Q1: Which of the following differential equation has as one of its particular solution?
as one of its particular solution?
A. 
B. 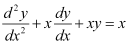
C. 
D. 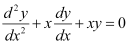
Ans: The given equation of curve is y = x.
Differentiating with respect to x, we get: 
Again, differentiating with respect to x, we get: 
Now, on substituting the values of y,  from equation (1) and (2) in each of the given alternatives, we find that only the differential equation given in alternative C is correct.
from equation (1) and (2) in each of the given alternatives, we find that only the differential equation given in alternative C is correct.
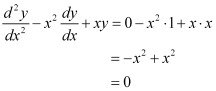
Hence, the correct answer is C.
Q2: 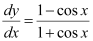
Ans: The given differential equation is:
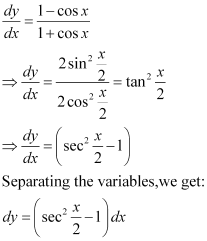
Now, integrating both sides of this equation, we get:
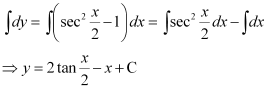
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q3: 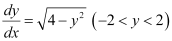
Ans: The given differential equation is:
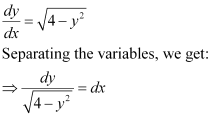
Now, integrating both sides of this equation, we get:
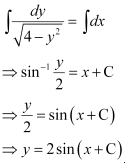
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q4: 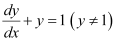
Ans: The given differential equation is:
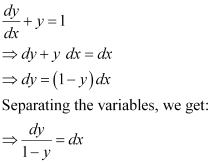
Now, integrating both sides, we get:
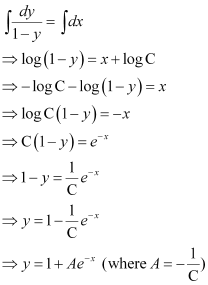
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q5: 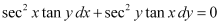
Ans: The given differential equation is:
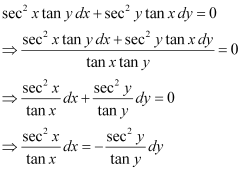
Integrating both sides of this equation, we get:
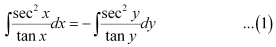
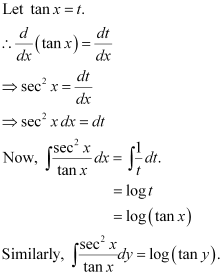
Substituting these values in equation (1), we get:
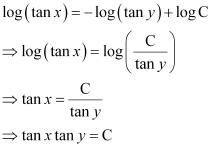
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q6: 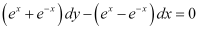
Ans: The given differential equation is:
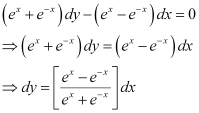
Integrating both sides of this equation, we get:
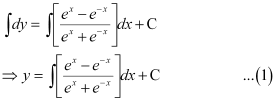
Let (ex e–x) = t.
Differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get:
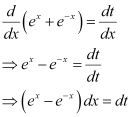
Substituting this value in equation (1), we get:
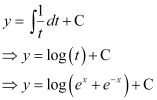
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q7: 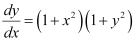
Ans: The given differential equation is:
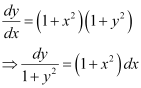
Integrating both sides of this equation, we get:
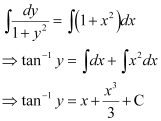
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q8: 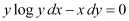
Ans: The given differential equation is:
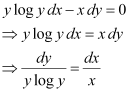
Integrating both sides, we get:
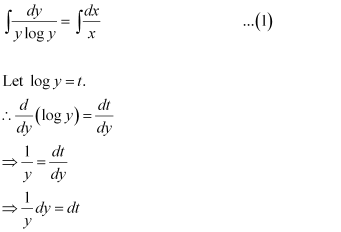
Substituting this value in equation (1), we get:
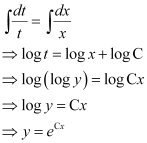
