Classical Approach (Priori Probability), Business Mathematics and Statistics | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
Introduction
The origin and development of the theory of probability date back to the seventeenth century.
Ordinarily speaking the probability of an event denotes the likelihood of its happening.
A value of the probability is a number ranges between 0 and 1. Different schools of thought have defined the term probability differently. One of which is Classical Approach which is mentioned below.
Classical Approach (Priori Probability)
- The classical approach is the oldest method of measuring probabilities and has its origin in gambling games.
- According to this approach, the probability is the ratio of favorable events to the total number of equally likely events. If we toss a coin we are certain that the head or tail will come up.
- The probability of the coin coming down is 1, of the head coming up is
and of the tail coming up is
.
- If an event can occur in ‘a’ ways and fail to occur in ‘b’ ways and these are equally to occur, then the probability of the event occurring,
is denoted by P. Such probabilities are also known as unitary or theoretical or mathematical probability.
P is the probability of the event happening and q is the probability of its not happening. - Therefore
P + q = 1
1 – P = q
1 – q = P
Probabilities can be expressed either as ratio, fraction or percentage, such as - or 0.5 or 50%
Limitations of Classical Approach
The limitations of Classical Approach are given below
1. This definition is confined to the problems of games of chance only and cannot explain the problem other than the games of chance.
2. We cannot apply this method when the total number of cases cannot be calculated.
3. When the outcomes of a random experiment are not equally likely, this method cannot be applied.
4. It is difficult to subdivide the possible outcome of experiment into mutually exclusive, exhaustive and equally likely in most cases.
Solved Examples
Example 1: What is the chance of getting a king in a draw from a pack of 52 cards?
Sol: The total number of cases that can happen = 52 (52 cards are there).
Total number of kings are 4 ; hence favourable cases=4
Therefore probability of drawing a king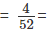
Example 2: Two coins are tossed simultaneously. What is the probability of getting a head and a tail ?
Sol :The possible combinations of the two coins turning up with head (H) or tail (T) are HH, HT, TH, TT.
The favourable ways are two out of these four possible ways and all these are equally likely to happen.
Hence the probability of getting a head and a tail is
Example 3 : One card is drawn at random from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. What is the probability that it will be
(a) a diamond
(b) a queen
Sol :
(a) There are 13 diamond cards in a pack of 52 cards. The number of ways in which a card can be drawn from that pack is 52.
The number favourable to the event happening is 13.
Hence probability of drawing a diamond(b) There are 4 queens in the pack ; and so the number of ways favourable to the event = 4
The probability
Example 4 Two cards are drawn from a pack of cards at random. What is the probability that it will be
(a) a diamond and a heart
(b) a king and a queen
(c) two kings ?
Sol :
(a) The number of ways of drawing 2 cards from out of 52 cards
The number of ways of drawing a diamond and a heart =13 x 13
The required probability
(b) The number of ways of drawing a king and a queen = 4 × 4
The required probability = 4x4/26 x 51 = 8/663(c) Two kings can be drawn out of 4 kings in
The probability of drawing 2 kings
Example 5: A bag contains 7 red, 12 white ,and 4 green balls. What is the probability that :
(a) 3 balls drawn are all white and
(b) 3 balls drawn are one of each color?
Sol : (a) Total number of balls = 7 +12 + 4 = 23
Number of possible ways of drawing 3 out of 12 white 12C3
Total number of possible ways of drawing 3 out of 23 balls 23C3
Therefore, probability of drawing 3 white balls
(b) Number of possible ways of drawing 1 out of 7 red — 7C1 Number of possible ways of drawing 1 out of 12 white = 12C1 Number of possible ways of drawing 1 out of 4 green - 4C1 Therefore the probability of drawing balls of different colours
= 0.1897
|
1335 videos|1436 docs|834 tests
|
FAQs on Classical Approach (Priori Probability), Business Mathematics and Statistics - SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year
| 1. What is the classical approach to probability in business mathematics? |  |
| 2. How is a priori probability calculated? |  |
| 3. What are some real-world applications of the classical approach in business? |  |
| 4. What are the limitations of the classical approach to probability? |  |
| 5. How does the classical approach differ from empirical probability? |  |
















