Concept of Goodwill - Valuation of Goodwill & Shares, Advanced Corporate Accounting | Advanced Corporate Accounting - B Com PDF Download
Methods of Valuation of Goodwill
It is very difficult to assess the value of goodwill, as it is an intangible asset. In case of sale of a business, its value depends on the mutual agreement between the seller and the purchaser of the business. There are many methods of valuing goodwill but some of the important methods are as follow:
A. Average Profit Method
B. Weighted Average Profit Method
C. Super Profit Method
D. Capitalization Method
E. Annuity Method
F. Purchase Method

(A) Average Profit Method
It is the most simple and widely used method for the calculation of goodwill. Under this method, the past profits of number of years are taken into consideration. The average of the past profits is multiplied by the number of years of purchase for the purpose of the valuation of goodwill. Following steps are followed for the valuation of goodwill under this method:
Goodwill = Average Profits × Number of Years’ of Purchase
Illustration: Calculate the value of goodwill as on 1.1.2021 on the basis of three years’ purchase of average profits of last six years. The profits and losses for the years were: 2015 Rs. 30,000, 2016 Rs. 40,000, 2017 Rs. 92,000, 2018 Rs. 55,000, 2019 Rs. 70,000, 2020 Rs. 90,000.
Sol: Total Profits = 30,000 – 40,000 + 92,000 + 55,000 + 70,000 + 90,000 = Rs. 2, 97,000
Average Profits = Total Profits/No. of years 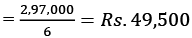
Goodwill = Average Profits × No. of years’ of purchase
Goodwill = 49,500 × 3 = Rs. 1, 48,500
(B) Weighted Average Profit Method
This method is the modified version of the simple average profit method. Under this method each year’s adjusted profits calculated in the step 2 above are multiplied with the respective number of weights in order to calculate the total product. The total of products is then divided by the total of weights to calculate the weighted average profits. Thereafter the weighted average profits are multiplied by the number of years’ of purchase. This method is generally used when the profits show the continuous increasing trend over the years.
Weighted Average Profits = Total of Products of Profits/Total of weights
Goodwill = Weighted average profits × No of years’ of purchase
Illustration: The profits of the firm from the last five years were as follows: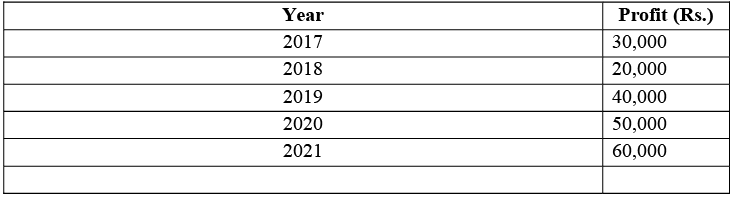
Calculate the goodwill on the basis of three years’ purchase of weighted average profits using weights 1,2,3,4 and 5 respectively.
Sol: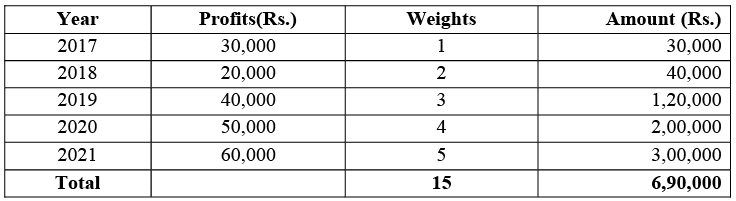
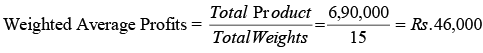 Goodwill = Weighted Average Profits × No. of years’ of purchase
Goodwill = Weighted Average Profits × No. of years’ of purchase
Goodwill = Rs. 46,000 × 3 = Rs. 1, 38,000
(C) Super Profit Method
Super profit method: In super profit method, the average/actual profits of the business are compared with the normal profit which would have earned with the same capital in the same type of business. If the average profit of the company exceeds the normal profit the difference is known as super profit. Under this method value of goodwill is calculated on the basis of super profit and the following steps are followed for this:
Step 1: Calculate Capital Employed by the following
Formula Capital employed = Fixed Assets + Working Capital
Or
Capital Employed = Capital + Reserve/Accumulated Profits – Fictitious Assets
Step 2: Calculation of Current Year profits after tax
Current years’ Profit after Tax = [Current year’s Profits – Abnormal Gain + Abnormal Loss – Normal Loss + Normal Gain] – Tax
Step 3: Calculation of Average Capital Employed
Average Capital Employed = Capital Employed – ½ of Current Year’s Profit after tax
Step 4: Calculate Normal Profits by the following formula Step 5: Calculate the Average Profit after tax as per the Average Profit Method
Step 5: Calculate the Average Profit after tax as per the Average Profit Method
Step 6: Super Profit = Average Profit after Tax – Normal Profit
Step 7: Goodwill = Super Profit × Number of years of Purchase
Calculation of Capital Employed
- The capital employed is important for figuring out the normal profits of a business.
