Pathological Conditions | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Necrosis: The local death of the tissue in a living body is necrosis and the death of the body as a whole is called somatic death. The changes that take place gradually in the cells while they are dying are known as necrobiosis.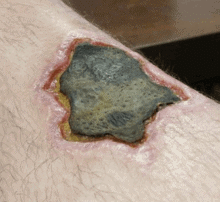
Gangrene: Necrosis of tissues with putrefaction by saprophytic bacteria is called gangrene.
Rigor Mortis: The contraction of muscles after death so that the joints become stiff and the body is rigid. Usually Rigor mortis appear in 1 to 8 hours after death and may disappear from 20 to 30 hours. Rigor mortis is helpful in detection of the time of death.
Gout: The deposition of crystals of uric acid or urates of sodium and calcium in the tissues.
Hyperemia or Congestion: The condition in which there is increased amount of blood in the blood vessels of the body.
Ischemia: Local deficiency of arterial blood in an organ.
Hemorrhage: Escape of blood from an artery, vein or capillary to the outside or into the body cavity or into tissue.
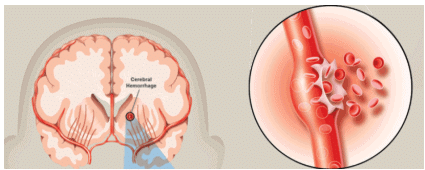 Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Epistaxis - Bleeding from nose
Hematemesis - Blood in vomit
Hemoptysis - Blood in sputum
Metrorrhagia - Bleeding from uterus
Enterorrhagia - Bleeding from Alimentary Canal.
Melena - Blood in stools.
Hematuria - Blood in urine
Hemothorax - Blood in the thoracic cavity.
Hemopericard - Blood in the pericardium
Hemetocele - Blooding into tunica vaginicis
Hemosalpinx - Bleeding in oviducts.
Hematoma - A tumor like accumulation of blood in the tissue.
Apoplexy - Hemorrhage into the brain with loss of consciousness
Petechiae - Pin point hemorrhage.
Extravasation - Extensive hemorrhages in the tissue.
Diapedesis - No actual break in the capillary wall but the red cell pass out through the capillary wall.
Thrombosis - Intravital, intravascular clotting of blood.
Embolism - The mechanism by which foreign material is transported through the circulation system.
Infraction - The necrosis of an area in the body due to sudden stop of arterial blood supply provided there is no collateral supply. Infraction in the heart is the cause of heart failure.
Shock: The decrease in effective circulatory blood volume and fall in blood pressure is referred as shock. A shock may be caused by severe hemorrhage, traumatic injury, severe burn, poisons and psychic stimuli. It may be of 3 types.
1. Hypovolumic Shock: Shock due to reduction in blood volume.
2. Vasculogenic shock: Shock due to changes in venous capacitance or peripheral resistance.
3. Cardiogenic shock: Shock due to acute changes in myocardial function.
Edema: Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the intercellular spaces and body cavities.
Hydrosalpinx: Edema of oviduct.
Hydroperitoneum or Ascites: Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
Hydropericardium: Fluid in pericardium.
Hydrocele: Fluid in the tunica vaginalis.
Hydrocephalus: Accumulation of fluid in the ventricles of brain.
Hydrothorax: Fluid in the thoracic cavity.
Burn: The tissue changes that occur on excessive absorption of heat by skin are known as burns.
Burns can be classified as:
(a) First degree of burn: Only epidermis alone is affected.
(b) Second degree of burn: Necrosis of epidermal tissue, vesicles formation.
(c) Third degree burn: Epidermis and dermis are damaged, blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat & sebaceous glands are destroyed.
(d) Fourth degree burn: Subcutaneous facia and deeper tissues are also affected.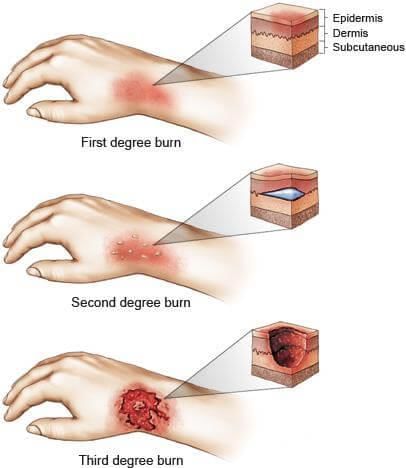
The Electrocardiogram: The changes in electrical potential associated with the initiation and spread of cardiac impulse can be recorded from the surface of the body by an appropriate instrument. The instrument is usually an extremely sensitive galvanometer known as the electrocardiograph. The graphic recordings made on a moving strip of paper are known as electrocardiogram (ECG).
