Introduction on Induction Machines | Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Induction Machines |

|
| What is an Induction Motor? |

|
| Power Flow |

|
| Types of Induction Motors |

|
| Working Principle of Induction Motor |

|
Induction Machines
The induction machine was invented by Nikola Tesla in 1888. Right from its inception, its ease of manufacture and its robustness has made it a very strong candidate for electromechanical energy conversion.
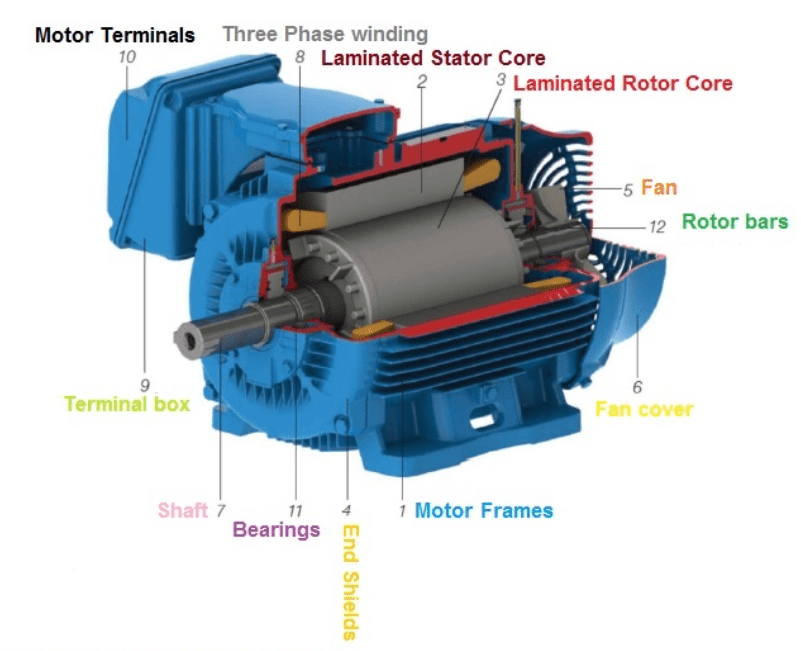 Induction Motor
Induction Motor
- It is available from fractional horsepower ratings to megawatt levels. It finds very wide usage in all various application areas.
- The induction machine is an AC electromechanical energy conversion device.
- The machine interfaces with the external world through two connections (ports) one mechanical and one electrical.
- The mechanical port is in the form of a rotating shaft and the electrical port is in the form of terminals where the AC supply is connected.
- There are machines available to operate from three-phase or single-phase electrical input.
- In this document, we will be discussing the three-phase induction machine. Single-phase machines are restricted to small power levels.
The induction machine can operate both as a motor and as a generator. As a generator, its performance is not satisfactory. However it is used in wind turbines. It is extensively used as a motor. It is also called as an asynchronous machine.
What is an Induction Motor?
- An induction motor (also known as an asynchronous motor) is a commonly used AC electric motor.
- In an induction motor, the electric current in the rotor needed to produce torque is obtained via electromagnetic induction from the rotating magnetic field of the stator winding.
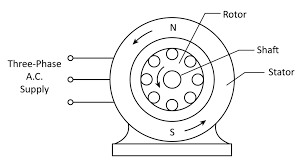
- The rotor of an induction motor can be a squirrel cage rotor or wound type rotor.
- Induction motors are referred to as "asynchronous motors" because they operate at a speed less than their synchronous speed. So the first thing to understand is: what is synchronous speed?
Synchronous Speed
- Synchronous speed is the speed of rotation of the magnetic field in a rotary machine, and it depends upon the frequency and number of poles of the machine.
- The induction motor always runs at a speed less than its synchronous speed.
- The rotating magnetic field produced in the stator will create flux in the rotor, hence causing the rotor to rotate.
- Due to the lag between the flux current in the rotor and the flux current in the stator, the rotor will never reach its rotating magnetic field speed (i.e. the synchronous speed).
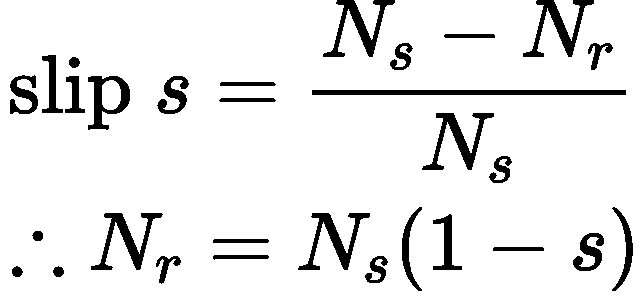
- There are basically two types of induction motors. The types of induction motor depend upon the input supply. There are single-phase induction motors and three-phase induction motors.
- Single-phase induction motors are not self-starting motors, and three-phase induction motors are self-starting motors.
Synchronous speed:
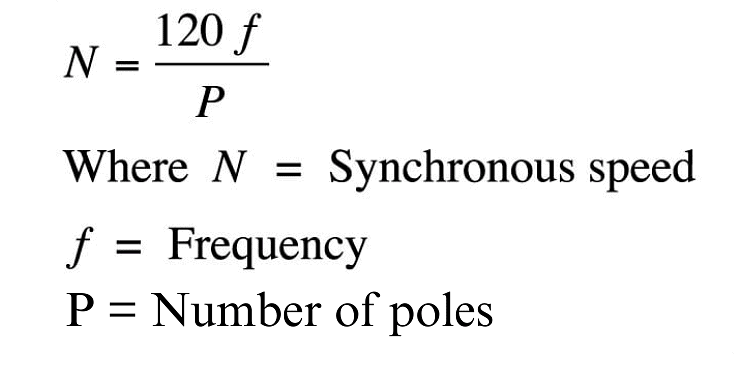
Example 1: A 3-phase induction motor is wound for 8 poles and is supplied from 50 Hz source. Calculate:
(1) Synchronous Speed
(2) Slip of the motor when speed is 720 RPM.
Solution:
(1) Synchronous Speed:
Ns = 120f/P = 120×50/8 = 750 rpm
(2) Slip of the motor, when
Nr = 720 rpm
s = (Ns−Nr)/NS=(750−720)/750 = 0.04 perunit
%s = (750−720)/750×100 = 4%
Power Flow