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q9: 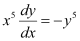
Ans: The given differential equation is:
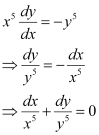
Integrating both sides, we get:
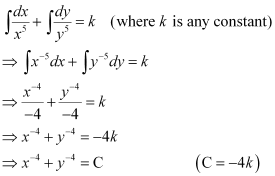
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q10: 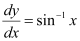
Ans: The given differential equation is:
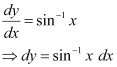
Integrating both sides, we get:
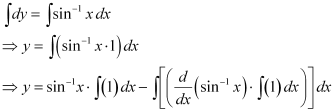
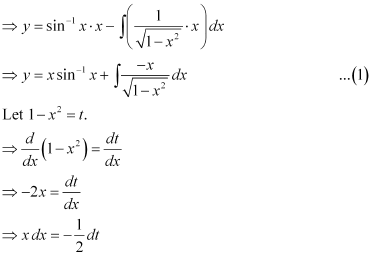
Substituting this value in equation (1), we get:
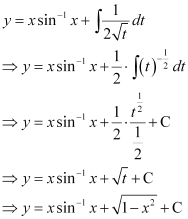
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q11: 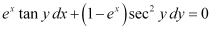
Ans: The given differential equation is:
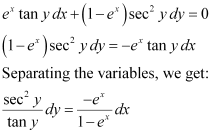
Integrating both sides, we get:
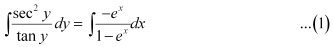
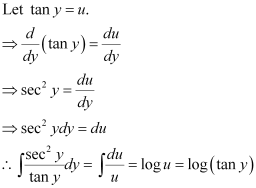
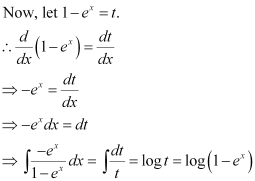
Substituting the values of  in equation (1), we get:
in equation (1), we get:
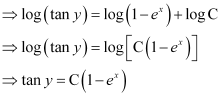
This is the required general solution of the given differential equation.
Q12: 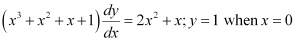
Ans: The given differential equation is:
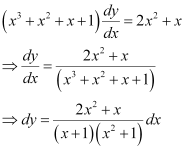
Integrating both sides, we get:
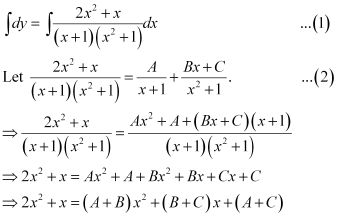
Comparing the coefficients of x2 and x, we get:
A + B = 2
B + C = 1
A + C = 0
Solving these equations, we get:
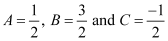
Substituting the values of A, B, and C in equation (2), we get:
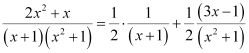
Therefore, equation (1) becomes:
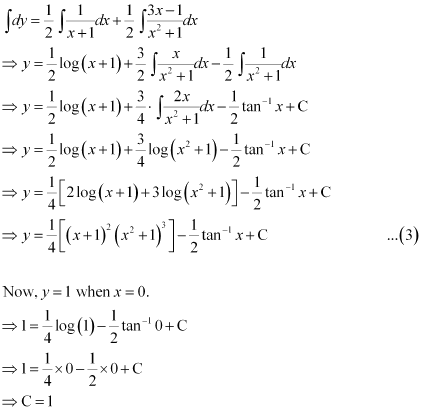
Substituting C = 1 in equation (3), we get:
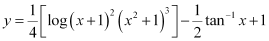
Q13: 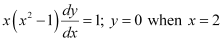
Ans:
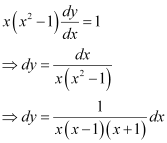
Integrating both sides, we get:
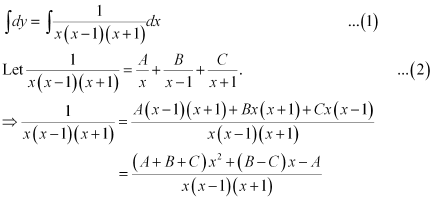
Comparing the coefficients of x2, x, and constant, we get:
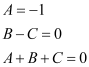
Solving these equations, we get 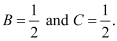
Substituting the values of A, B, and C in equation (2), we get:
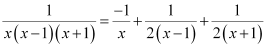
Therefore, equation (1) becomes:
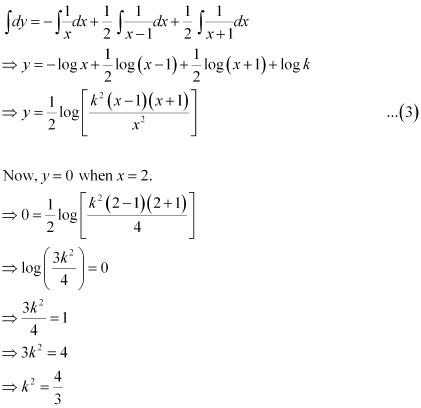
Substituting the value of k2 in equation (3), we get:
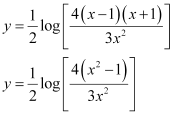
Q14: 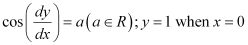
Ans:
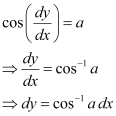
Integrating both sides, we get:
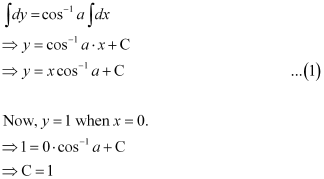
Substituting C = 1 in equation (1), we get:
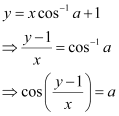
Q15: 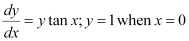
Ans:
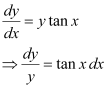
Integrating both sides, we get:
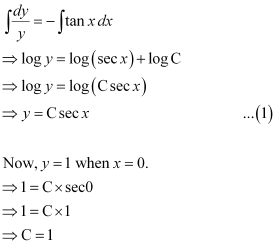
Substituting C = 1 in equation (1), we get:
y = sec x
Q16: Find the equation of a curve passing through the point (0, 0) and whose differential equation is .
.
Ans: The differential equation of the curve is:
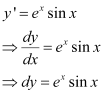
Integrating both sides, we get:

