Conditions and Warranties - The Sale of Goods Act(1930) , Business Law | Business Law - B Com PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Conditions in a Contract |

|
| Types of Conditions |

|
| Warranties |

|
| Types of Warranties |

|
| Doctrine of Caveat Emptor (Buyer is Responsible for Their Actions) |

|
Conditions in a Contract
Meaning: Condition in a contract is a fundamental requirement that is crucial to the main purpose of the agreement. It is a stipulation that must be met for the contract to be valid.
Key Points:
- A condition is essential to the core objective of the contract.
- If a condition is breached, the aggrieved party has the right to terminate the contract, reject the goods, and recover the price paid.
- The non-fulfillment of a condition undermines the entire contract.
Example:
Let's say A (the buyer) informs B (the car dealer) that he wants to buy a car for touring purposes. B recommends a Maruti car to A for this purpose. However, after purchasing the car, A realizes that it is not suitable for touring. In this case, A has the right to return the car to B and receive a refund.
Explanation of the Example:
- In the scenario, there was a condition that the car should be suitable for touring. When A later discovers that this condition was not met, he has the right to terminate the contract and recover the money he paid to the car dealer.
Types of Conditions
Express Conditions:
- These are conditions that are explicitly stated or mentioned by the parties in the contract.
- Express conditions can be included either orally or in writing.
Implied Conditions:
- Implied conditions are those that are automatically incorporated or applicable by law, conduct, or behavior in the contract.
- These conditions are not explicitly stated but are understood to be part of the agreement.
Various implied conditions include:
1. Condition as to Title/Ownership:
- The seller has the right to sell the goods only if they have the title or ownership of the goods.
- If the seller is selling stolen goods, for example, they do not have the right, title, or ownership of those goods.
- In such cases, the buyer has the right to cancel the contract, return the goods, and recover the price paid for the goods.
2. Condition as to Sale by Description:
- This implied condition applies when the seller is selling goods by providing a description to the buyer.
- The goods must correspond with the description given by the seller.
3. Condition as to Sale by Sample:
- When the seller provides a sample of the goods to the buyer, this implied condition requires that the goods supplied must correspond with the sample for all future orders placed by the buyer.
4. Condition as to Sale by Sample and Description:
5. Condition as to Quality/Fitness:
- Generally, it is the buyer's responsibility to examine the goods and determine whether they are suitable for their purposes.
- However, if the buyer specifically informs the seller about the intended purpose and relies on the seller's skills and judgment, the seller is responsible for providing a quality product.
- If the seller fails to meet this standard, it constitutes a breach of the implied condition regarding quality or fitness.
6. Condition as to Merchantability:
- This condition implies that the goods supplied should be free from defects and suitable for sale.
7. Condition as to Wholesomeness:
- Goods supplied should not be adulterated and should be suitable for consumption.
Warranties

