Classification of Costs | Cost Accounting - B Com PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Fixed Cost behaviour |

|
| Variable Cost Behaviour |

|
| Semi-Variable Cost Behaviour |

|
| Fixed Costs rising in Steps |

|
Introduction
- Costscan be divided into different types based on the need for information. The main categories are:
- Fixed Costs
- Variable Costs
- Semi-variable Costs
- Step Costs
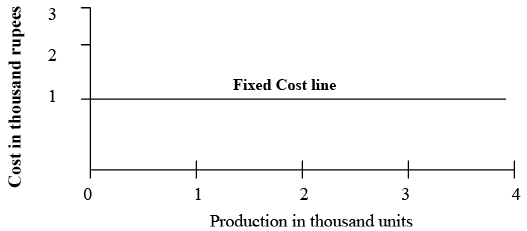
- Fixed Costs:These costs do not change regardless of how much is produced, as long as production remains within the established capacity. Common examples include:
- Rent
- Insurance fees
- Salaries for management
- Fixed Costs
- If the rent for a factory is Rs.6,000 and it produces 1,000 units, the rent per unit is Rs.6.
- If production increases to 1,200 units, the rent per unit drops to Rs.5.
- If production decreases to 800 units, the rent per unit rises to Rs.7.50.
- Fixed Costs
- Committed Fixed Costs: These are fixed costs that come from owning equipment, buildings, and having a basic organizational structure. For example, after a building is built and equipment is installed, costs like depreciation, property taxes, insurance, and salaries for key staff cannot be easily reduced without affecting the organization's ability to achieve long-term goals.
- Discretionary Fixed Costs:These costs are set at a fixed amount for certain time periods by management during budgeting. They reflect the policies of top management and do not directly relate to production levels. If necessary, these costs can be reduced or completely cut. Examples include:
- Research and development expenses
- Advertising and promotional costs
- Donations
- Fees for management consulting
Fixed Cost behaviour
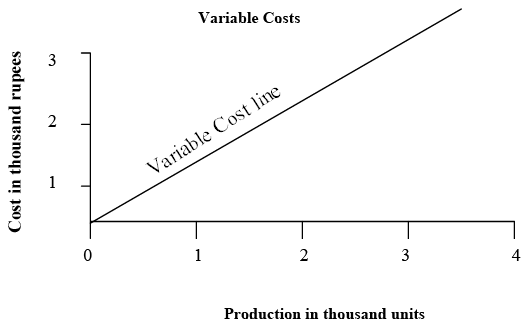
Variable Costs: These are the costs which vary in direct proportion to output. They increase or decrease in the same proportion in which the output increases or decreases. The example of such costs are direct material, direct labour, power, etc.
Variable costs may be said to be constant per unit of output. For example, if a factory incurs Rs. 1,000 on raw material for an output of 1,000 units, the cost of raw material per unit would amount to Real. In case the output increases to 2,000 units, the cost of raw material would proportionately increase to Rs. 2,000 (i.e Re. 1 x 2,000). Similarly if the output decreases to 800 units, the cost of raw material would also decrease to Rs 800 (i.e Re.1 x 800) Variable costs are also referred to as product costs.
Variable Cost Behaviour
 Semi-variable Costs: These are the costs which do vary but not in direct proportion to output. They are made up of both fixed and variable cost elements such as depreciation, repairs, light, heat, telephone, etc.
Semi-variable Costs: These are the costs which do vary but not in direct proportion to output. They are made up of both fixed and variable cost elements such as depreciation, repairs, light, heat, telephone, etc. Semi-Variable Cost Behaviour
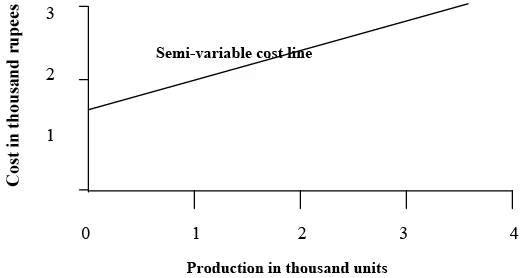
Identification of fixed and variable elements of semi-variable costs is important for the management for planning their business activities. Different methods are available for this purpose which will be discussed in the next unit.
Step Costs: Fixed cost in general remain fixed over a range of activity and then jump to a new level as activity changes. For example, a foreman can supervise a given number of workers. Beyond this number, it is necessary to hire a second foreman, then a third and so on. Similarly, the rental cost of delivery vehicles also follows the same pattern.
The general characteristic of fixed cost rising in steps is depicted
Fixed Costs rising in Steps
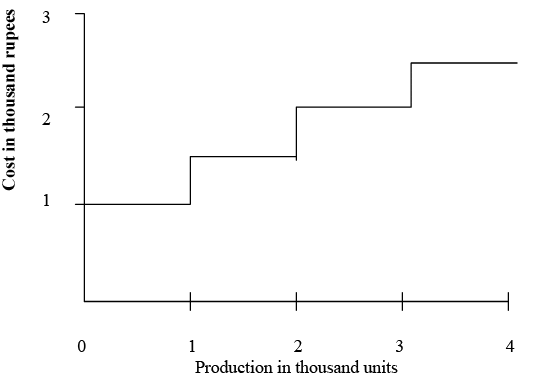
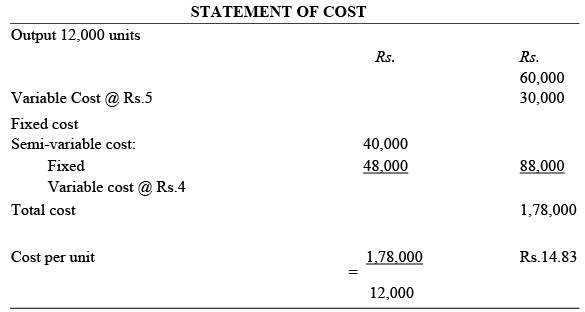
Illustration: A company has provided the following information to you in respect of 10,000 units of output. Let us calculate the total cost for 12,000 units of output and the cost per unit with the following information: 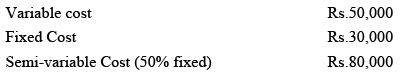
 Direct and Indirect Cost
Direct and Indirect Cost
- Direct Costs: These are costs which can be directly, conveniently and wholly traced to a product , service or job. Example of such costs are: direct material, direct labour and direct expenses.
- Indirect Costs: These are costs which cannot be directly, conveniently and wholly identified with a specific product, service or job. They include all overhead costs such as salaries of time keepers, stores keepers, foreman , printing and stationery costs, etc.
Indirect or overhead cost are apportioned to different jobs, products or services on a reasonable basis. For example, the indirect factory labour cost may be apportioned over different jobs according to their direct labour cost. Similarly, the selling overheads can be charged to different products according to their sales values. It may be noted that the more the share of the direct cost in relation to the total cost of the product, the greater is the exactness in costing. The reason for this is that indirect costs are allocated (or apportioned) on an estimated basis.
|
103 videos|131 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Classification of Costs - Cost Accounting - B Com
| 1. What is cost accounting? |  |
| 2. What is the classification of costs in cost accounting? |  |
| 3. What is cost ascertainment in cost accounting? |  |
| 4. What is cost estimation in cost accounting? |  |
| 5. Why is cost accounting important for businesses? |  |





