- When calculating the capital employed, consider the following points:
- Both current assets and fixed assets should be part of the capital employed. These assets need to be valued at their current market prices.
- Do not include certain assets such as:
- Fictitious assets, like discounts on shares or debentures and preliminary expenses.
- Outside investments should also be excluded.
- Goodwill listed on the balance sheet should not be counted.
- From the total assets, you must subtract outside liabilities. These liabilities include:
- Debentures
- Creditors
- Provisions for tax
- Outstanding expenses
- Bills payable
- Loans
So, Net Capital Employed = Fixed Assets + Current Assets – Outside Liabilities
Illustration: The Balance Sheet of X Ltd. discloses the following information as on 31 st March, 2021.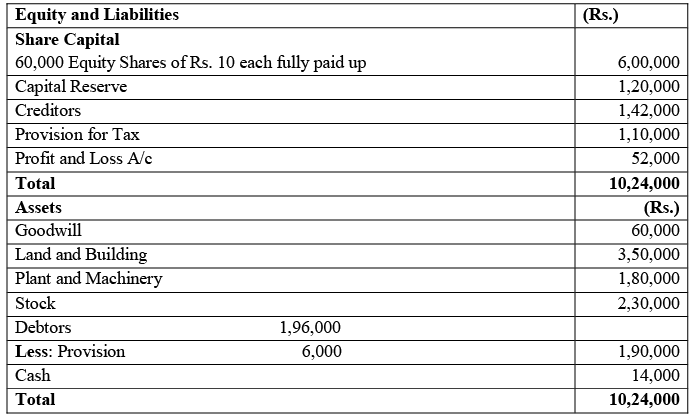 Calculate the Value of Goodwill on the basis of two years purchase of Average Super Profits on the basis of the following information: (i) The reasonable return on average capital employed invested in the class of business done by the company is 12%.
Calculate the Value of Goodwill on the basis of two years purchase of Average Super Profits on the basis of the following information: (i) The reasonable return on average capital employed invested in the class of business done by the company is 12%.
(ii) The rate of tax is 50%.
(iii) Profits of the co mpany before tax are Rs. 2, 20,000.