Meaning: A warranty is a stipulation that is not essential to the main purpose of the contract.
Key Points:
- The breach of warranty gives the aggrieved party the right to claim damages but not the right to reject the goods.
- Even if there is a breach of warranty, the main contract can be completed.
- Breach of warranty cannot be treated as breach of condition.
Example:
- A (buyer) told B (shop keeper) that he wants to buy a good watch.
- B showed him a watch saying that it is made in Thailand.
- A buys the watch and later on realizes that the watch is made in China and not Thailand.
Explanation:
- In this example, the main purpose was for A to buy a good watch.
- B assured A that the watch was made in Thailand, which was later proven wrong.
- A has the right to claim damages but cannot reject the watch.
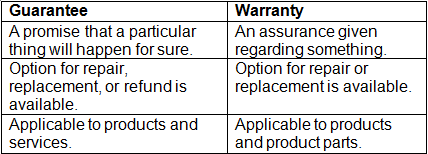
Difference between Guarantee and Warranty
Important Note:
- What can be called a condition or warranty depends on the nature, type, or construction of the contract.
- A stipulation may be a condition in one context and a warranty in another, or vice versa.
Types of Warranties
(a) Express Warranties
An express warranty is a guarantee that is explicitly stated and included by the parties in a contract.
(b) Implied Warranties
Implied warranties are those that are automatically imposed or applicable by law, regardless of whether they are mentioned in the contract.
- For instance, when you purchase a new car from a dealership, there is an implied warranty that the car is in working condition. Similarly, when you order a burger at a restaurant, there is an implied warranty that the burger is safe to eat.
Here are some examples of implied warranties:
1. Implied Warranty of Quiet Possession
- This warranty ensures that once goods are sold to a buyer, there will be no disturbances or interruptions to their possession of the goods, either by the seller or any third party.
2. Implied Warranty to Disclose Dangerous Nature of Goods
- When selling goods that are inherently dangerous, there is an implied warranty that the seller must disclose all relevant information about the dangers to the buyer.
- If the seller fails to provide this information, they may be held liable for any damages incurred by the buyer.
- Examples of dangerous goods include disinfectants, chemicals, and hazardous materials.
3. Implied Warranty as to Quality/Fitness
- This warranty ensures that the quality or fitness of goods for a particular purpose is communicated to the buyer in advance.
- For instance, any potential damages or defects in the goods should be disclosed to the buyer beforehand.
- Failing to do so may constitute a breach of warranty.
4. Implied Warranty as to Free from Liability/Loan Charges
- When goods are sold, there is an implied warranty that they are free from any liens, loans, or liabilities.
- For example, if a person named A took a loan from a bank by pledging their bike as collateral and later sold the bike to C, there is an implied warranty that A cannot sell the bike to C because it is not free from the bank's lien.
- In such cases, C would have the right to seek damages from A for the breach of warranty.
Doctrine of Caveat Emptor (Buyer is Responsible for Their Actions)
Caveat Emptor, which translates to "buyer beware," emphasizes the buyer's responsibility in a transaction. This principle asserts that the buyer must be cautious and aware of the potential risks or dangers associated with the purchase. Essentially, it places the onus on the buyer to make an informed decision without relying on the seller to disclose any defects in the goods.
Key Points of the Doctrine of Caveat Emptor:
- Buyer’s Duty to Inspect: It is the buyer's responsibility to thoroughly examine the goods before making a purchase.
- No Blame for Defects: The buyer cannot hold anyone accountable if the goods turn out to be defective or unsuitable for their needs.
- Seller’s Obligation: The seller is not obligated to disclose any defects in the goods.
- Suitability of Goods: There is no implied guarantee from the seller that the goods will meet the buyer's specific requirements.
Exceptions to the Doctrine of Caveat Emptor:
- Reliance on Seller's Judgment: If the buyer relies on the seller's expertise regarding the quality of the goods, the seller may be held responsible.
- Sale by Sample: When goods are sold based on a sample provided by the seller.
- Sale by Description: When goods are sold based on a detailed description provided by the seller.
- Sale by Sample and Description: When goods are sold based on both a sample and a description.
- Sale by Fraud or Misrepresentation: If the seller engages in fraudulent practices or misrepresentation.
- Adulteration: Goods must be free from adulteration; otherwise, the seller will be held responsible.
- Merchantable Quality: Goods must be of merchantable quality, meaning they should be fit for the purpose for which they are bought.
Example of Merchantable Quality:
- Cold Drinks and Chocolates: If the seal of a cold drink or the wrapper of a chocolate is damaged, these products may not be considered of merchantable quality.
|
30 videos|99 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Conditions and Warranties - The Sale of Goods Act(1930) , Business Law - Business Law - B Com
| 1. What are the conditions and warranties under the Sale of Goods Act (1930)? |  |
| 2. How do conditions and warranties differ in the Sale of Goods Act (1930)? |  |
| 3. Can conditions and warranties be implied in a contract under the Sale of Goods Act (1930)? |  |
| 4. What remedies are available to the buyer in case of breach of conditions or warranties under the Sale of Goods Act (1930)? |  |
| 5. Can the seller limit or exclude liability for breach of conditions and warranties under the Sale of Goods Act (1930)? |  |
















