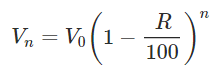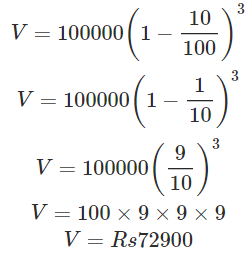Points to Remember: Comparing Quantities | Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 PDF Download
Facts That Matter
- Comparing quantities means looking at two amounts and seeing how they relate to each other in terms of size.
- It helps us understand which one is bigger or smaller, or if they are equal. It's like figuring out the differences between them to see which one is more or less.
- There are many things we can compare, but we can only directly compare things that are measured in the same way.
- To make fair comparisons, we need to use the same measurements.
- It's also important to have a standard way of comparing things. This means using the same rules or methods for everyone so that the comparisons are fair.
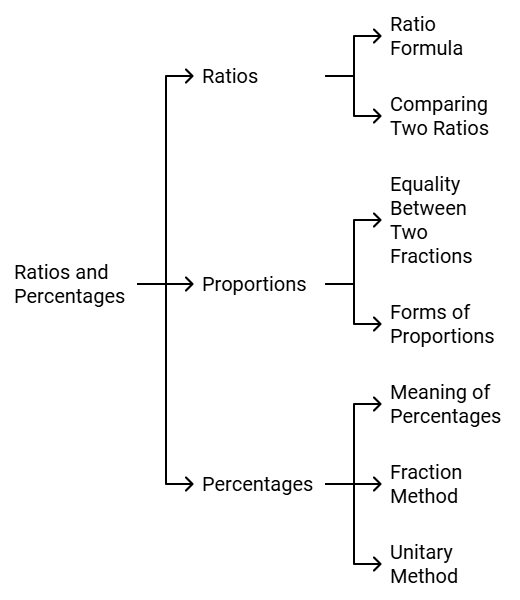
Ratios and Percentages
- Ratio shows the relation between two quantities or to compare two quantities.
- Comparing two ratios involves the conversion of both ratios into equivalent fractions with matching denominators.
- Ratio formula m:n = m/n
- A proportion signifies the equality between two fractions or ratios.
- Essentially, a proportion is a clear assertion of the equality between two ratios. This assertion can be represented in either of the following forms:
a:b=c:d
a:b::c:d - Percentage is another way to compare the quantities. It means for every hundred. In the fraction form if the denominator is 100 then the numerator is the percentage and is represented by a special symbol %, read as a percent.
- Two methods of determining percentages:
Fraction Method: To make the denominator hundred we need to multiply both the denominator and numerator with 2.
Unitary Method: In the unitary method, first, we need to find the value of one unit then multiply it with the required number of units.
Finding Discounts
- It’s very common these days to have a sale and the products are at a discounted price.
- Basically, a discount is a reduction in the Market price to increase sales and to promote the products.
- We can get the discount by subtracting the sale price from the market price.
- Discount = Market price – Sale Price
- To calculate the discount percentage
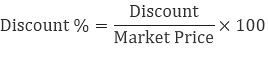
Estimation in Percentages
Q: If the price of a product in the mall is 498.80 and it is available at a discount of 15 % then how would you estimate the amount to be paid?
Sol:
These are the steps to estimate the percentage-
a. Round off the value 498.80 to the nearest tens i.e. 500.
b. Calculate the 10% of 500.i.e.
c. Find the half of it i.e. 1/2 × 50 = 25.
d. Add both the values 50 + 25 = 75.
Therefore the bill amount will be reduced by approximately 75 Rs and you may have to pay 425 Rs.
Terms Related to Buying and Selling
- Cost Price (CP)
The cost price is the actual amount which is paid by the manufacturer to produce it or to provide the service. - Selling Price (SP)
It is the amount at which the retailer sells the product in the market. - Profit
After selling a product, if the seller has some financial gains, then it is said to be a profit.
Profit = SP – CP
- Loss
It is the negative financial revenue that a seller has to bear while selling the product.
Loss = CP – SP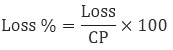
While buying an item if a shopkeeper made some additional expense then these expenses are called Overhead Expenses. It will be included in the cost price.
Sales Tax/Value Added Tax/Goods and Services Tax
- The amount charged by the government on the sale of an item is called Sales Tax.
- The shopkeeper collects it from the customer and gives it to the government. So, the sales tax will always be based on the selling price of the item and will be added to the value of the bill.
- Earlier, you must have seen Sales tax on the bill, nowadays; you will mostly see Value Added Tax
- If the tax is x%, then the Total price after including tax would be

Interest
- Interest is the extra money paid by the banks on our money at a fixed rate of interest.
- Simple Interest Formula:
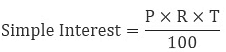 Where P = Principal amount R = Rate of interest
Where P = Principal amount R = Rate of interest
T = Time period for which the interest is paid - The interest calculated both on the principal and the interest earned is called compounded interest
- The Formula for Compound Interest:
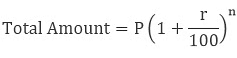
- Compound Interest (CI) = Amount (A) – Principal (P)
Important Formulas Related to Comparing Quantities
- Profit = Selling price – Cost price
- Loss = Cost price – Selling price
- If Selling Price (SP) > Cost Price (CP), then it’s a profit.
- If SP = CP, then it’s neither profit nor loss.
- If CP > SP, then it’s a loss.
- Discount = Marked Price – Sale Price
- Discount Percentage = (Discount × 100) / Marked Price
- Profit Percentage = (Profit / Cost Price) × 100
- Loss Percentage = (Loss / Cost Price) × 100
- Percentage Increased = Change in Value / Original Value
- Simple Interest = (Principal × Rate × Time) / 100
- Compound Interest Formula = Amount – Principal
- Sales Tax or VAT = Tax on Selling Price = (Cost Price × Rate of Sales Tax) / 100
- Billing Amount = Selling price + VAT
Solved Examples
Q1: In a survey of 50 students, 80% of students liked Science, and 20% of students liked Arts. How many numbers of students liked Science?
Sol:
We know that 80% of students liked science in the survey of 50 students
∴ Number of students who liked Science = 80/100 × 50 = 40
Q2: In Yashoda hospital 35 old-aged patients died out of 210 admitted in 2016. In 2017, 10 old-aged patients died out of 150. What’s the increase or decrease of the death rate in the hospital?
Sol:
Here, the base value is different for both the cases. Therefore, converting both the data into a percentage:
Death rate (%) in 2016 = 35/210 × 100 = 16.66%
Death rate (%) in 2017 = 10/150 × 100 = 6.66%
Clearly, there is a decrease in death rate in the hospital in 2017 when compared to that in 2016.
∴ Decrease in death rate (%) = (16.66−6.66)/100 × 100 = 10%
Q3: The value of a residential flat constructed at a cost of Rs100000 is depreciating at the rate of 10% per annum. What will be its value 3 years after construction?
Sol:
We have: V0= Initial value= Rs 100000, R= Rate of depreciation = 10% per annum, n = 3 years. Therefore: Value after n years,
after putting value of n and R, we get:
|
81 videos|423 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Points to Remember: Comparing Quantities - Mathematics (Maths) Class 8
| 1. What are some important topics covered in the Comparing Quantities Class 8 exam? |  |
| 2. How can ratios and percentages be useful in comparing quantities? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of finding discounts in buying and selling scenarios? |  |
| 4. How do sales tax, value added tax, and goods and services tax affect the final price of a product? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to understand interest when comparing quantities? |  |