Class 9 Maths Chapter 8 Question Answers - Quadrilaterals
Q1: In the adjoining figure, if ∠ B = 68°, then find ∠ A, ∠ C and ∠ D.
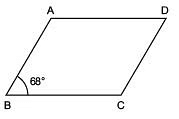 Solution: Because the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal
Solution: Because the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal
Therefore, ∠ B= ∠ D
⇒ ∠ D = 68° [∵ ∠B = 68°, given]
∵ ∠ B and ∠ C are supplementary.
∴ ∠ B + ∠ C = 180°
⇒ ∠ C = 180° - ∠ B = 180° - 68° = 112°
Since ∠A and ∠C are opposite angles.
∴ ∠ A= ∠ C
⇒ ∠ A = 112° [∵ ∠ C = 112°]
Thus, ∠ A = 112°, ∠ D = 68° and ∠ C = 112°.
Q2: In the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. If AB = 4.5 cm, then find other sides of the parallelogram when its perimeter is 21 cm.
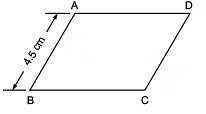 Solution: ∵ Opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal.
Solution: ∵ Opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal.
∴ AB = CD = 4.5 cm, and BC = AD
Now, AB + CD + BC + AD = 21 cm
⇒ AB + AB + BC + BC = 21 cm
⇒2[AB + BC] = 21 cm
⇒ 2[4.5 cm + BC] = 21 cm
⇒ 9 cm + 2BC = 21 cm
= 2BC = 12
Therefore, BC=AD=6
Thus, BC = 6 cm, CD = 4.5 cm and AD = 6 cm.
Q3: In a parallelogram ABCD, if (3x - 10)° = ∠ B and (2x + 10)° = ∠ C, then find the value of x. Solution: Since the adjacent angles of a parallelogram are supplementary
∴ ∠ B + ∠ C = 180°
⇒ (3x - 10)° + (2x + 10)° = 180°
⇒ 3x + 2x - 10° + 10° = 180°
⇒ 5x = 180°
⇒ x= (1800/5)= 36°
Thus, the required value of x is 36°.
Q4: The adjoining figure is a rectangle whose diagonals AC and BD intersect at O. If ∠ OAB = 27°, then find ∠ OBC.
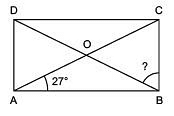 Solution: Since the diagonals of a rectangle are equal and bisect each other.
Solution: Since the diagonals of a rectangle are equal and bisect each other.
∴ OA = OB
⇒ ∠ OBA = ∠ OAB = 27°
Also, each angle of a rectangle measures 90°.
∴ ∠ ABC = 90°
⇒ ∠ ABO + ∠ CBO = 90°
⇒ ∠ OBA + ∠ OBC = 90°
⇒ 27° + ∠ OBC = 90°
⇒ ∠ OBC = 90° - 27° = 63°
Q5: In a quadrilateral, ∠ A : ∠ B : ∠ C : ∠ D = 1 : 2 : 3 : 4, then find the measure of each angle of the quadrilateral.
Solution: Since ∠ A : ∠ B : ∠ C : ∠ D = 1 : 2 : 3 : 4
∴ If ∠ A = x, then ∠ B = 2x, ∠ C = 3x and ∠ D = 4x. ∴ ∠ A + ∠ B + ∠ C + ∠ D = 360°
⇒ x + 2x + 3x + 4x = 360° ⇒ 10x = 36°
⇒ x= (3600/10)= 36°
∴ ∠ A = x = 36°
∠ B = 2x = 2 x 36° = 72°
∠ C = 3x = 3 x 36° = 108°
∠ D = 4x = 4 x 36° = 144°
Q6: In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD. If ∠ A = 36° and ∠ B = 81°, then find ∠ C and ∠ D.
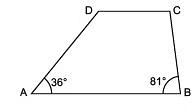 Solution: ∵ AB || CD and AD is a transversal. [∵ ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD]
Solution: ∵ AB || CD and AD is a transversal. [∵ ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD]
∴ ∠ A + ∠ D = 180°
⇒ ∠ D = 180° - ∠ A = 180° - 36° = 144°
Again, AB || CD and BC is a transversal.
∴ ∠ B + ∠ C = 180°
⇒ ∠ C = 180° - ∠ B = 180° - 81° = 99°
∴ The required measures of ∠ D and ∠ C are 144° and 99° respectively.
Q7: In the figure, the perimeter of Triangle ABC is 27 cm. If D is the mid-point of AB and DE || BC, then find the length of DE.
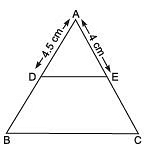 Solution: Since D is the mid-point of AB and DE || BC.
Solution: Since D is the mid-point of AB and DE || BC.
∴ E is the mid-point of AC, and DE = (1/2) BC.
Since the perimeter of DABC = 27 cm
∴ AB + BC + CA = 27 cm
⇒ 2(AD) + BC + 2(AE) = 27 cm
⇒ 2(4.5 cm) + BC + 2(4 cm) = 27 cm
⇒ 9 cm + BC + 8 cm = 27 cm
∴ BC = 27 cm - 9 cm - 8 cm = 10 cm
∴ (1/2)BC =(10/2) = 5 cm
⇒ DE = 5 cm.
Q8: In the adjoining figure, DE || BC and D is the mid-point of AB. Find the perimeter of ΔABC when AE = 4.5 cm.
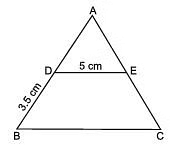 Solution: ∵ D is the mid-point of AB and DE || BC.
Solution: ∵ D is the mid-point of AB and DE || BC.
