Accounting for Share Capital Chapter Notes | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Features of a Company |

|
| Types of Companies |

|
| Share Capital of a Company |

|
| Nature and Classes of Shares |

|
| Issue of Shares |

|
| Forfeiture of Shares |

|
Introduction
- A company refers to an organisation that is registered under the Companies Act, 2013 or any previous Companies Acts.
- The company form of organisation is the third stage in the development of organisational structures.
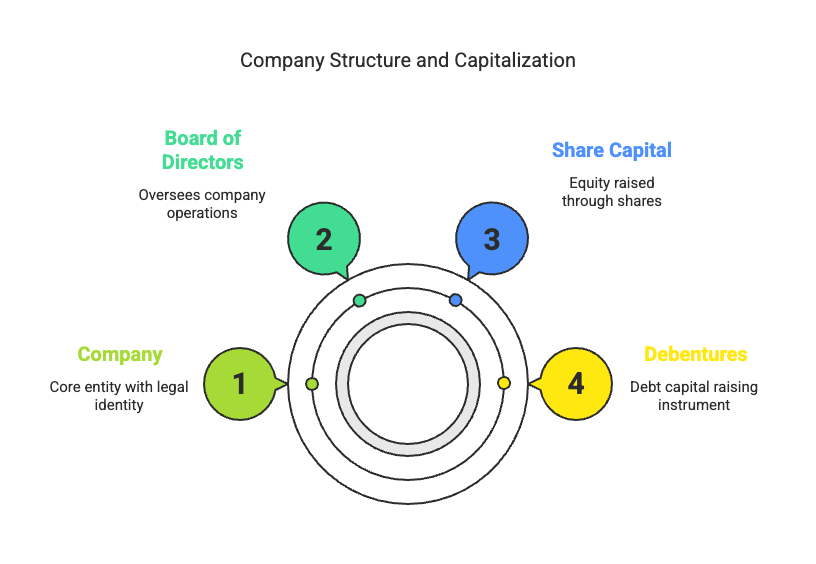
- It signifies a group of individuals who contribute money or assets for a shared purpose. A company is an artificial entity with its own legal identity, separate from its members (shareholders), and uses a common seal as its signature.
- However, it is not feasible or desirable for all members to manage the company directly. Instead, they select a Board of Directors to oversee the company's operations.
- The company generates capital through shares (known as share capital) and debentures (which provide debt capital). This section focuses on the accounting for the share capital of companies.
Key Definitions:
- Company: A company is an artificial entity created by law, known as a "person" in legal terms. It is intangible, invisible, and exists only in the eyes of the law. The properties and powers of a company are defined by its charter, which is granted at the time of its creation.
- Share Capital: Share capital refers to the funds raised by a company through the issuance of shares. This represents ownership in the company and is a primary source of capital.
- Debentures: Debentures are a form of debt capital raised by a company. They represent a loan made to the company by debenture holders and typically come with fixed interest rates.

