Cost Sheet | Accountancy and Financial Management - B Com PDF Download
What is a cost sheet?
A cost sheet is a document that outlines the different components of the total cost for a product and presents previous data for comparison. It helps in determining the ideal selling price of a product.
A cost sheet can be created using either historical cost or estimated costs. A historical cost sheet is based on the actual costs incurred for a product, while an estimated cost sheet is prepared using projected costs before production starts.
Importance and objectives of cost sheet
Cost sheets play a crucial role in several important business activities:
- Determining cost: The primary purpose of a cost sheet is to calculate the accurate cost of a product, showing both the total cost and the cost per unit.
- Fixing selling price: A cost sheet is essential for setting the selling price of a product by providing a detailed breakdown of its production costs.
- Cost comparison: It allows management to compare the current cost of a product with previous per-unit costs. This comparison helps in identifying any increase in costs, prompting corrective actions.
- Cost control: A cost sheet is vital for controlling production costs. By using an estimated cost sheet, businesses can track labor, material, and overhead costs at each stage of production.
- Decision-making: Management uses the cost sheet to make informed decisions, such as whether to produce or purchase components, or how to quote prices in tenders.
Types of costs in cost accounting
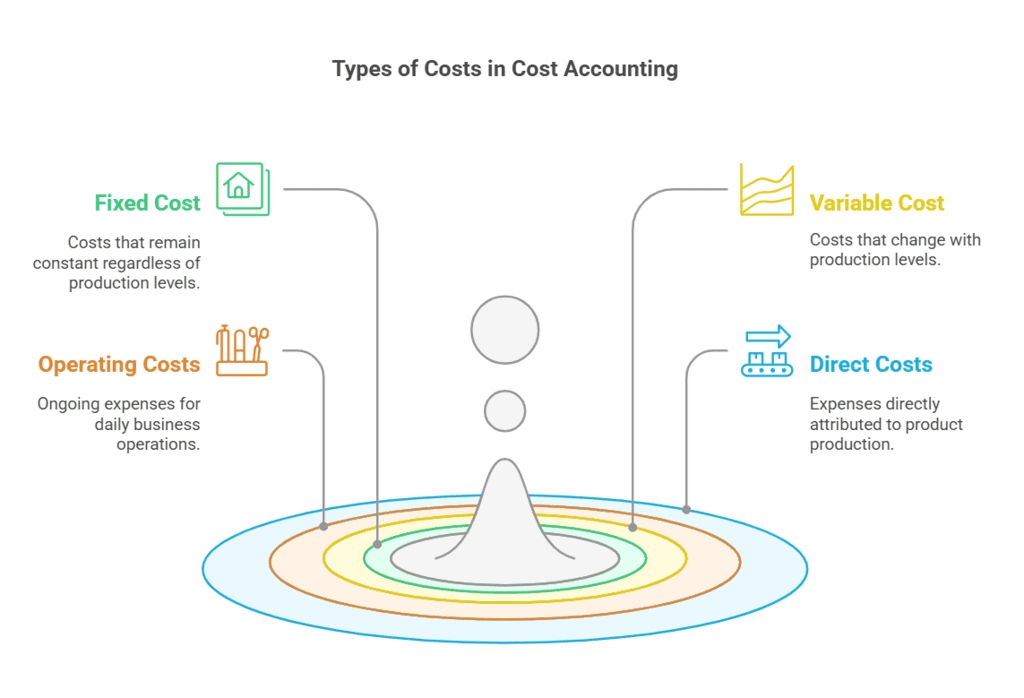
Costs are generally categorized into four types: fixed cost, variable cost, direct cost, and indirect cost.
- Fixed cost: These are costs that remain constant regardless of the number of items produced. Examples include the depreciation of a building or the cost of equipment.
- Variable cost: These costs vary depending on the production level. For instance, a bakery incurs $10 in labor and $5 in raw materials for each cake baked. The total variable cost changes with the number of cakes produced.
- Operating costs: These are the ongoing expenses required to run the business on a daily basis, such as travel expenses, telephone bills, and office supplies.
- Direct costs: These are expenses that can be directly attributed to the production of a product. For example, in a furniture manufacturing company, the direct costs of producing a couch include the raw materials and labor charges for the number of days spent on production.
Components & Elements of Total Cost
The total cost consists of several components, including prime cost, factory cost, office cost, and cost of sales.