Infectious Diseases: These are conveyed from one person to another by
(a) Air, Example: Tuberculosis, Influenza, Small-Pox
(b) Inanimate objects (such as clothes , books, furniture), Example: Scarlet fever and small pox.
(c) Water and food, Example: Cholera, Dysentery
(d) Through some wound in the skin, Example: Anthrax tetanus.
(e) Living creatures (especially insects), Example: Cholera (through flies), Malaria (through mosquitoes)
(f) Direct contact, Example: Small pox, Venereal diseases
Filaria: It is caused by the bite of a male mosquito. It generally occurs in Bengal, Bihar, Orissa and practically all places with poor drainage.
American yellow fever: It is caused by the bite of Culex mosquito.
Diabetes: It is due to inability of pancreas to secrete sufficient insulin to make use of sugar in the food.
Scarlet fever: The infection spreads by breath and secretions of the nose, mouth, and throat. The onset is sudden with shivering, vomiting and sore throat. The cheeks become flushed and there is marked pale circle round the mouth. The temperature is high.
Meningitis: It means inflammation proximal principles in the right proportion required for the maintenance of health. We cannot get all these in right proportion, we have to mix certain articles in our diet and thus we require a mixed diet or a balanced diet.
Sporadic: A disease which occurs here and there in an area with apparently no connection with its origin.
Pandemic: A disease which affects two or more countries or even continents, such as the flu of 1956.
Quarantine: The detention of a traveller at the airport or seaport for a specified number of days (incubation period) when he is coming from an infected place, till he is declared to be free of that contagious disease.
Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis of lungs is called Pthisis or Consumption. It is caused by tuberclebacillus. Weak chest, dusty occupation, over-work, chronic worry, starvation, early marriage, malaria, influenza, all these increase susceptibility to T.B. by lowering general vitality.
Small pox: It is a viral disease. The onset is sudden, with headache and back ache followed by vomiting fever and running of the nose. Eruption on the skin, small red pimples become pocks on the third day. Scabs fall on the 14th day leaving behind pits or scars on the skin.
Cholera: It is causes by Vibrio Cholerae characterised by passing copious of the meningi. It generally attacks children and the symptoms are headache, vomiting and high fever, there is pain in the back as well as in the legs, and there is stiffness of the neck. Sulpha drugs are best treatment.
Cancer: It i s caused due to irregular growth of some cells in the body. These cells interfere with the normal activities of other healthy cells. Irregular growth of cells is caused by exposure to abnormal heat, radiation and chemical fumes. At present, there is no remedy for this disease except exposing the cancerous cells to radioactive rays (cobalt-60). Cancer can affect any part of the body.
Inoculation: Inoculation means the introduction of germs of the same disease below the skin so as to produce the disease in a mild form and thus gain immunity from a severe attack of the same disease. Inoculation is done as a preventive measure against plague, cholera, typhoid etc.
Balanced diet: Balanced diet is that diet which contains all the necessary from bacterial attacks.
Plasma: Plasma is a pale yellow liquid and contains 90% water, the corpuscles float in it.
Blood transfusion: It is the introduction of the blood of similar composition and nature into a person suffering from bloodlessness. One can donate 250 c.c. or 8% of the total blood at a time. It was first introduced by Landsteiner.
Audiometer: An instrument to measure difference in hearing.
Clinical Thermometer: A thermometer for measuring the temperature of human body.

Sphygmomanometer: An apparatus for measuring blood pressure.
Stethoscope: A medical instrument for hearing and analysing the sound of heart and lungs.
|
146 videos|358 docs|249 tests
|
FAQs on Pathological Conditions - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are some common pathological conditions that affect the human body? |  |
| 2. How are pathological conditions diagnosed by healthcare professionals? |  |
| 3. Can pathological conditions be prevented? |  |
| 4. What are the treatment options for pathological conditions? |  |
| 5. Are there any support groups or resources available for individuals with pathological conditions? |  |
|
146 videos|358 docs|249 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|


