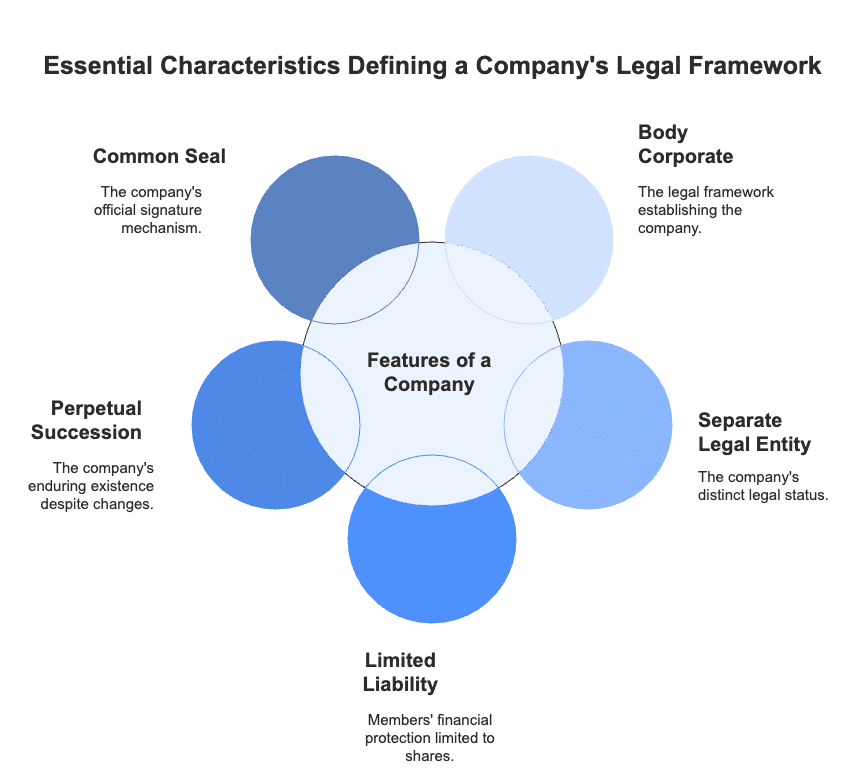
Features of a Company
- Body Corporate:. company is created following the laws in force at the time. In India, companies are typically established and registered under the Companies Act, except for banks and insurance firms, which have separate legislation.
- Separate Legal Entity:. company is recognised as a separate legal entity, distinct from its members. It can own and manage various types of property, enter contracts, and even maintain a bank account in its own name.
- Limited Liability: The members of a company have their liability limited to the unpaid amount of their shares. For companies limited by guarantee, members' liability is confined to the amount they guaranteed if the company is wound up.
- Perpetual Succession: As an artificial person created by law, a company continues to exist regardless of changes in its membership. It can only be dissolved by legal means, and the death, mental incapacity, or insolvency of any member does not affect the company's existence.
- Common Seal: As an artificial entity, a company cannot sign documents itself, so it must have a common seal, which acts as its official signature. Any document without this seal is not legally binding on the company.
- Transferability of Shares: The shares of a public limited company can be transferred freely. Approval from the company or consent from other members is not required for share transfers, though the company's Articles may specify the process for such transfers.
- May Sue or be Sued:. company, recognised as a legal person, can enter contracts and enforce its rights. It can initiate or face lawsuits in its own name if there is a breach of contract.
Types of Companies
Companies can be categorized based on the liability of their members and the number of members. Let's explore these classifications:
Based on Liability of Members:
- Companies Limited by Shares: The liability of members is limited to the nominal value of shares they hold. If a member has paid the full amount for their shares, they are not liable for the company's debts beyond that. Liability can be enforced during the company's existence and winding up.
- Companies Limited by Guarantee: Members' liability is limited to the amount they agree to contribute in case of winding up. This liability only arises during winding up.
- Unlimited Companies: There is no limit on members' liability. If the company's assets are insufficient to cover its debts, members' private properties can be used to settle the debts. Such companies are rare in India, despite being allowed by the Companies Act.

Based on the Number of Members:
- Public Company: A company that is not a private company and not a subsidiary of a private company.
- Private Company: A company that restricts the transfer of shares, requires at least two members (except for one-person companies), and limits the number of members to 200 (excluding employees).
- One Person Company (OPC): A company with only one member. It must be formed by a natural person who is an Indian citizen and resident, cannot engage in non-banking financial investment activities, and has a paid-up share capital of no more than Rs. 50 Lakhs, and an average annual turnover not exceeding Rs. 2 Crores.

Share Capital of a Company
- A company, being an artificial entity, cannot generate its own capital and must collect it from various individuals known as shareholders.
- The amount contributed by these shareholders is called share capital.
- Since there are often a large number of shareholders, it is impractical to maintain a separate capital account for each one.
- Instead, all these contributions are pooled together into a common account known as the Share Capital Account.
Categories of Share Capital:
- Authorised Capital: This is the highest amount of share capital a company is allowed to issue according to its Memorandum of Association. It is also referred to as Nominal or Registered capital. The company can adjust this amount by following the procedures set out in the Companies Act. Not all authorised capital needs to be issued immediately; shares can be issued as necessary, but not exceeding this limit. The part of authorised capital that is not yet available for public subscription is called unissued capital, which can be offered later.
- Issued Capital: This is the segment of authorised capital that is actually offered to the public for subscription. It includes shares allocated to vendors and the individuals who signed the company’s memorandum.
- Subscribed Capital: This is the part of issued capital that has been subscribed by the public. If all offered shares are fully subscribed, the issued and subscribed capitals will be identical. Subscribed capital can be equal to or less than issued capital. If fewer shares are subscribed than offered, only those shares are allocated. If more shares are subscribed than offered, the allocation is limited to what was offered.
- Called-up Capital: This is the portion of subscribed capital that the company has requested payment for. The company can call for the entire amount or part of the face value of the shares. For instance, if a share has a face value of Rs. 10 and the company calls for Rs. 7 per share, the called-up capital is Rs. 7 per share.
- Paid-up Capital: This is the segment of called-up capital that has been received from shareholders. Paid-up capital equals called-up capital when all amounts requested are paid. If any shareholder does not pay, the unpaid amount is known as calls in arrears.
- Uncalled Capital: This is the part of subscribed capital that has not yet been called for payment. The company can call for this amount whenever it requires additional funds.
- Reserve Capital: This is a section of uncalled capital that a company may set aside to call only in the case of winding up. Reserve capital is accessible only to creditors when the company is winding up.