Sol:
Step 1: Calculation of Capital Employed
Capital Employed = Fixed Assets + Current Assets – Outside Liabilities Step 2: Calculation of Current year’s Profit after tax
Step 2: Calculation of Current year’s Profit after tax
 Step 3: Calculation of Average Capital Employed
Step 3: Calculation of Average Capital Employed
Average Capital Employed: Capital Employed – ½ of Current Year’s Profit and Tax
Average Capital Employed: 7, 12,000 – ½ × 1, 10,000 = RS. 6, 57,000
Step 4: Calculation of Normal Profit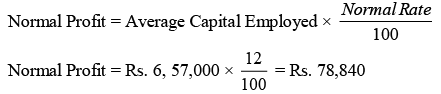
Step 5: Calculation of Average/Actual profit after Tax

Step 6: Calculation of Super Profit
Super Profit = Average/Actual Profit after Tax – Normal Profit
Super Profit = Rs. 1, 10,000 – Rs. 78,840 = Rs. 31,160
Step 7: Calculation of Goodwill
Goodwill = Super Profit × Number of Years of Purchase
Goodwill = Rs. 31,160 × 2 = Rs. 62,320
Value of Goodwill = Rs. 62,320
(D) Capitalization Method
Capitalization Method: Under this method, Goodwill is calculated in two ways:
1. Capitalization of Super Profit Method
2. Capitalization of Average Profit Method
Capitalization of Super Profit Method
Step 1: Calculate super profit according to the super profit method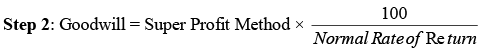
Capitalization of Average Profit Method
Step 1: Calculate average profit after tax as per average profit method
Step 2: Calculate capitalized value of average profits as under
Capitalized value of average profit 
Step 3: Calculate Average Capital Employed as calculated in Super Profit Method
Step 4: Goodwill = Capitalized Value of Average Profit – Average Capital Employed
Note: The use of average or actual capital employed will deepened on the rate of return which is mentioned in the question. If rate is on actual capital employed then actual capital employed will be used for the purpose otherwise average capital employed.
(E) Annuity Method: The reason for using the super profit method is that the amount paid for the goodwill in lump sum will be recovered in the coming years. For example, Rs. 60,000 goodwill is paid today but this amount purchaser will get in the shape of super profits as Rs. 20,000 in the first year, another Rs. 20,000 in the second year, and Rs. 20,000 in the third year. The purchaser will lose the amount of interest over Rs. 60,000. In the annuity method the loss of interest is compensated.
(F) Purchase Method: The purchase considerat ion is the price received for the sale o f the assets. Goodwill is the excess of purchase consideration over the net assets of the business.
Goodwill = Purchase consideration – Net Assets of the firm
Net Assets = Assets – Outside Liabilities
Illustration: The profits of the company during the last four years were Rs. 32,000, Rs. 56,000, Rs. 40,000 and Rs. 64,000. The capital employed is Rs. 4, 00,000 and return in similar business is 10% on the capital employed. Calculate goodwill by annuity method based on super profits. The present value of Rs. 0.282012 annuity for 4 years @5% return is Rs. 1.
Sol:
Step 1: Calculation of Normal Profit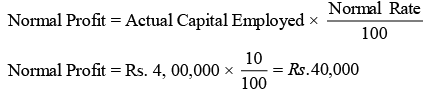 Step 2: Calculation of Average/Actual Profit after Tax
Step 2: Calculation of Average/Actual Profit after Tax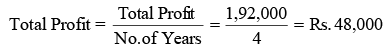 Step 3: Calculation of Super Profit
Step 3: Calculation of Super Profit
Super Profit = Average/Actual Profit after Tax – Normal Profit
Super Profit = Rs. 48,000 – Rs. 40,000 = Rs. 8,000
Step 4: Calculation of Goodwill
When annuity is 0.282012, present value = Rs. 1
When annuity is Rs. 1, present value 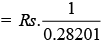
When annuity is Rs. 8,000, present value 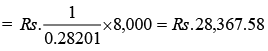
Goodwill = Rs. 28,367.58
|
89 videos|82 docs|20 tests
|
FAQs on Concept of Goodwill - Valuation of Goodwill & Shares, Advanced Corporate Accounting - Advanced Corporate Accounting - B Com
| 1. What is the meaning of goodwill in the context of advanced corporate accounting? |  |
| 2. What are the characteristics of goodwill? |  |
| 3. What factors can affect the value of goodwill in a business? |  |
| 4. Why is there a need for the valuation of goodwill in advanced corporate accounting? |  |
| 5. How is the valuation of goodwill and shares interconnected in advanced corporate accounting? |  |

















