Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Science Class 9 > Short Notes: Is Matter Around Us Pure
Is Matter Around Us Pure? Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 2
| Table of contents |

|
| Pure Substances |

|
| Mixtures |

|
| Solution |

|
| Types of Pure Substances |

|
Pure Substances
- Pure substances, like elements or compounds such as diamond or carbon dioxide, consist of a single type of entity and cannot be broken down further through chemical or physical methods.
- Elements, in particular, are pure materials made up of only one type of atom, ensuring consistency in composition and properties.
- These substances exhibit homogeneity, with constant boiling and melting points.
- In chemical reactions, pure substances play a role, producing predictable outcomes due to their stable nature.
Mixtures
It is made up of two or more elements or compounds mixed in any ratio/proportion.Properties
- It may be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
- The properties of constituent substances are retained.
- No new compound is formed after mixing.
- Constituents of a mixture can be separated by simple physical processes.
- It does not have a fixed melting and boiling point.

Question for Short Notes: Is Matter Around Us Pure
Try yourself:Mixture can be
View Solution
Solution
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances (e.g., Lemonade, soda water).
Table:Difference between Solute and Solvent.

Concentration of Solution
- The amount of solute that has dissolved in a specific amount of solvent or solution is measured as solution concentration.
- A concentrated solution is one that has a significant amount of dissolved solute in it.
- A diluted solution is one that has a small amount of dissolved solute in it.

Alloys
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of metals or a mixture of a metal and another element that cannot be separated into their components by physical methods.Examples:
- Steel – a combination of iron (metal) and carbon (non-metal).
- Bronze – a combination of copper (metal) and tin (metal).
- Brass – a mixture of copper (metal) and zinc (metal).
Suspension
A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which the solute particles do not dissolve but remain suspended throughout the bulk of the medium. Ex: Chalk in water, smoke in the air
Properties of Suspension :
- It is a heterogeneous mixture.
- Particles of a suspension are visible to the naked eye.
- The size of the particles is greater than 1000 nm.
- It is an unstable mixture. Solute settles down at the bottom over the period.
- If the solution is passed through filter paper, the solute and solvent get separated.
- It scatters light when light is passed through the solution i.e. it shows the Tyndall effect.
Colloidal Solution
A colloid solution is a heterogeneous mixture in which the size of particles lies between the true solutions and suspensions.
- Colloidal particles can easily scatter a beam of visible light.
- This phenomenon is called the Tyndall effect.
Properties of Colloidal Solution:
- The particles of colloids can’t be seen by the naked eye individually.
- It is a heterogeneous mixture and thus solute and solvent can’t be separated by filter paper.
- The size of particles is smaller than suspensions but greater than solutions (1 nm to 100 nm).
- It is a stable mixture. Particles do not settle down at the bottom over a period of time.
- They do not settle down when left undisturbed which means colloid is quite stable.
Question for Short Notes: Is Matter Around Us Pure
Try yourself:In sugar solution,
View Solution

Physical and Chemical Change
 |
Download the notes
Short Notes: Is Matter Around Us Pure
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Types of Pure Substances
The pure substance is divided in two types based on their chemical composition:
(i) Elements
According to Antoine Laurent Lavoisier, the element is a basic form of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions. It is divided into three types which are metals, non-metals and metalloids.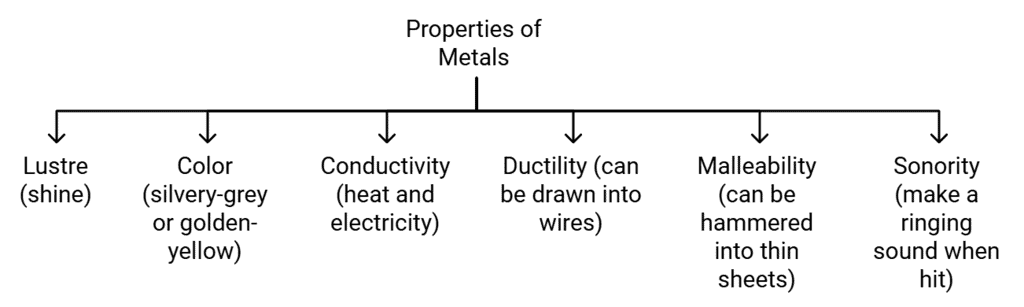 Properties of Metals
Properties of Metals
Examples:Gold, Silver, Copper, Iron, Sodium, Potassium etc. are Metals
Note:Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature.
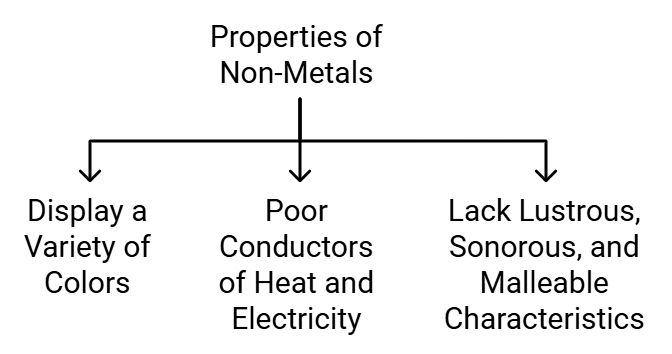 Properties of Non-Metals
Properties of Non-Metals
Examplesof non-metals are hydrogen, oxygen, iodine, carbon (coal, coke), bromine, chlorine etc.
Metalloids: Elements having intermediate properties between those of metals and non-metals are called metalloids. Examples are boron, silicon, germanium etc.
Question for Short Notes: Is Matter Around Us Pure
Try yourself:
What is a solution?View Solution
(ii) Compounds
A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements, chemically combined with one another in a fixed proportion.Characteristics
- The properties of a compound differ from those of its constituents.
- The compound has a fixed melting point and boiling point.
- A compound is a homogeneous substance.
- Constituent elements can be separated by chemical processes.
Difference between Compounds and Mixtures

Summary

The document Is Matter Around Us Pure? Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 2 is a part of the Class 9 Course Science Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
84 videos|394 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Is Matter Around Us Pure? Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 2
| 1. What is a pure substance? |  |
| 2. How do mixtures differ from pure substances? |  |
Ans. Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that retain their individual properties. Unlike pure substances, mixtures can be separated by physical methods, and their composition can vary. Examples include air and salad.
| 3. What is a solution, and how is it different from other mixtures? |  |
Ans. A solution is a homogeneous mixture where one substance (the solute) is dissolved in another (the solvent). Solutions have a uniform composition throughout, unlike heterogeneous mixtures where the components can be easily distinguished. Examples include saltwater and sugar dissolved in tea.
| 4. What are the types of pure substances? |  |
Ans. Pure substances are classified into two main types: elements and compounds. Elements are made of only one type of atom (e.g., oxygen, gold), while compounds consist of two or more types of atoms chemically bonded together (e.g., water, carbon dioxide).
| 5. How can we determine if a substance is pure or a mixture? |  |
Ans. To determine if a substance is pure or a mixture, one can observe its physical properties and behavior during separation. If the substance has a consistent composition and cannot be separated into different components by physical means, it is likely a pure substance. Conversely, if it can be separated and shows different properties in its components, it is a mixture.
Related Searches