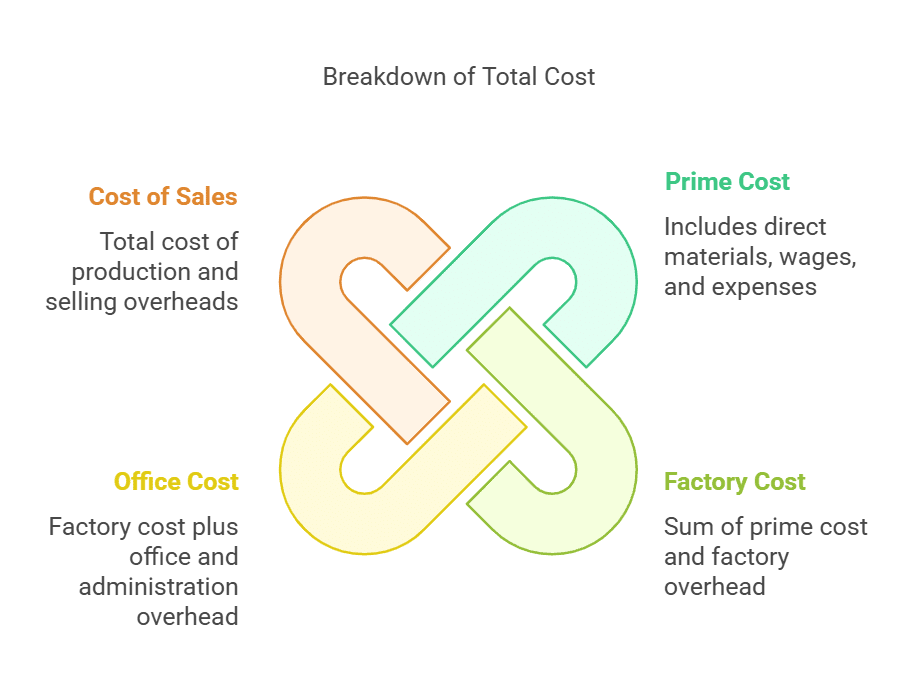
Let's break down each of these elements:
- Prime cost: This includes direct material, direct wages, and direct expenses. It is also known as basic cost, first cost, or flat cost. It represents the total of the material used, wages paid for production, and other direct expenses incurred.
Prime cost = Direct material + Direct wages + Direct expenses
Direct material cost refers to the cost of raw materials used in production. To calculate the material consumed, we use the formula:
Material consumed = Material purchased + Opening stock of material – Closing stock of material - Factory cost: Factory cost is the sum of prime cost and factory overhead, which includes indirect wages, indirect material, and other indirect expenses. It is also known as works cost, production cost, or manufacturing cost.
Factory cost = Prime cost + Factory overhead - Office cost: Also referred to as administration cost or total cost of production, office cost includes factory cost along with office and administration overhead.
- Total cost or cost of sales: This is the sum of the total cost of production and the selling and distribution overheads.
Total cost = Cost of goods sold + Selling and distribution overhead
Work-in-progress: In the production process, some units may not be finished at the end of the period. These are called work-in-progress, and adjustments must be made for opening and closing stock to calculate the net factory cost. The cost of unfinished units includes direct material, direct expenses, and factory overheads.
Adjustments for inventories are made as follows:
(a) Direct material consumed: Opening stock of direct material + Purchases of direct material – Closing stock of direct material
(b) Works cost: Gross works cost + Opening work in progress – Closing work in progress
(c) Cost of production of goods sold: Cost of production + Opening stock of finished goods – Closing stock of finished goods
How to Prepare a Cost Sheet?
