. Its retina has a large number of rods but only a few cones. These features enable an owl to see in the night. During the day, the large pupil allows so much light in the eye that the owl cannot see objects.
The document Facts that Matter - Light | Science Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Facts that Matter - Light - Science Class 8
| 1. What is the role of light in vision? |  |
Ans. Light is essential for vision as it enables the eyes to perceive images. When light enters the eye, it is focused by the lens onto the retina, where photoreceptors (rods and cones) convert it into electrical signals that are sent to the brain for interpretation.
| 2. How does the eye focus on objects at different distances? |  |
Ans. The eye focuses on objects at varying distances through a process called accommodation. The lens changes its shape, becoming thicker for nearby objects and thinner for distant ones, allowing the eye to maintain a clear image on the retina.
| 3. What are the common eye conditions caused by light exposure? |  |
Ans. Common eye conditions linked to light exposure include cataracts, which cloud the lens, and macular degeneration, which affects the retina. Prolonged exposure to UV light can also lead to photokeratitis, a painful condition similar to sunburn of the eye.
| 4. How do different colors of light affect our vision? |  |
Ans. Different colors of light can influence our vision and perception. For example, blue light has a shorter wavelength and can cause more strain on the eyes, while warmer colors like red and orange are less straining. Additionally, color perception can vary based on lighting conditions.
| 5. What can be done to protect eyes from harmful light? |  |
Ans. To protect eyes from harmful light, one can wear sunglasses that block UV rays, use blue light filters on screens, and ensure proper lighting when reading or working. Regular eye check-ups and maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants can also support eye health.
Related Searches
