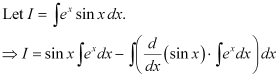
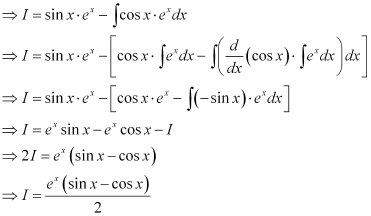
Substituting this value in equation (1), we get:
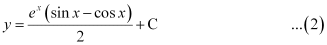
Now, the curve passes through point (0, 0).
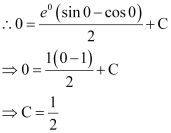
Substituting  in equation (2), we get:
in equation (2), we get:
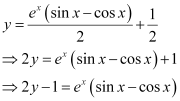
Hence, the required equation of the curve is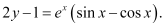
Q17: For the differential equation  find the solution curve passing through the point (1, –1).
find the solution curve passing through the point (1, –1).
Ans: The differential equation of the given curve is:
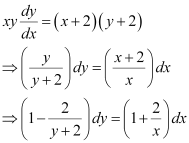
Integrating both sides, we get:
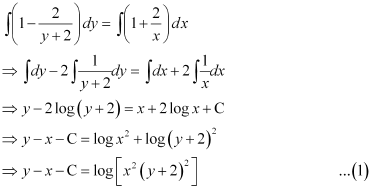
Now, the curve passes through point (1, –1).
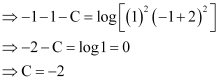
Substituting C = –2 in equation (1), we get:
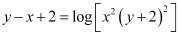
This is the required solution of the given curve.
Q18: Find the equation of a curve passing through the point (0, –2) given that at any point  on the curve, the product of the slope of its tangent and y-coordinate of the point is equal to the x-coordinate of the point.
on the curve, the product of the slope of its tangent and y-coordinate of the point is equal to the x-coordinate of the point.
Ans: Let x and y be the x-coordinate and y-coordinate of the curve respectively.
We know that the slope of a tangent to the curve in the coordinate axis is given by the relation,
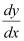
According to the given information, we get:
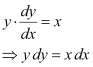
Integrating both sides, we get:
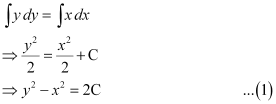
Now, the curve passes through point (0, –2).
∴ (–2)2 – 02 = 2C
⇒ 2C = 4
Substituting 2C = 4 in equation (1), we get:
y2 – x2 = 4
This is the required equation of the curve.
Q19: At any point (x, y) of a curve, the slope of the tangent is twice the slope of the line segment joining the point of contact to the point (–4, –3). Find the equation of the curve given that it passes through (–2, 1).
Ans: It is given that (x, y) is the point of contact of the curve and its tangent.
The slope (m1) of the line segment joining (x, y) and (–4, –3) is 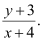
We know that the slope of the tangent to the curve is given by the relation,
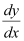