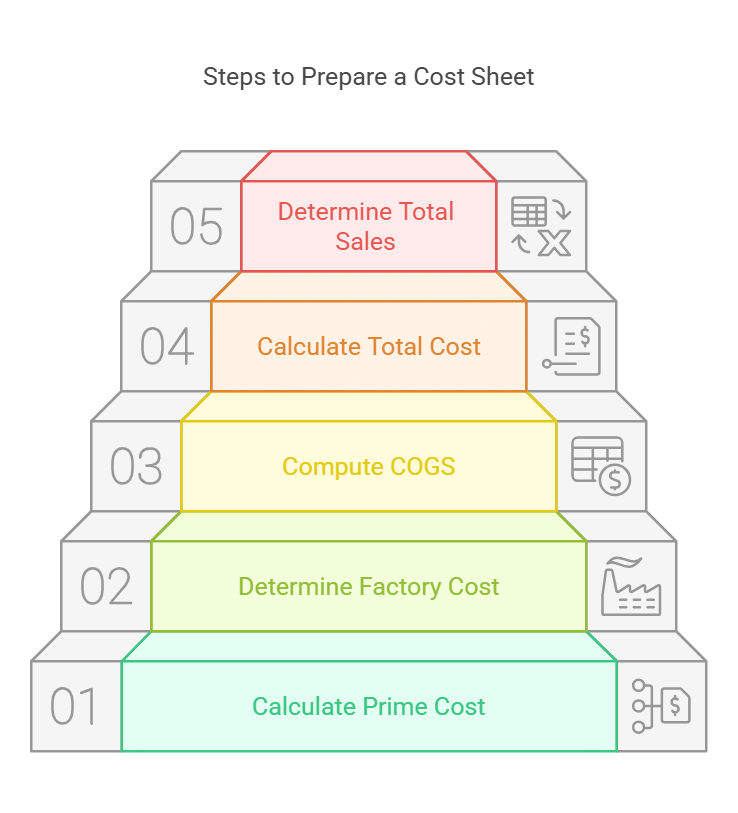
The steps to prepare a cost sheet are as follows:
- Step 1: Calculate the prime cost by adding all the direct costs, such as direct materials, direct labor, and direct expenses.
- Step 2: After determining the prime cost, calculate the factory cost. This is the sum of the prime cost and factory overheads. Also, include the opening stock of work-in-progress and subtract the closing stock of work-in-progress.
- Step 3: Next, calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS). COGS is the sum of factory cost, office and administrative overheads, and the opening stock of finished goods. Then, subtract the closing stock of finished goods.
- Step 4: Calculate the total cost by adding the selling and distribution overheads to the cost of goods sold.
- Step 5: The final step is to calculate total sales. Sales is the sum of total cost and profit. In case of a loss, subtract the amount from the total cost.
Format of Cost Sheet
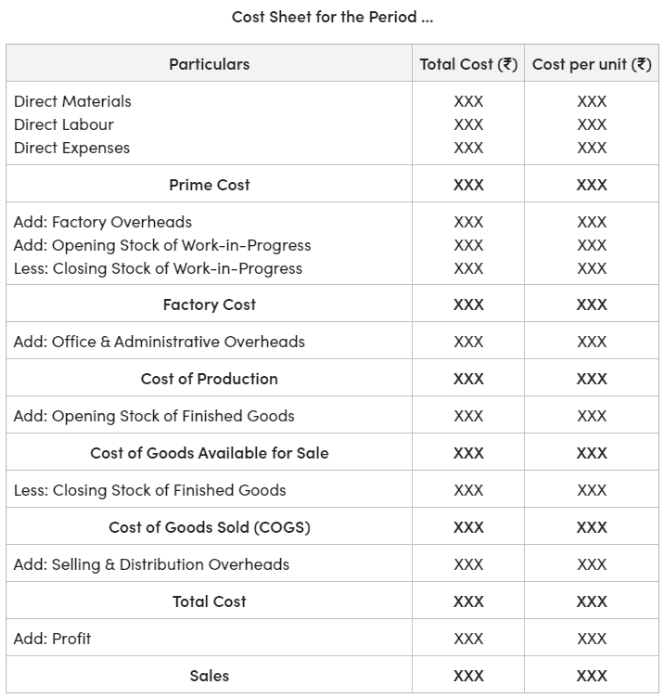
 |
Download the notes
Cost Sheet
|
Download as PDF |
Cost Sheet Example
Example: Following is the cost record of ABC Ltd. Prepare the cost sheet.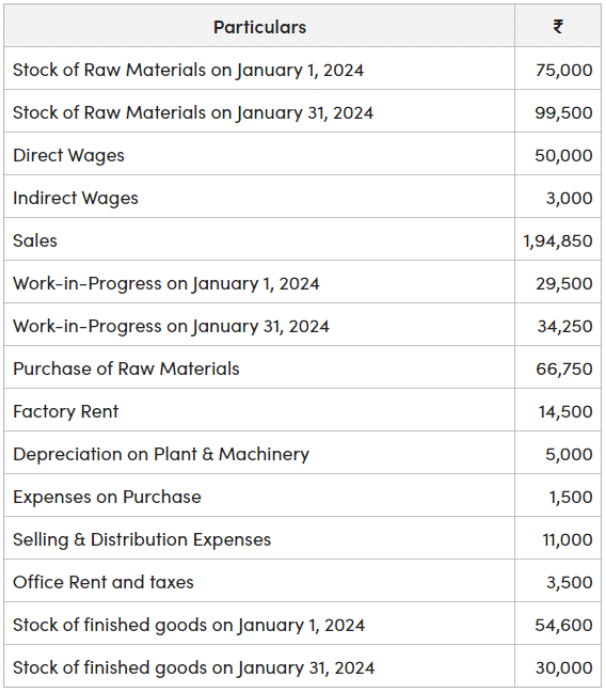
Solution: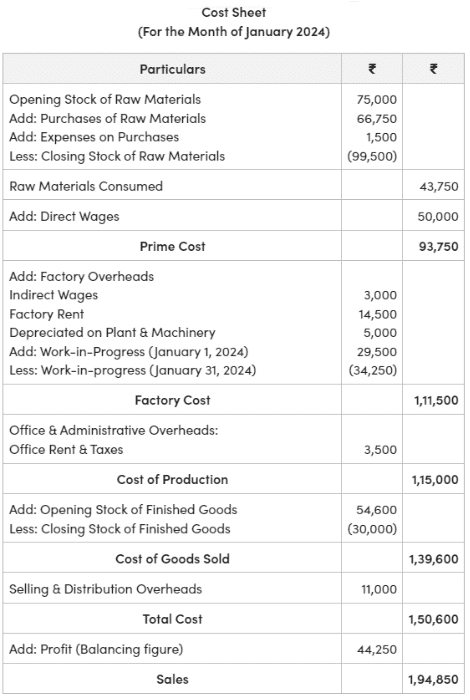
Limitations of Cost Sheet
- Time Consuming: Preparing a cost sheet is a time-consuming process. Before creating the cost sheet, detailed data on costs from various production stages must be compiled. This data is crucial for ensuring accuracy in the cost sheet. Additionally, when preparing an estimated cost sheet, management must analyze past cost data, current market conditions, and price trends.