Let us take the following example and show how the share capital will be shown in the balance sheet. Sunrise Company Ltd., New Delhi, has registered its capital as Rs. 40,00,000, divided into 4,00,000 shares of Rs. 10 each. The company offered to the public for subscription of 2,00,000 shares of Rs. 10 each, to be received as Rs. 2 on application, Rs.3 on allotment, Rs.3 on first call and the balance on final call. The company received applications for 2,50,000 shares. The company finalised the allotment of 2,00,000 shares and rejected applications for 50,000 shares. The company did not make the final call. The company received all the amount except on 2,000 shares where call money has not been received. The above amounts will be shown in the Notes to Accounts of the balance sheet of Sunrise Company Ltd. as follows:
Notes to Accounts:

Nature and Classes of Shares
Shares represent the units into which a company's total share capital is divided. A share is essentially a fractional part of the share capital and signifies ownership interest in the company. Individuals who invest money by purchasing shares are known as shareholders.
The amount of authorized capital and the number of shares it is divided into are specified in the Memorandum of Association. However, the types of shares, along with their associated rights and obligations, are detailed in the Articles of Association. According to the Companies Act, a company can issue two main types of shares:
- Preference Shares
- Equity Shares (also referred to as ordinary shares)
Preference Shares
- Definition:. Preference share has specific conditions: (a) It provides a preferential right to dividends, either as a fixed sum for preference shareholders or calculated based on a fixed rate of the nominal value of each share, paid before dividends to equity shareholders. (b) In terms of capital, it has or will have the right to repayment before equity shareholders when the company is wound up.
- Dividend Preference: Preference shares receive dividends before equity shareholders, either as a fixed amount or a rate based on the nominal value of each share.
- Capital Repayment Preference: In the event of winding up, preference shares are repaid their capital before equity shareholders receive anything.
- Participation in Surplus: Holders of preference shares may participate in any surplus profits of the company, either partially or fully, as stated in the company’s Memorandum or Articles.
- Types of Preference Shares: Preference shares can be classified as:
- Participating or Non-Participating
- Cumulative or Non-Cumulative
- Redeemable or Irredeemable

Equity Shares
- Definition: Equity shares, as per Section 43 of the Companies Act, 2013, are shares that do not have any preferential rights in terms of dividend payment or capital repayment. Essentially, they are shares that are not classified as preference shares.
- Dividend Rights: Equity shareholders are entitled to share the company's distributable profits after the preferential dividend rights of preference shareholders have been satisfied. The dividend on equity shares is not fixed and can vary from year to year based on the profits available for distribution.
- Equity Share Capital Types: Equity share capital can be classified as:
- With Voting Rights
- With Differential Rights regarding voting, dividends, or other matters, as specified in the company's Articles of Association.
Issue of Shares

- Shares represent ownership in a company and are a way for companies to raise capital.
- Companies can issue shares gradually, collecting the money in instalments to meet their financial needs.
- The first instalment is called application money, followed by allotment money, and then subsequent instalments are called calls (first call, second call, etc.). The last instalment is referred to as the final call.
- However, companies can also demand the full amount for shares at the time of application if they choose to.
The process of issuing shares involves several key steps:
- Issue of Prospectus: The company issues a prospectus to the public, inviting them to invest in the newly formed company. The prospectus contains detailed information about the company and how funds will be collected from investors.
- Receipt of Applications: Interested investors submit applications, along with application money, to a scheduled bank as specified in the prospectus. The company must receive a minimum subscription within 120 days of issuing the prospectus. If not, shares cannot be allotted, and application money must be refunded within 130 days.
- Allotment of Shares: If the minimum subscription is met, shares are allotted after completing legal formalities. Letters of allotment are sent to successful applicants, and letters of regret are sent to unsuccessful ones. Allotment creates a valid contract between the company and the shareholders.

