Methods of Valuation of Goodwill - Valuation of Goodwill & Shares, Advanced Corporate Accounting | Advanced Corporate Accounting - B Com PDF Download
Valuation of Goodwill
Goodwill is an intangible asset which is not visible or cannot be touched but can be purchased and traded and is real. The value of an enterprise’s brand name, solid consumer base, functional consumer associations, good employee associations and any patents or proprietary technology represent some instances of goodwill.
In other words, goodwill is a firm worth or reputation established over time. In partnership, the valuation of goodwill is very significant.
The valuation of goodwill is based on the assumption obtained by the valuer. A successful business earns a reputation in the industry, develops trust with its clients, and has more extensive business links, unlike new companies. All these points contribute while evaluating the business, and its financial worth that a customer is eager to give is knowns as goodwill.
Customers who buy a company looking at its goodwill hopes to gain super-profits. Hence, goodwill applies to only firms that make super-profits and not to those who earn regular losses or profits.
Methods of Valuation of Goodwill
Various ways are used in the valuation of goodwill. However, the valuation methods are based on the situation of an individual company and different practices of the trade.
Methods to be adopted in valuation of goodwill would depend on circumstances of each case and is often based on the customs of the trade.
The various methods that can be adopted for valuation of goodwill are follows:
- Average Profit Method
- Super Profit Method
- Capitalization Method
- Annuity Method.
1. Average Profit Method
Under this method the value of Goodwill is calculated by multiplying the Average Future profit by a certain number of year’s purchase.
Goodwill = Future maintainable profit after tax x No. of years purchase
The first step under this method is the calculation of average profit based on past few years’ profit. Past profit are adjusted in respect of any abnormal items of profit or loss which may affect future profit. Average profit may be based on simple average or weighted average.
If profits are constant, equal weight-age may be given in calculating the average profits i.e., simple average may be calculated. However, if the trend shows increasing or decreasing profit, it is necessary to give more weight-age to the profits of recent years.
Number of year’s purchase:
After calculating future maintainable average profits, the next step is to determine the number of years’ purchase. The number of years of purchase is determined with reference to the probability of new business to catch up with an existing business. It will differ from industry to industry and from firm to firm. Normally the number of years ranges between 3 to 5.
Steps Involved under Average Profits Method:
- Calculate past profits before tax.
- Calculate future-maintainable profit before tax after making past adjustments.
- Calculate Average Past adjusted Profits (taking simple average or weighted average as applicable).
- Multiply Future Maintainable Profits by number of years’ purchase.
Value of Goodwill = Future Maintainable Profits x No. of years’ purchase.
Illustration:
Y Ltd. proposed to purchase business carried on by Mr. A. Goodwill for this purpose is agreed to be valued at 3 year’s purchase of the weighted average profits of the past four years.
The profit for these years and respective weights to be assigned are as follows: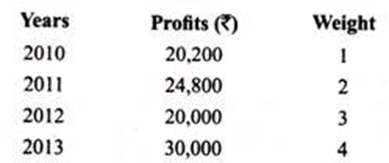 On a scrutiny of the accounts, the following matters are revealed:
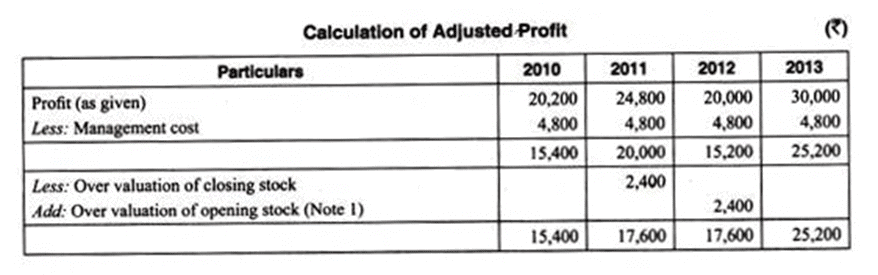
On a scrutiny of the accounts, the following matters are revealed:
(a) On 1st September, 2012 a major repair was made in respect of plant incurring Rs. 6,000 which was charged to revenue, the said sum is agreed to be capitalized for goodwill calculation subject to adjustment of depreciation of 10% p.a. on reducing balance method.
(b) The closing stock for the year 2011 was over valued by Rs. 2,400; and
(c) To cover management cost an annual charge of Rs. 4,000 should be made for the purpose of goodwill valuation.