Types of Induction Motors
The types of induction motors can be classified depending on whether they are a single phase or three phase induction motor.
(a) Single Phase Induction Motor
The types of single phase induction motors include:- Split Phase Induction Motor
- Capacitor Start Induction Motor
- Capacitor Start and Capacitor Run Induction Motor
- Shaded Pole Induction Motor
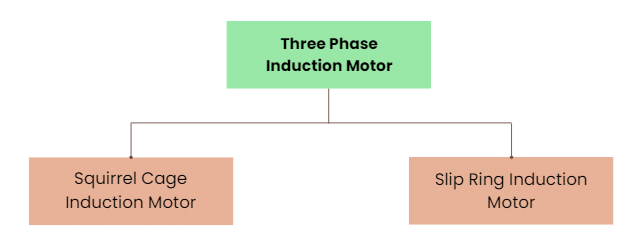
(b) Three Phase Induction Motor
The types of three phase induction motors include:
- A 3-phase induction motor is a machine that is constructed to work on the 3-phase supply.
- The three-ø induction motor is also known as the asynchronous. Its working is depending on the principle of the revolving magnetic field.
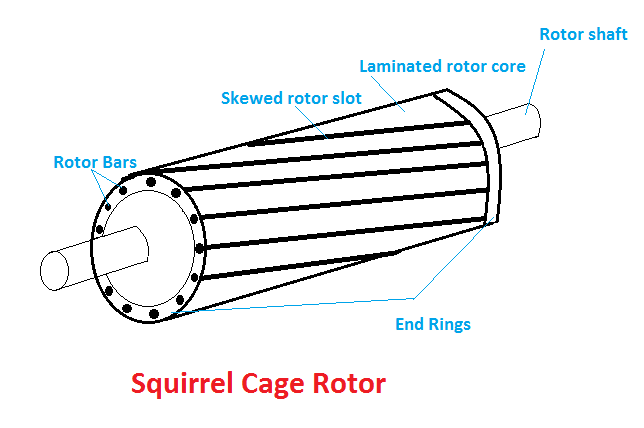
- As we discussed in a single-phase induction motor that it is not self-starting, but three-phase motors are self-starting devices there is no need for any separate starter for this motor.
- The construction of this motor is very modest, rugged, less cost and its repairing is very easy, and this motor is available in many power ratings.
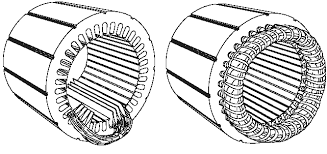 Slip Ring Induction Motor
Slip Ring Induction Motor
- This motor works at a constant speed in case of no load or full load conditions.
We have already mentioned above that the single-phase induction motor is not a self-starting motor, and that the three-phase induction motor is self-starting.
What is a Self-Starting Motor?
- When the motor starts running automatically without any external force applied to the machine, then the motor is referred to as ‘self-starting’. For example, we see that when we put on the switch the fan starts to rotate automatically, so it is a self-starting machine.
- Point to be noted that fan used in home appliances is a single-phase induction motor which is inherently not self-starting. How?
Why is Three Phase Induction Motor Self Starting?
- In a three phase system, there are three single phase lines with a 120° phase difference. So the rotating magnetic field has the same phase difference which will make the rotor to move.
- If we consider three phases a, b, and c when phase a gets magnetized, the rotor will move towards the phase a winding a, in the next moment phase b will get magnetized and it will attract the rotor, and then phase c. So the rotor will continue to rotate.
Working Principle of Induction Motor
- We need to give double excitation to make a DC motor rotate. In the DC motor, we give one supply to the stator and another to the rotor through brush arrangement.
- But in induction motor, we give only one supply, so it is interesting to know how an induction motor works. It is simple, from the name itself we can understand that here, the induction process is involved.
- When we give the supply to the stator winding, a magnetic flux gets produced in the stator due to the flow of current in the coil.
- The rotor winding is so arranged that each coil becomes short-circuited. The flux from the stator cuts the short-circuited coil in the rotor. As the rotor coils are short-circuited, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, the current will start flowing through the coil of the rotor. When the current through the rotor coils flows, another flux gets generated in the rotor.