Shares can be issued at par or at a premium:
- At par: When the issue price is equal to the nominal value of the shares.
- At a premium: When the issue price exceeds the nominal value, with the excess amount called a premium.
Regardless of par or premium, share capital can be collected in instalments at different stages.
Minimum Subscription
- The minimum subscription is the least amount that, in the opinion of the directors, needs to be raised to support the company's business operations. This includes:
- Property Costs: The price of any property purchased or to be purchased, which will be financed wholly or partly from the proceeds of the share issue.
- Preliminary Expenses: Initial costs that the company has to pay, along with any commission related to the share issue.
- Repayment of Borrowed Money: Any money borrowed by the company for the above-mentioned purposes needs to be repaid.
- Working Capital: Funds required for the day-to-day operations of the business.
- Other Expenditure: Any additional expenses necessary for the regular conduct of business operations.
- According to SEBI (Disclosure and Investor Protection) Guidelines, 2000, the minimum subscription cannot be less than 90% of the issued amount. If this condition is not met, the company must refund the entire subscription amount received.
- If there is a delay in refunding beyond 8 days from the closure of the subscription list, the company is liable to pay the amount with interest at the rate of 15% as per Section 73(2).
Accounting Treatment:
- On Application: The money paid with various instalments represents a contribution to share capital and should ultimately be credited to share capital. However, for convenience, individual accounts are initially opened for each instalment.
- All money received along with the application is deposited with a scheduled bank in a separate account opened for this purpose. The journal entry for this transaction is as follows:

- On Allotment: Once the minimum subscription has been received and the necessary legal formalities for the allotment of shares have been completed, the directors of the company proceed to allot the shares. The allotment of shares signifies a contract between the company and the applicants, who now become the allottees and assume the status of shareholders or members.
Allotment of Shares:
Implications from an Accounting Perspective
- It is standard practice to request an amount known as Allotment Money from the shareholders as soon as the shares are allotted to them.
- Upon accepting the offer made by the applicants, the application money received is transferred to the share capital account, as it officially becomes part of the capital.
- Any money received from rejected applications must be fully refunded to the applicants within the timeframe set by law or the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- If fewer shares are allotted than were applied for, the excess application money must be adjusted against the amount due on allotment from the allottees.
- The last two steps essentially close the share application account, which is a temporary account used for share capital transactions.
The journal entries with regard to the allotment of shares are as follows:

Note:- The journal entries (2) and (4) can also be combined as follows:

Share Application and Allotment Account:
- Sometimes, a company opens a combined account called ‘Share Application and Allotment Account’ to manage share applications and allotments together.
- This combined account is based on the idea that allotment without application is not possible, and application without allotment is meaningless. These two stages of share capital are closely linked.
- When maintaining a combined account, journal entries are recorded in a specific manner to reflect both share applications and allotments simultaneously.

Understanding ASBA in IPOs and Rights Issues:
- Application Money Payment Methods: When subscribing to Initial Public Offers (IPOs) or Rights Issues of securities like shares, debentures, or other financial instruments, application money can be paid through various banking instruments such as cheques, pay orders, drafts, debit to bank accounts, or through the Applications Supported by Blocked Amount (ASBA) method.
- What is ASBA? ASBA, or Applications Supported by Blocked Amount, is a process introduced by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to facilitate applications for IPOs and Rights Issues. It allows applicants to authorize their banks to block a certain amount in their accounts for the application money, which is only debited if the applicant is allotted securities.
- How ASBA Works:Under the ASBA method:
- The applicant instructs the bank to block the application money in their account for subscribing to the securities.
- If the applicant is allotted securities, the bank debits the account for the specified amount.
- If no securities are allotted, the bank releases the block on the funds, making them available again.
- Application Amount Blocking: In ASBA applications, the application amount for the securities applied is blocked by the bank, marking a lien on the funds. Once the company allocates the securities, the bank debits the applicant's account for the amount due for the allotted securities and releases the lien on the remaining balance.
Calls are important for making shares fully paid up and collecting the full amount from shareholders.
- If shares are not fully called up by the end of the allotment, directors can request the remaining amount at their discretion.
- Sometimes, the timing for shareholders to pay calls is specified in the prospectus at the time of share issuance.
- Two key points about calls on shares:
- The call amount cannot exceed 25% of the share's face value.
- There must be at least a one-month gap between two calls unless the company's articles of association state otherwise.
When a call is made and the amount of the same is received, the journal entries are as given below:

Share Call Account Naming
- The terms First, Second, or Third should be added between "Share" and "Call" in the Share Call account based on the identity of the call made.
- For example:
- First call: "Share First Call Account"
- Second call: "Share Second Call Account"
- Third call: "Share Third Call Account"
- If a call is the last one, add "and Final"to it. For instance:
- If the second call is the last: "Second and Final Call"
- If the third call is the last: "Third and Final Call"
- Sometimes, the entire balance after allotment may be collected in one call. In such cases, the first call will be termed as "First and Final Call."
Points to Consider When Issuing Share Capital for Public Subscription:
- Application Money: The application money should be a minimum of 5% of the share's face value.
- Calls: Calls should be made in accordance with the provisions outlined in the articles of association.
- Default Articles of Association: If there are no specific articles of association, the following provisions from Table A will apply:
- Timing Between Calls: A period of one month must elapse between two calls.
- Amount of Call: The amount of each call should not exceed 25% of the share's face value.
- Notice Period: A minimum of 14 days' notice must be given to shareholders for payment.
- Uniformity of Calls: Calls must be made uniformly on all shares within the same class.
- Accounting for Share Issues: The accounting procedure for issuing both equity and preference shares is identical. To differentiate between the two, the words 'Equity' and 'Preference' should be prefixed to each installment.
Example: Mona Earth Mover Limited decided to issue 12,000 shares of Rs.100 each payable at Rs.30 on application, Rs.40 on allotment, Rs.20 on first call and balance on second and final call. Applications were received for 13,000 shares. The directors decided to reject application of 1,000 shares and their application money being refunded in full. The allotment money was duly received on all the shares, and all sums due on calls are received except on 100 shares. Record the transactions in the books of Mona Earth Movers Limited
Ans:


Calls in Arrears:
When shareholders fail to pay the call amount by the due date, the amount due on allotment or on any of the calls is referred to as 'Calls in Arrears' or 'Unpaid Calls.' Calls in Arrears represent the debit balance of all the calls accounts. If a company maintains a 'Calls in Arrears' account, it is necessary to pass an additional journal entry to reflect this.

The Articles of Association of a company may give directors the authority to charge interest on overdue calls at a specified rate. If the Articles do not mention this, the rule in Table F applies.
- According to Table F, interest cannot exceed 10% per annum on unpaid amounts for shares, calculated from the due date until the actual payment date.
- When the call amount is received along with interest, the interest portion is credited to the interest account, while the call money is credited to the respective call account or calls in arrears account.
When the shareholder makes the payment of calls in arrears together with interest, the entry will be as follows:
 Note: If nothing is specified, there is no need to take the interest on calls in arrears account and record the above entry
Note: If nothing is specified, there is no need to take the interest on calls in arrears account and record the above entry
Example: Cronic Limited issued 10,000 equity shares of Rs. 10 each payable at Rs. 2.50 on application, Rs. 3 on allotment, Rs. 2 on first call, and the balance of Rs. 2.50 on second and final call. All the shares were fully subscribed and paid except of a shareholder having 100 shares who could not pay for second and final call. Give journal entries to record these transactions.
Ans:


Calls in Advance:
- Sometimes, shareholders pay part or all of the amount for calls that have not yet been made. This amount received from shareholders is called "Calls in Advance."
- The money received in advance is considered a liability for the company and is credited to the "Call in Advance Account."
- This amount will be adjusted towards the payment of calls when they become due.
- According to Table F of the Companies Act, interest on calls in advance can be paid at a rate not exceeding 12% per annum.
The following journal entry is recorded for the amount of calls received in advance.