Required:
Compute the value of goodwill of the firm.
Solution:
Before calculating goodwill, it is necessary to compute adjusted profit on the basis of information given.
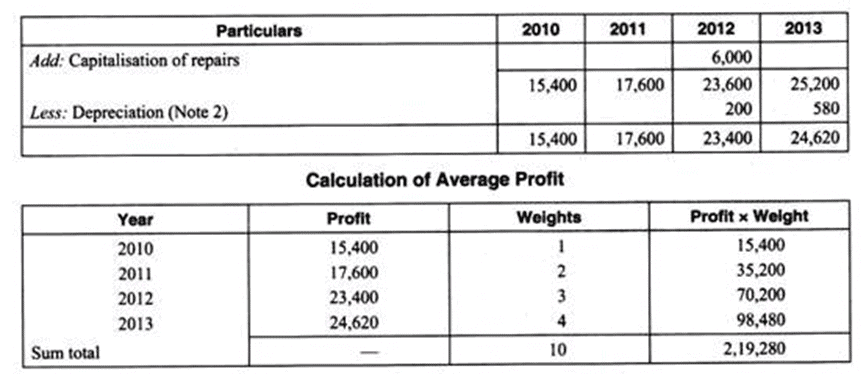
Weighted Average Profit
= ₹ 2,19,280/10
= ₹ 21,928
Goodwill
= 3 years' purchase of weighted average profit
= ₹ 21,928 × 3
= ₹ 65,784
Notes:
(i) Closing Stock of 2011 becomes Opening Stock of 2012.
(ii) Depreciation of 2012 = 10% of ₹ 6,000 for 4 months ending on 31st December, 2012.
= 200
Depreciation of 2013
= 10% of (₹ 6,000 - ₹ 200)
= ₹ 5,800
2. Super Profit Method
Super profit is the excess of estimated future maintainable profits over normal profits. An enterprise may possess some advantages which enable it to earn extra profits over and above the normal profit that would be earned if the capital of the business was invested in some other business with similar risks. The goodwill under this method is ascertained by multiplying the super profits by certain number of year’s purchase.
Steps Involved in Calculating Goodwill under Super Profit Method:
Step 1: Calculate capital employed (it is the aggregate of Shareholders’ equity and long term debt or fixed assets and net current assets).
Step 2: Calculate Normal Profits by multiplying capital employed with normal rate of return.
Step 3: Calculate average maintainable profit.
Step 4: Calculate Super Profit as follows:
Super Profit = Average maintainable profits – Normal Profits.
Step 5: Calculate goodwill by multiplying super profit by number of year’s purchase.
3. Capitalization Method
Goodwill under this method can be calculated by capitalizing average normal profit or capitalizing super profits.
(i) Capitalisation of Average Profit Method:
Under this method goodwill is ascertained by deducting Actual Capital Employed (i.e., Net Assets as on the valuation date) from the capitalised value of the average profits on the basis of normal rate of Return (also known as value of the firm or capitalised value of business)
Goodwill = Capitalised Value – Net Assets of Business
Steps involved in calculating goodwill as per capitalisation of Average Profits Method:
Step 1: Calculate Average future maintainable profits
Step 2: Calculate Capitalised value of business on the basis of Average Profits
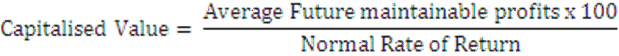
Step 3: Calculate the value of Net Assets on the valuation date
Net Assets = All Assets (other than goodwill, fictitious assets and non-trade investments) at their current values – Outsider’s Liabilities
Step 4: Calculate Goodwill
Goodwill = Capitalised Value – Net assets of business.