- Now there are two fluxes, one is stator flux, and another is rotor flux.
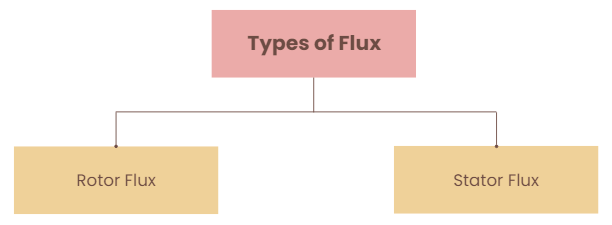
- The rotor flux will be lagging with respect to the stator flux. Because of that, the rotor will feel a torque which will make the rotor rotate in the direction of the rotating magnetic field.
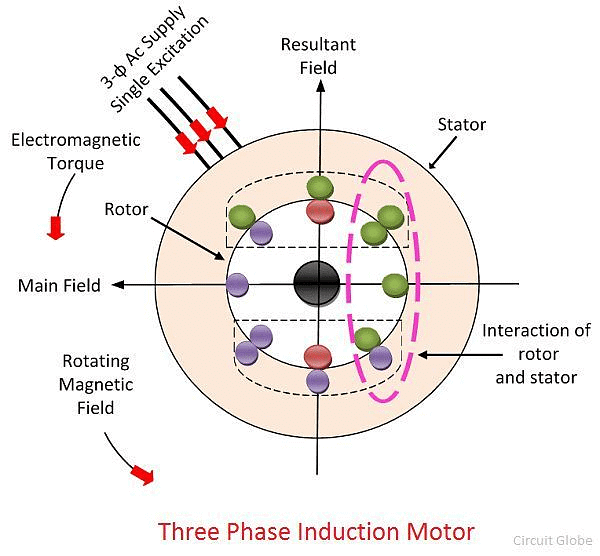
This is the working principle of both single and three-phase induction motors.
1. Features of a Three Phase Induction Motor
- A three-phase induction motor is self-starting and hence there is no need for a special starter for this motor.
- This motor does not have brushes which cause to remove the sparking of the motor.
- This motor is Vigorous in structure.
- It is a less expensive motor.
- The repairing of this motor is very easy due to this feature is mostly used.
2. Applications of a Three Phase Induction Motor
- This motor is used in elevators.
- A three-phase induction motor is used in Cranes.
- This motor is also used in Huge volume exhaust fans.
- It is used in Engine Supplementary propels.
- It works as the Engine blower fan motor.
3. Advantagesof a Three Phase Induction Motor
- These motors are vigorous and modest in structure with very limited moving portions.
- These motors proficiently work in a rough and strict atmosphere like in oceangoing containers.
- The repairing price of the three-ø induction motor is fewer and dissimilar that of direct current or synchronous motor, the induction motor does not have the brush, and slip rings.
- It can operate in an inherent atmosphere as they do not have brushes which can source the sparking and can be hazardous to such an environment.
- Three-ø induction motor does not need any extra starting device or arrangement as they can produce starting torque when a 3-ø alternating voltage is provided.
- The ultimate results of a 3-ø motor are approximately (1.5) times the rating of a 1-ø motor of the identical ratings.
4. Disadvantages of a Three Phase Induction Motor
- In its starting process, it takes the higher preliminary initial current when connected to a weighty load.
- It sources a loss in voltage at the starting time of the motor.
- Induction motor works at lagging P.F which consequences in an increment of the (I2R) losses and decreases efficiency, particularly at light load. To recover the P.F stationary capacitor banks are used with the motor.
- The speed controller of the 3-ø induction motor is challenging as associated with direct current motors. An adjustable frequency driver can be combined with the induction motor for speed regulation.
|
19 videos|90 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction on Induction Machines - Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is the working principle of an induction motor? |  |
| 2. What are the types of induction motors commonly used? |  |
| 3. How does power flow in an induction motor? |  |
| 4. What are the key components of an induction motor? |  |
| 5. How is an induction motor different from a synchronous motor? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|



