On the due date of the calls, the amount of ‘Calls in Advance’ is adjusted by the following entry :

Balance in 'Calls in Advance' Account
- Shown under 'current liabilities' in the company's balance sheet.
- Listed as a sub-head 'others current liabilities.'
- Not added to the paid-up capital.
Interest on Calls in Advance
- 'Calls in Advance' is considered a liability, and the company may be obligated to pay interest on this amount if specified in the Articles of Association.
- The rate of interest is typically outlined in the Articles. If not specified, Table F applies, which sets the interest rate at a maximum of 12% per annum.
The accounting treatment of interest on Calls in Advance is as follows:

Over Subscription
- Over-subscription occurs when a company receives more applications for shares than it has available for public subscription. This is common with well-managed and financially strong companies.
- In such cases, the directors have three options to handle the situation:
- Accept some applications in full and reject others entirely.
- Make a pro-rata allotment to all applicants.
- Combine both approaches, which is the most common practice.
- The issue of over-subscription is resolved through the allotment of shares. From an accounting perspective, it is better to consider over-subscription within the broader context of application and allotment. This includes the receipt of application money, the amount due on allotment, and its receipt from shareholders.
- First Alternative: If directors choose to fully accept some applications and reject others entirely, the application money received from rejected applications is refunded in full. For instance, if a company invites applications for 20,000 shares and receives applications for 25,000 shares, the directors may reject 5,000 excess applications and refund their application money completely.
In this case, the journal entries on application and allotment will be as follows :

Second Alternative: Pro-rata Allotment
- When directors choose to allocate shares proportionately to all applicants (known as 'pro-rata' allotment), any excess application money received is typically adjusted against the amount due on allotment.
- If the excess application money exceeds the amount due on the allotment, the surplus may either be refunded or credited to calls in advance.
- For instance, if applications are invited for 20,000 shares but the total applications received are for 25,000 shares, and it is decided to allot shares in the ratio of 4:5 to all applicants, this represents a pro-rata allotment. The excess application money received for 5,000 shares would be adjusted towards the allotment amount for the 20,000 shares.
In this case, the journal entries on application and allotment will be as follows.

Third Alternative:
- When applications for certain shares are rejected outright, a pro-rata allotment is made to the remaining applicants.
- The money from rejected applications is refunded.
- The excess application money received from applicants who receive a pro-rata allotment is adjusted towards the amount due on the allotment of shares.
Under Subscription
- This occurs when the number of shares applied for is less than the number of shares offered for subscription.
- For instance, if a company offers 2 lakh shares to the public but only receives applications for 1,90,000 shares, it is considered under subscription.
- In such cases, the allotment will be confirmed for the number of shares applied for (1,90,000 in this example), and the necessary accounting entries will be made accordingly.
- However, it is crucial to ensure that the company has received the minimum subscription as required.
- If the minimum subscription is not met, the company is obligated to refund the entire subscription amount received.
Issue of Shares at a Premium
- Shares of financially strong and well-managed companies are often issued at a premium, meaning at an amount greater than the nominal or par value. For example, if a share with a nominal value of Rs. 100 is issued at Rs. 105, it is issued at a premium of 5 percent.
- When shares are issued at a premium, the premium amount can be called at any stage during the issue process. However, it is typically called along with the amount due on allotment, sometimes with the application money, and rarely with the call money.
- The premium amount is credited to a separate account known as the 'Securities Premium Account.' This account is shown under the 'Equity and Liabilities' section of the company’s balance sheet, specifically under 'Reserves and Surpluses.'
- The funds in the Securities Premium Account can only be used for specific purposes, including:
(a) Issuing fully paid bonus shares up to the extent of unissued share capital.
(b) Writing off the preliminary expenses of the company.
(c) Writing off expenses, commission paid, or discount allowed on any securities of the company.
(d) Paying premium on the redemption of preference shares or debentures of the company.
(e) Buying back its own shares (i.e., share buyback).