∴ E is the mid-point of AC and DE = (1/2)BC.
⇒ 2DE = BC
⇒ 2 x 5 cm = BC
⇒ BC = 10 cm
Now DB = 3.5 cm
∴ AB = 2(DB) = 2 x 3.5 cm = 7 cm [D is the mid-point of AB]
Similarly, AC = 2(AE) = 2 x 4.5 cm = 9 cm
Now, perimeter of ΔABC = AB + BC + CA = 7 cm + 10 cm + 9 cm = 26 cm
Q9: If the angle of a parallelogram is (4/5) of its adjacent angle, then find the measures of all the angles of the parallelogram. Solution: Let ABCD is a parallelogram in which ∠ B = x
∴ ∠ A= (4/5)x
Since the adjacent angles of a parallelogram are supplementary.
∴ ∠ A + ∠ B = 180°
⇒ (4/5)x + x = 180°
⇒ 4x + 5x = 180° x 5
⇒ 9x = 180° x 5
⇒
∴ ∠ B = 100°
Since ∠ B= ∠ D [Opposite angles of parallelogram]
∴ ∠ D = 100°
Now, ∠ A= (4/5)x =(4/5) x 100° = 80°
Also ∠ A= ∠ C [Opposite angles of parallelogram]
∴ ∠ C = 80°
The required measures of the angles of the parallelogram are: ∠ A = 80°, ∠ B = 100° ∠ C = 80° and ∠ D = 100°
Q10: Find the measure of each angle of a parallelogram, if one of its angles is 15° less than twice the smallest angle.
Solution: Let the smallest angle = x
Since, the other angle = (2x ∠ 15°)
Thus, (2x ∠ 15°) + x = 180° [∵ x and (2x ∠ 15°) are the adjacent angles of a parallelogram]
⇒ 2x ∠ 15° + x = 180°
⇒ 3x ∠ 15° = 180°
⇒ 3x = 180° + 15° = 195°
⇒ x= (1950/3)= 65°
∴ The smallest angle = 65°
∴ The other angle = 2x - 15° = 2(65°) - 15° = 130° -15° = 115°
Thus, the measures of all the angles of a parallelogram are: 65°, 115°, 65° and 115°.
Q11: The lengths of the diagonals of a rhombus are 24 cm and 18 cm respectively. Find the length of each side of the rhombus. Solution: Since the diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
∴ O is the mid-point of AC and BD
⇒ AO =(1/2)AC and DO =(1/2)BD
Also ∠ AOD = 90°.
Now, ΔAOD is a right triangle, in which
AO = (1/2)AC =(1/2)(24 cm) = 12 cm
and DO = (1/2)BD =(1/2)(18 cm) = 9 cm
Since, AD2 = AO2 + DO2
⇒ AD2 = (12)2 + (9)2
= 144 + 81 = 225 = 152
⇒ AD = √(15)2 = 15
⇒ AD = AB = BC = CD = 15 cm (each)
Thus, the length of each side of the rhombus = 15 cm.
Q12: One angle of a quadrilateral is of 108° and the remaining three angles are equal. Find each of the three equal angles.
Solution: ABCD is a quadrilateral
∴ ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
⇒ 108° + [∠B + ∠C + ∠D] = 360°
⇒ [∠B + ∠C + ∠D]
= 360° - 108° = 252°
Since,
∠D = ∠B = ∠C
∴ ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 252°
⇒ ∠B + ∠B + ∠B = 252°
⇒ 3∠B = 252°
⇒ ∠B = (2520/3) = 84°
∴ ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 84°
Thus, the measure of each of the remaining angles is 84°.
Q13: In the figure, AX and CY are respectively the bisectors of opposite angles A and C of a parallelogram ABCD. Show that AX || CY
Solution: Given, ABCD is a parallelogram
AX and CY are the bisectors of the angles A and C.
We have to show that AX || CY
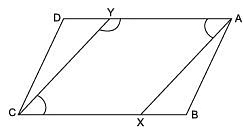
∠DAB = 2x
∠DCB = 2y
We know that opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
So, ∠A = ∠C
2x = 2y
x = y
As DC || AB, XC || AY
∠XCY = ∠CYB [Alternate angles]
∠CYB = x
∠XAY = x
As ∠XAY and ∠CYB are corresponding angles
AX || CY
Therefore, AX is parallel to CY.
Q14: E and F are respectively the midpoints of the non-parallel sides AD and BC of a trapezium ABCD. Prove that: EF || AB and EF = (1/2)(AB + CD)
Solution: Let us join BE and extend it to meet CD produced at P.
In ΔAEB and ΔDEP, we get AB || PC and BP is a transversal,
∴ ∠ABE = ∠EPD [Alternate angles]
AE = ED [∵ E is the midpoint of AB]
∠AEB = ∠PED [Vertically opp. angles]
⇒ ΔAEB ≌ ΔDEP
⇒ BE = PE and AB = DP [SAS]
⇒ BE = PE and AB = DP
Now, in ΔEPC, E is a midpoint of BP and F is midpoint of BC
∴ EF || PC and EF =(1/2)PC [Mid point theorem]
i.e., EF || AB and EF = (1/2) (PD + DC)
= (1/2) (AB + DC)
Thus, EF || AB and EF = (1/2) (AB + DC)
|
40 videos|471 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Maths Chapter 8 Question Answers - Quadrilaterals
| 1. What are the different types of quadrilaterals? |  |
| 2. What is the sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral? |  |
| 3. How do you determine if a quadrilateral is a parallelogram? |  |
| 4. What are the properties of a rectangle? |  |
| 5. How can you calculate the area of a trapezium? |  |

