Illustration:
From the following calculate the value of goodwill according to capitalisation of Average Profits Method: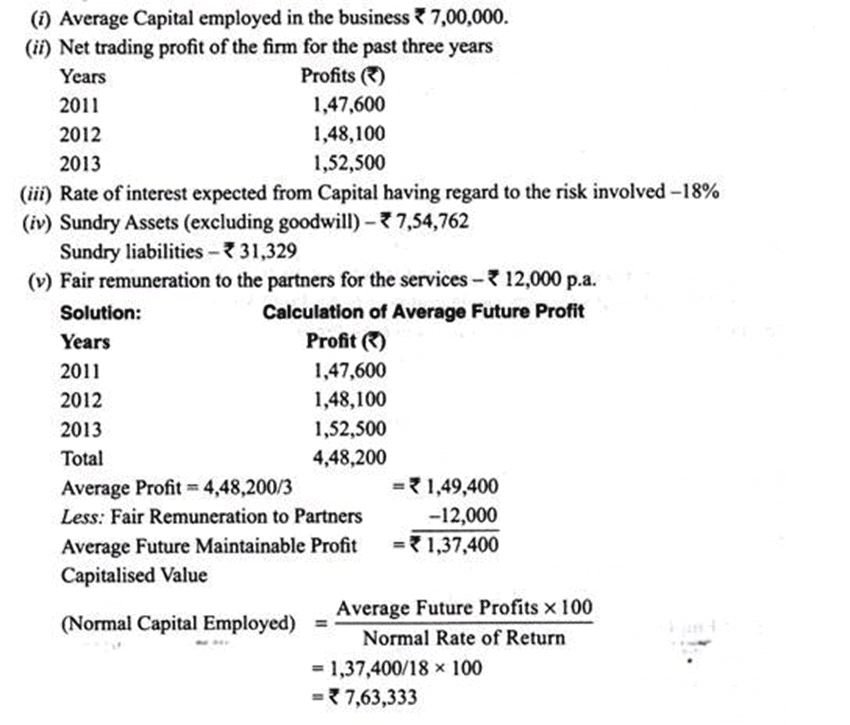

(ii) Capitalisation of Super Profit Method:
The goodwill under this method is ascertained by capitalizing the super profits on the basis of normal rate of return. This method assesses the capital needed for earning the super profit.
The value of goodwill is computed as follows: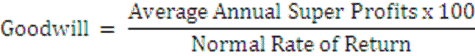
Illustration:
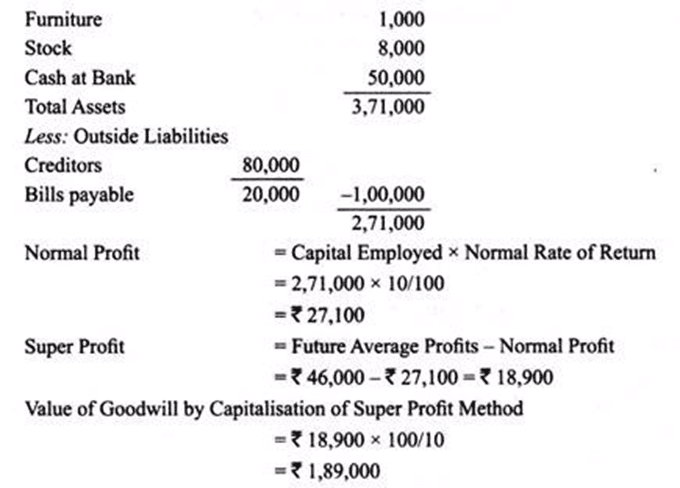
Balance Sheet of X Ltd. on 31st March, 2013 was as under: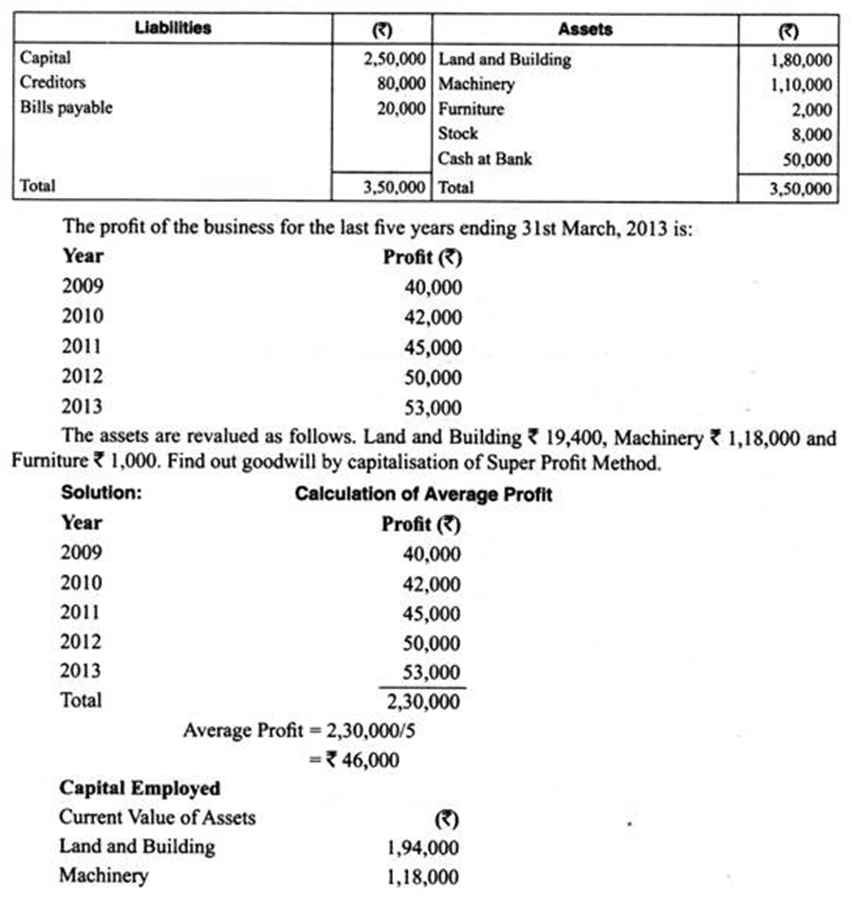
4. Annuity Method
Under this method, goodwill is calculated by taking average super profit as the value of an annuity over a certain number of years. The present value of this annuity is computed by discounting at the given rate of interest (normal rate of return). This discounted present value of the annuity is the value of goodwill. The value of annuity for Rupee 1 can be known by reference to the annuity tables.
If the value of annuity is not given, it can be calculated with the help of following formula: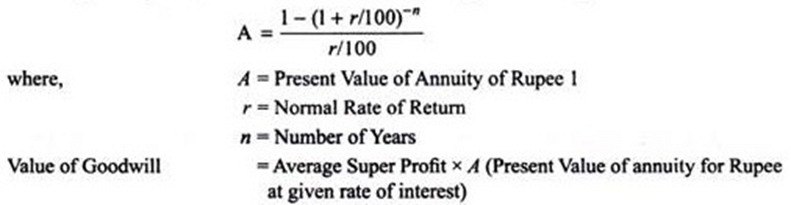
Illustration:
The net profit of a company after providing for taxation for the past five years is: The net tangible assets in the business are Rs. 4, 00,000 on which the normal rate of return is expected to be 10%. It is also expected that the company will be able to maintain its super profits for next five years. Calculate the value of goodwill of the business on the basis of an annuity of super profits, taking present value of an annuity of Rs. 1 for five years at 10% interest is Rs. 3.78.
The net tangible assets in the business are Rs. 4, 00,000 on which the normal rate of return is expected to be 10%. It is also expected that the company will be able to maintain its super profits for next five years. Calculate the value of goodwill of the business on the basis of an annuity of super profits, taking present value of an annuity of Rs. 1 for five years at 10% interest is Rs. 3.78.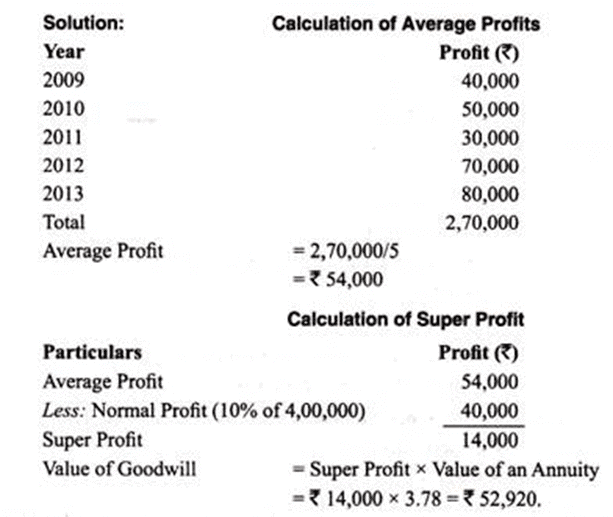
|
89 videos|82 docs|20 tests
|
FAQs on Methods of Valuation of Goodwill - Valuation of Goodwill & Shares, Advanced Corporate Accounting - Advanced Corporate Accounting - B Com
| 1. What is the meaning of "goodwill" in the context of business valuation? |  |
| 2. What are the different methods used to value goodwill? |  |
| 3. How is goodwill different from other intangible assets? |  |
| 4. Why is the valuation of goodwill important? |  |
| 5. What are some challenges in valuing goodwill? |  |

















