Classification of Inventory - Operations, Logistics Management | Logistics Management - B Com PDF Download
Classification of Inventory
In business, the inventory may be defined as the goods held for sale in the ordinary course of business or the goods that are used to manufacture goods to be sold. Inventories usually make up a large part of the total current assets of a company.
The proper reporting and accounting of inventory increase the usefulness of financial statements for potential and actual investors. Merchandising and manufacturing companies maintain and report inventories differently.
Inventory in merchandising (retail) companies:
Merchandising companies buy goods that are ready to use and sell them to customers at a profit. Because merchandising companies do not produce anything, the financial statements of these companies show only one inventory account that is “Merchandise Inventory”.
The following is an example of current assets section of merchandising companies:
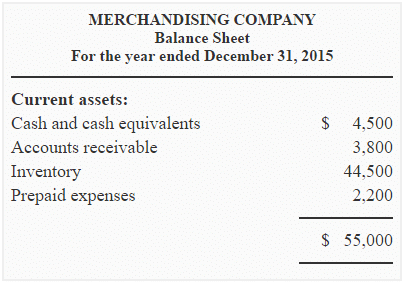
Inventory in manufacturing companies:
Manufacturing companies produce goods and sell them to customers or merchandising companies. Manufacturing companies normally maintain three inventory accounts. These are: raw materials inventory, work in process inventory and finished goods inventory. These are briefly explained below:
Raw materials inventory:
Raw material is the basic material that is processed and converted into finished goods. The cost incurred to obtain raw materials that have not yet been placed into production is reported as raw materials inventory in the current assets section of the balance sheet. Examples of raw materials include wood for the manufacturers of cricket bat and steel for the manufacturers of cars.
Work-in-process inventory:
The units that remain incomplete at the end of a period are known as work-in-process inventory. These units need the addition of more materials, labor or manufacturing overhead to be completed int the coming period. Like raw materials, work-in-process inventory is reported in the current assets section of the balance sheet.
Finished goods inventory:
Finished goods are completed but unsold goods. The total cost incurred to complete these unsold goods are reported as finished goods inventory along with raw materials and work-in-process inventory in the current assets section of the balance sheet.
The above three types of inventory are reported in the balance sheet of manufacturing company as follows:
The three inventory accounts described above are common among manufacturing companies; however, a fourth inventory account known as manufacturing or factory supplies account is some time maintained by manufacturing companies. It includes items that are not the basic raw material to be process but are used to manufacture a product. Examples of such items include nails, glue, cleaning materials, packaging materials, lubrication, machine oils etc. The inventory of such items on hand at the end of a period is also presented on the balance sheet. The packaging materials presented in the current asset section of the manufacturing company is an example of such material.
|
33 videos|35 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Classification of Inventory - Operations, Logistics Management - Logistics Management - B Com
| 1. What is inventory management in operations and logistics management? |  |
| 2. What are the main objectives of inventory management in operations and logistics management? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of inventory in operations and logistics management? |  |
| 4. How is inventory classified in terms of value in operations and logistics management? |  |
| 5. How does effective inventory management contribute to cost reduction in operations and logistics management? |  |





















