Hardness of Water, Acids, Bases & Salts | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
A sample of water containing soluble salts of calcium, magnesium or iron is called hard water as it is hard to get lather when soap is added to a sample of water. On the contrary, the sample of water is termed as soft water when it lathers with soap profusely.  Hard water and soft water
Hard water and soft water
The hardness of water is of two types:
Temporary Hardness: It is caused by the presence of bicarbonates of metals of calcium and magnesium, etc. These bicarbonates decompose on prolonged heating or boiling.
Permanent Hardness: It is caused by the presence of sulphates, chlorides, nitrates etc. of calcium, magnesium and other metals.
Softening of water
Softening of water is mainly done by the removal of calcium and magnesium salts as the quantity of iron, aluminium and magnesium salts in water is generally very little.
The following methods are adopted for softening water:-
Boiling: The soluble bicarbonates decompose on boiling and are precipitated as carbonates. Clark’s method: By addition of milk of time. By adding washing soda By addition of sodium hexa-phosphates.
Permutit Process:
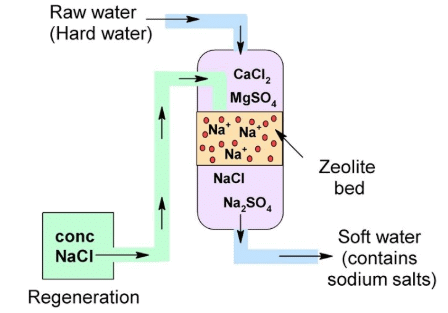 Permutit Process
Permutit Process
It is an artificial zeolite which is chemically known as Sodium aluminium silicate.
Ion Exchange Resins: Water is allowed to flow through a tank partly filled with the granules of a resin which removes positive ions.
Acids, Bases and Salts:
Acids
A compound in reaction loses electron is called an acid. An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water has hydrogen available which can be replaced by a metal to form a salt. It is this available hydrogen which accounts for many common properties.
- In strong acids, there is more available hydrogen than in weak acids. Mineral or Inorganic acids such as sulphuric acid, Hydrochloric acid, Nitric acid, etc. are strong acids. Organic acids are weak acids.
- Cold drinks contain some carbonic acid which gives them a tingling taste.
- Vinegar contain acetic acid. Citrus fruits contain acids too.
- Lemon is one of the best natural source of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). Oranges contain citric acid.
- Apples contain maleic acid, and grapes tartaric acid. An acid have a sour taste.
- It turns blue litmus red, methyl orange red but have no effect on phenolphthalein solution.
 Reaction on litmus paper after dipped in acid and base
Reaction on litmus paper after dipped in acid and base
Bases
The compound, which in reaction accepts electron is called Base. A base is a compound which reacts with an acid to give a salt and water. Soluble bases, e.g. NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH2) are called alkalies.
All bases, except ammonium hydroxide, consists of one metallic element combined with one or more hydroxide group. Hence, bases are named metal hydroxide (except ammonium hydroxide).
- Ammonia is a base, Milk of magnesia and lime water are also bases.
- Washing soda is used to remove grease from utensils, soap cleans hands and clothes, partly by dissolving and greasy material that holds the dirt.
- Lye, washing soda and soap, which dissolve in water, produce compounds that are bases.
- Bases have a bitter taste. It turns red litmus blue, methyl orange yellow and phenolphthalein solution pink.
pH Value
pH is a value which represents acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is defined as the logarithm of the reciprocal of the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. Pure neutral solution like pure water has pH value 7. After this value the alkalinity of the solution increases. Similarly, lowering values increase acidity.
Salts
A salt is a compound which can be formed by replacing the hydrogen of an acid with a metal or its equivalent (e.g. an NH4 radical):
Example: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Types of Salts:
Normal Salts: If all the replaceable hydrogen atoms are replaced by a metal ion in a reaction, then the salt formed is called normal salt.
Acid Salts: The acid salts are those which give hydronium ions.
Facts to be remembered
- Potassium Carbonate. It is a very weak base.
- Potassium Hydroxide. It is a very strong base and furnishes a large number of hydrogen ions.
- Solution. Here the particles dispersed in a solvent cannot be seen with the help of ultra-microscope.
- Suspension. Here the particles dispersed in a solvent are of such a large size that they can be seen with a naked eye.
- Washing Soda. It is sodium carbonate and is a white crystalline solid.
- Caustic Soda. It is sodium hydroxide and is a white amorphous solid.
- Graphite. It is crystalline form of carbon.
- Wood Charcoal. It is an amorphous form of carbon.
- Physical Change. It is temporary change and can be easily reversed. In this change a new substance is formed.
- Chemical Change. It is a permanent change and cannot be reversed. In this change a new substance is formed.
- Hard water. It is the water which produces no lather with soap. However, on adding excess of soap, it gives lather.
- Soft water. It is the water which produces lather with soap very easily.
- Soda water. It is the aerated water which contains compressed carbon dioxide.
- Welding. It is the process of joining two metal surfaces by melting them and then fusing them together.
- Soldering. It is the process of joining two metal surfaces by solder which is an alloy for joining metals.
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Hardness of Water, Acids, Bases & Salts - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the hardness of water? |  |
| 2. How does hardness in water affect household appliances? |  |
| 3. What are some common methods to remove hardness from water? |  |
| 4. What are acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 5. How do acids, bases, and salts react with each other? |  |






















