ICAI Notes 6.2: Final Accounts of Non Manufacturing Entities - 4 - CA Foundation PDF Download
5. CERTAIN ADJUSTMENTS AND THEIR TREATMENTS
1. Abnormal loss of Inventory by accident or fire : Sometimes loss of goods occurs due to fire, theft, etc. If due to accident or fire, a portion of Inventory is damaged, the value of loss is first to be ascertained. Thereafter, Abnormal Loss Account is to be debited and Purchase Account or Trading Account is to be credited.
Abnormal Loss Account is to be transferred to Profit & Loss Account. If amount of loss is recoverable from insurance company, then insurance company is to be debited instead of Profit & Loss Account. Till the money is not received from the insurance company, Insurance Company’s Account will be shown in the Assets side of the Balance Sheet. If any part of the loss is recoverable from the insurance company, then the portion not compensated by the insurance company should be debited to Profit & Loss Account. For example, if goods worth 6,000 are destroyed by fire and the insurance company admits the claim for
4,500, the Journal entries will be:-
(i) Loss by Fire Account To Purchases/Trading Account | Dr. 6,000 6,000 |
(ii) Insurance Company’s A/c (Insurance Claim) Profit & Loss A/c To Loss by Fire A/c | Dr. 4,500 Dr. 1,500 6,000 |
2. Goods sent on Approval basis : Sometimes goods are sold to customers on sale or return basis or on approval basis. It should not be treated as actual sale till the time it is not approved by the customer. When goods were sold we have passed the entry for actual sales. Therefore, at the year end, if the goods are still lying with the customers for approval, following entries are to be passed:
For example -
Goods costing 10,000 sent to a customer on sale or return basis for
12,000. The entry for such unapproved sale shall be
(i) Sales A/c To Trade receivables A/c | Dr. 12,000 12,000 |
(ii) Inventory with Customers A/c To Trading A/c | Dr. 10,000 10,000 |
3. Goods used other than for sale : Sometimes goods are used for some other purposes, such as distributed as free samples, used in construction of any assets or used by proprietor for personal use. In such cases the amount used for other purposes is subtracted from Purchases A/c and depending upon the specific use done, the suitable account head is debited.
For example :-
When goods are given away as donation -
Donation A/c To Purchases A/c | Dr. |
When goods are used by the proprietor for his personal use |
|
Drawings A/c To Purchases A/c | Dr. |
| When goods are distributed as free samples :- | |
Free Samples / Advertisement A/c To Purchases A/c | Dr.
|
| When goods are used in business for construction of Building or the Machinery :- | |
| Building A/c / Plant & Machinery A/c | Dr. |
| To Purchases A/c | |
| When goods are used for maintenance of business premises/ Machinery : - | |
| Repair & Maintenance A/c | Dr. |
| To Purchases A/c |
4. Sales Tax : If Sales Tax is charged from the customers, along with the price of the goods sold, amount of sales tax should be shown separately in the sales day book. Periodically this sales tax is to be deposited with the Sales Tax Department of the Government. The following entries are passed
(i) At the time of sale
Cash/Trade receivables A/c To Sales A/c To Sales Tax Payable A/c | Dr.
|
| (ii) On payment of sales | |
Sales Tax Payable A/c To Bank A/c | Dr.
|
If any balance remains in the Sales Tax Payable Account, it should be shown in the Balance Sheet as liability.
5. Commission based on profit : Sometimes commission is payable to manager based on net profit; in such a case calculation is done as follows: (i) Commission on net profit before charging such commission =

(ii) Commission on net profit after charging such commission =
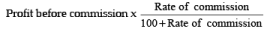
Commission is recorded by following journal entry
Commission A/c To Commission Payable A/c | Dr. |
(Being commission payable to Mr ….. @ …..% on net profit after charging such commission, net profit before charging commission being Rs ……..)
Commission will be debited in the Profit & Loss Account and Commission Payable Account will be shown in the Balance Sheet on liability side.
Illustration 6
The following is the Trial Balance of C. Wanchoo on 31st Dec. 2011.
Trial Balance on 31st December, 2011

Prepare closing entries for the above items.
Solution
Journal
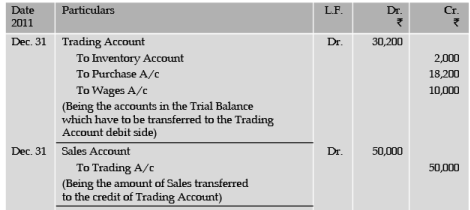
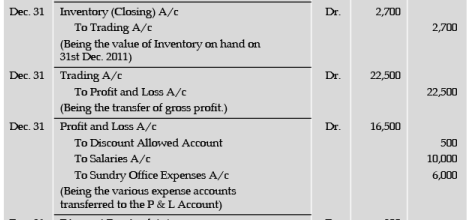

Illustration 7 From the data given in illustration 6, prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account.
Solution
C. WANCHOO
Trading Account of the year ended December 31, 2011
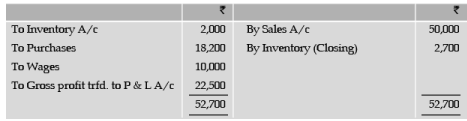
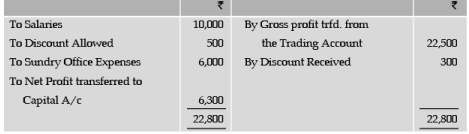
Profit and Loss Account for the year ended December 31, 2011
FAQs on ICAI Notes 6.2: Final Accounts of Non Manufacturing Entities - 4 - CA Foundation
| 1. What are final accounts of non-manufacturing entities? |  |
| 2. What is the purpose of preparing final accounts for non-manufacturing entities? |  |
| 3. What components are included in the final accounts of non-manufacturing entities? |  |
| 4. How are final accounts of non-manufacturing entities different from manufacturing entities? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of final accounts for non-manufacturing entities in decision-making? |  |