- Lack of Accuracy: Cost sheets involve assumptions and estimates, particularly when estimating costs and allocating indirect costs. If these assumptions and estimates are incorrect, it can lead to inaccurate cost data, affecting the reliability of the information and potentially resulting in poor decision-making.
- Overlooks Non-Monetary Factors: A significant limitation of the cost sheet is that it focuses solely on monetary factors, ignoring non-monetary elements. Non-monetary factors, such as product quality, employee motivation, and brand image, play a crucial role in business decisions but are not reflected in the cost sheet. These factors can greatly influence business outcomes but are not quantifiable in financial terms.
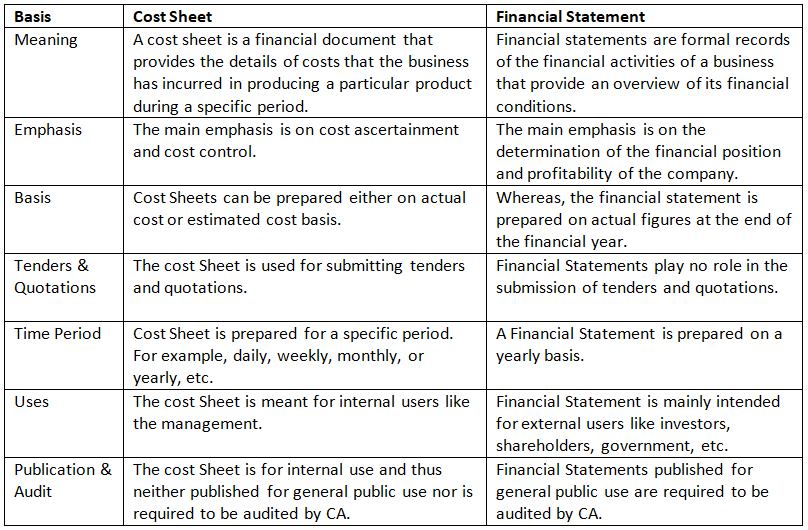
Difference Between Cost Sheet and Financial Statement
Conclusion
The cost sheet is a vital tool for effective decision-making. It provides essential cost data that helps businesses make informed decisions regarding production, material and equipment purchases, cost savings, and setting selling prices. By tracking all production-related expenses, cost sheets allow firms to adapt to market changes more effectively and efficiently, ensuring better financial management and strategic planning.
|
44 videos|75 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Cost Sheet - Accountancy and Financial Management - B Com
| 1. What is a cost sheet in accounting? |  |
| 2. How do you prepare a cost sheet? |  |
| 3. What are the main components of a cost sheet? |  |
| 4. Why is a cost sheet important for businesses? |  |
| 5. What are the differences between a cost sheet and a balance sheet? |  |
