According to the given information:
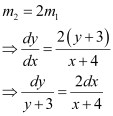
Integrating both sides, we get:
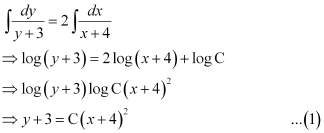
This is the general equation of the curve.
It is given that it passes through point (–2, 1).
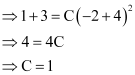
Substituting C = 1 in equation (1), we get:
y + 3 = (x + 4)2
This is the required equation of the curve.
Q20: The volume of spherical balloon being inflated changes at a constant rate. If initially its radius is 3 units and after 3 seconds it is 6 units. Find the radius of balloon after t seconds.
Ans: Let the rate of change of the volume of the balloon be k (where k is a constant).

Integrating both sides, we get:
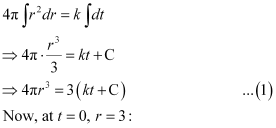
⇒ 4π × 33 = 3 (k × 0 C)
⇒ 108π = 3C
⇒ C = 36π
At t = 3, r = 6:
⇒ 4π × 63 = 3 (k × 3 + C)
⇒ 864π = 3 (3k + 36π)
⇒ 3k = –288π – 36π = 252π
⇒ k = 84π
Substituting the values of k and C in equation (1), we get:
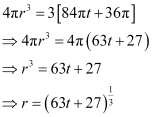
Thus, the radius of the balloon after t seconds is .
.
Q21: In a bank, principal increases continuously at the rate of r% per year. Find the value of r if Rs 100 doubles itself in 10 years (loge 2 = 0.6931).
Ans: - Let p, t, and r represent the principal, time, and rate of interest respectively.
It is given that the principal increases continuously at the rate of r% per year.
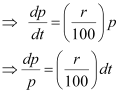
Integrating both sides, we get:
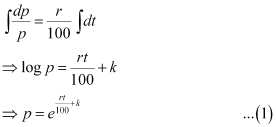
It is given that when t = 0, p = 100.
⇒ 100 = ek … (2)
Now, if t = 10, then p = 2 × 100 = 200.
Therefore, equation (1) becomes:
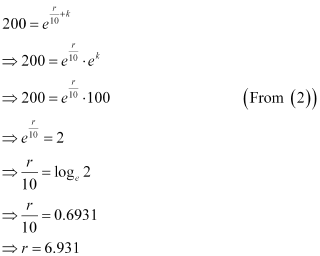
Hence, the value of r is 6.93%.
Q22: In a bank, principal increases continuously at the rate of 5% per year. An amount of Rs 1000 is deposited with this bank, how much will it worth after 10 years .
.
Ans: Let p and t be the principal and time respectively.
It is given that the principal increases continuously at the rate of 5% per year.
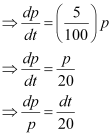
Integrating both sides, we get:
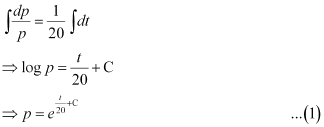
Now, when t = 0, p = 1000.
⇒ 1000 = eC … (2)
At t = 10, equation (1) becomes:
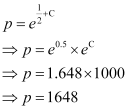
Hence, after 10 years the amount will worth Rs 1648.
Q23: In a culture, the bacteria count is 1,00,000. The number is increased by 10% in 2 hours. In how many hours will the count reach 2,00,000, if the rate of growth of bacteria is proportional to the number present?
Ans: Let y be the number of bacteria at any instant t.
It is given that the rate of growth of the bacteria is proportional to the number present.
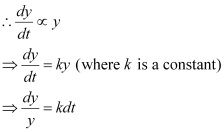
Integrating both sides, we get:

Let y0 be the number of bacteria at t = 0.
⇒ log y0 = C
Substituting the value of C in equation (1), we get:
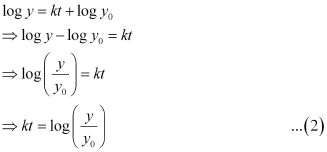
Also, it is given that the number of bacteria increases by 10% in 2 hours.