The journal entries for shares issued at a premium are as follows:

Example: Jupiter Company Limited issued 35,000 equity shares of Rs. 10 each at a premium of Rs.2 payable as follows:
On Application - Rs. 3
On Allotment - Rs. 5 (including premium)
Balance on First and Final Call
The issue was fully subscribed. All the money was duly received.
Record journal entries in the books of the Company.
Ans:

Issue of Shares at a Discount
- Shares can sometimes be issued at a discount, meaning at a price lower than their nominal or par value.
- The difference between the nominal value and the issue price represents the discount on the share issue.
- For example, if a share with a nominal value of Rs. 100 is issued at Rs. 98, it is issued at a discount of 2%.
- Generally, companies are not allowed to issue shares at a discount.
- Exceptions include cases like the reissue of forfeited shares and the issuance of sweat equity shares.
Issue of Shares for Consideration other than Cash
- Sometimes, a company agrees to pay vendors for purchased assets by issuing fully paid shares instead of cash.
- In such cases, shares can be issued at par, at a premium, or at a discount.
- The number of shares issued depends on the issue price and the amount payable to the vendor.
The number of shares to be issued to the vendor will be
calculated as follows: For example, Rahul Limited purchased a building from Handa Limited for
For example, Rahul Limited purchased a building from Handa Limited for
Rs.5,40,000 and the payment is to be made by the issue of shares of Rs.100
each. The number of shares to be issued shall be worked out as follows in different
situations:
The journal entries recorded for the shares issued for consideration other than cash in above situations will be as follows :

Private Placement of Shares
- According to the Companies Act, 2013 (Section 42), Private Placement refers to the offer or invitation to subscribe for securities to a specific group of individuals through a private placement offer letter.
Employees Stock Option Plan (ESOP)
- An Employees Stock Option Plan (ESOP) allows a company to offer its employees and employee directors the option to purchase shares at a price lower than the market value or fair value at a future date.
- ESOPs are considered a form of Sweat Equity, which is a broader category.
- When issuing options, a company must meet certain conditions:
1. Shares must be of the same class as those already issued.
2. A special resolution must authorize the issuance.
3. The resolution should specify details such as the number of shares, current market price, consideration, and the class of directors or employees eligible for the shares.
4. At least one year must have passed since the company commenced business.
5. Issuance must comply with SEBI regulations if the shares are listed.Important Terms of ESOP
- Grant: Refers to giving employees the option to subscribe to company shares at a predetermined price.
- Grant Date: The date of agreement between the company and employees regarding the terms of the ESOP.
- Vesting: The process of giving employees the right to apply for company shares.
- Vesting Date: The date when employees become entitled to apply for shares after meeting vesting conditions.
- Vesting Period: The duration between the grant date and the date when all vesting conditions must be met.
- Exercise: The act of applying for shares against the vested option.
- Exercise Period: The timeframe after vesting during which employees must exercise their right to apply for shares.
- Exercise Price: The price payable by employees to exercise the option under the ESOP.
- Value of Option: The difference between the market price and the issue price of the security.
Forfeiture of Shares
- If some shareholders do not pay one or more instalments, such as allotment money or call money, the company has the right to forfeit their shares.
- This means the company cancels the allotment and keeps the amount already received.
- The company’s articles, often based on Table F, allow directors to forfeit shares for non-payment of calls.
- Directors must follow a specific procedure for this.
- When shares are forfeited, all accounting entries related to the forfeited shares, except for those related to the premium, must be reversed.
- The share capital account is debited with the called-up amount for the forfeited shares.
- The respective unpaid calls accounts or calls in arrears account is credited with the amount already received.

Thus, the journal entry will be as follows:
(a) Forfeiture of Shares issued at Par:

- When shares are forfeited, all entries related to those shares must be reversed, except for any entry related to share premium received. - The share capital is debited to the extent of called-up capital and credited to:
(i) Respective unpaid calls account (i.e., calls in arrears)
(ii) Share forfeiture account with the amount already received on shares. - The balance in the shares forfeited account is added to the total paid-up capital of the company under the head ‘Share Capital’ in the Balance Sheet, under the title ‘Equity and Liabilities,’ until the forfeited shares are reissued.
Example: Honda Limited issued 10,000 equity shares of 100 each payable as follows: Rs. 20 on application, Rs. 30 on allotment, Rs. 20 on first call and Rs. 30 on second and final calls 10,000 shares were applied for and allotted. All money due was received with the exception of both calls on 300 shares held by Supriya. These shares were forfeited. Give necessary journal entries.
Ans: 

Forfeiture of Shares Issued at a Premium:
- If shares are issued at a premium and the premium has been fully realized, but some shares are forfeited due to non-payment of call money, the accounting treatment for forfeiture is similar to that of shares issued at par.
- When forfeiting shares issued at a premium, it's crucial to note that the securities premium account should not be debited at the time of forfeiture if the premium has been received for the forfeited shares.
- The amount of forfeiture should be calculated excluding the premium amount.
- However, if the premium amount has not been received, either wholly or partially, for the forfeited shares, the Securities Premium Reserve Account will be debited along with the Share Capital Account at the time of forfeiture.
- This situation typically arises when the amount due on allotment has not been received.
Thus, the journal entry to record the forfeiture of shares issued at a premium on which the premium has not been fully received will be :


Example: Sahil, a share holder, failed to pay the money for second and final call of Rs. 20 on 1,000 shares issued to him at Rs. 120 (face value of Rs. 100 per share). His shares were forfeited after the second and final call. Give the necessary journal entry for forefeiture of the shares.
Ans: 
Reissue of Forfeited Shares:
- Directors have the option to either cancel or reissue forfeited shares. In most instances, they choose to reissue these shares.
- Forfeited shares can be reissued as fully paid at par, premium, or discount. However, it's important to note that the discount on reissue cannot exceed the amount received on the forfeited shares at the time of the initial issue.
- The discount allowed on the reissue of forfeited shares should be debited to the 'Forfeited Share Account.'
- Any remaining balance in the Share Forfeited Account related to reissued shares should be treated as capital profit and transferred to the Capital Reserve Account.
- For example, if a company forfeits 200 shares of Rs. 10 each, with Rs. 600 received, it can allow a maximum discount of Rs. 600 on their reissue.
- If the company reissues these shares for Rs. 1,800 as fully paid, the necessary journal entry will be made to reflect this transaction.

This shall leave a balance of Rs. 400 in the share forfeited account which should be transferred to the Capital Reserve Account by recording the following journal entry:
- It's important to understand that capital profit only occurs from the reissued forfeited shares, not from all forfeited shares.
- When only a portion of the forfeited shares is reissued, the entire balance of the share forfeiture account cannot be transferred to the capital reserve.
- In this case, only the proportionate amount of the balance related to the reissued forfeited shares should be moved to the capital reserve.
- This ensures that the remaining balance in the share forfeiture account reflects the amount forfeited on shares that have not yet been reissued.
Example: The director of Poly Plastic Limited resolved that 200 equity shares of Rs.100 each be forfeited for non-payment of the second and final call of Rs.30 per share. Out of these, 150 shares were re-issued at Rs.60 per share to Mohit. Show the necessary journal entries.
Ans:

- Body Corporate:. company is created following the laws in force at the time. In India, companies are typically established and registered under the Companies Act, except for banks and insurance firms, which have separate legislation.
- Separate Legal Entity:. company is recognised as a separate legal entity, distinct from its members. It can own and manage various types of property, enter contracts, and even maintain a bank account in its own name.
- Limited Liability: The members of a company have their liability limited to the unpaid amount of their shares. For companies limited by guarantee, members' liability is confined to the amount they guaranteed if the company is wound up.
- Perpetual Succession: As an artificial person created by law, a company continues to exist regardless of changes in its membership. It can only be dissolved by legal means, and the death, mental incapacity, or insolvency of any member does not affect the company's existence.
- Common Seal: As an artificial entity, a company cannot sign documents itself, so it must have a common seal, which acts as its official signature. Any document without this seal is not legally binding on the company.
- Transferability of Shares: The shares of a public limited company can be transferred freely. Approval from the company or consent from other members is not required for share transfers, though the company's Articles may specify the process for such transfers.
- May Sue or be Sued:. company, recognised as a legal person, can enter contracts and enforce its rights. It can initiate or face lawsuits in its own name if there is a breach of contract.
|
42 videos|199 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Accounting for Share Capital Chapter Notes - Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the main features of a company? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of companies? |  |
| 3. What is share capital, and why is it important for a company? |  |
| 4. What are the different classes of shares that a company can issue? |  |
| 5. What is the process of forfeiture of shares, and under what circumstances can it occur? |  |





