Substituting this value in equation (2), we get:
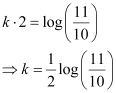
Therefore, equation (2) becomes:
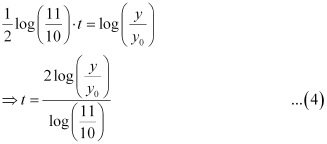
Now, let the time when the number of bacteria increases from 100000 to 200000 be t1.
⇒ y = 2y0 at t = t1
From equation (4), we get:
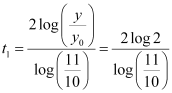
Hence, in  hours the number of bacteria increases from 100000 to 200000.
hours the number of bacteria increases from 100000 to 200000.
Q24: The general solution of the differential equation 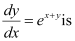
A. 
B. 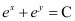
C. 
D. 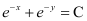
Ans:
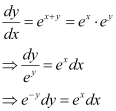
Integrating both sides, we get:
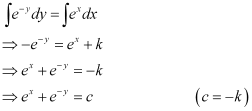
Hence, the correct answer is A.
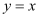 as one of its particular solution?
as one of its particular solution?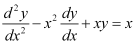
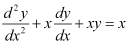
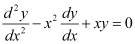
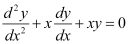


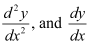 from equation (1) and (2) in each of the given alternatives, we find that only the differential equation given in alternative C is correct.
from equation (1) and (2) in each of the given alternatives, we find that only the differential equation given in alternative C is correct.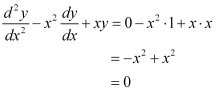
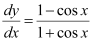
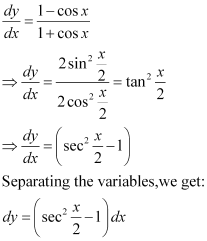
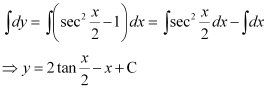
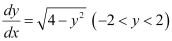
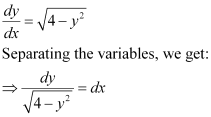
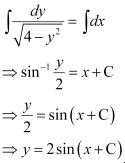
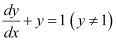
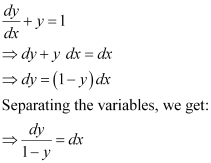
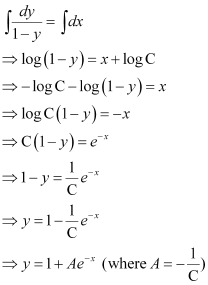
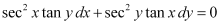
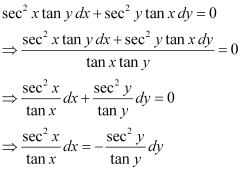
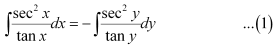
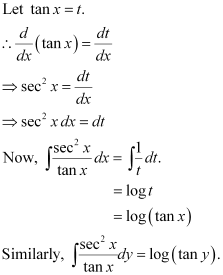
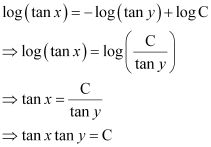
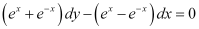
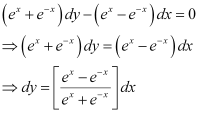
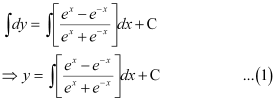
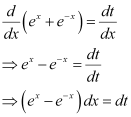
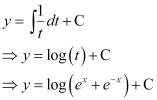




















 in equation (1), we get:
in equation (1), we get:






















 .
.





 in equation (2), we get:
in equation (2), we get:

 find the solution curve passing through the point (1, –1).
find the solution curve passing through the point (1, –1).



 on the curve, the product of the slope of its tangent and y-coordinate of the point is equal to the x-coordinate of the point.
on the curve, the product of the slope of its tangent and y-coordinate of the point is equal to the x-coordinate of the point.











 .
.


 .
.









 hours the number of bacteria increases from 100000 to 200000.
hours the number of bacteria increases from 100000 to 200000.