Buckling and Stability & Euler Load - Columns and Struts, Strength of Materials | Strength of Material Notes - Agricultural Engg - Agricultural Engineering PDF Download
Buckling and Stability
Lateral bending of a straight slender member from its longitudinal position due to compression is referred to as buckling. Buckling is encountered in many practical columns. Load at which buckling occurs depends on many factors such as material strength, geometry of the column, end conditions etc. In this module we will learn different methods for determining buckling load of slender columns.
Euler Load for Columns with Pinned End
Assumptions
- Member is prismatic and perfectly straight.
- The material is homogeneous and linear elastic.
- One end of the member is hinged and the other is restrained against horizontal movement as shown in Figure 22.2a.
- The compressive load is acting along the longitudinal axis of the member.
- Lateral deformation of the member is small.
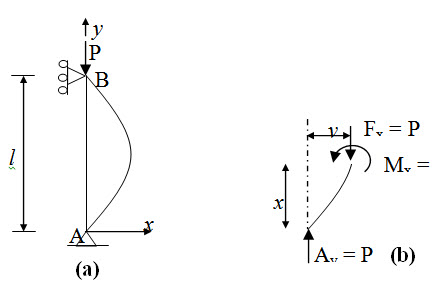 Fig. 22.2.
Fig. 22.2.
From equation of elastic line (lesson 3), we have,.
\[{{{d^2}y} \over {d{x^2}}}=-{{{M_x}} \over {EI}}\] (22.1)
\[\Rightarrow {{{d^2}y} \over {d{x^2}}} + {P \over {EI}}y = 0\] (22.2)
Equation (22.2) is a second order linear differential equation with constant coefficients. Boundary conditions are,
\[y(x = 0) = y(x = l) = 0\] (22.3)
Equations (22.2) – (22.3) define a linear eigenvalue problem, whose solution may be written as,
\[y = A\cos kx + B\sin kx\] (22.4)
where, \[{k^2} = {P / {EI}}\] . Constants A and B may be determined from the boundary conditions (Equation 22.3),
Imposing y(x = 0) = 0 we have A = 0.
Imposing y(x = l) = 0 we have,
\[B\sin kl = 0\] (22.5)
As B ≠ 0 , \[\sin kl = 0 \Rightarrow kl = n\pi \]
where,
Hence,
\[{k^2} = {P \over {EI}} = {{{n^2}{\pi ^2}} \over {{l^2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {P_{crn}} = {{{n^2}{\pi ^2}} \over {{l^2}}}EI\] (22.6)
The eigenvalues \[{P_{crn}}\] are the critical loads at which buckling takes place in different modes which are given by,
\[y = B\sin {{n\pi x} \over l}\] (22.7)
The smallest Euler buckling load is (n = 1),
\[{P_E} = {{{\pi ^2}EI} \over {{l^2}}}\] (22.8)
3 Euler Load for Columns with Different End Conditions
Equation (22.8) may be recast as,
\[{P_E} = {{{\pi ^2}EI} \over {l_{eff}^2}}\] (22.8)
where, leff is the effective length of the column. For column with both ends hinged, leff = l. Different end condition may increase or decrease the effective length and consequently change the critical buckling load. Effective lengths of column with different end conditions are given below.
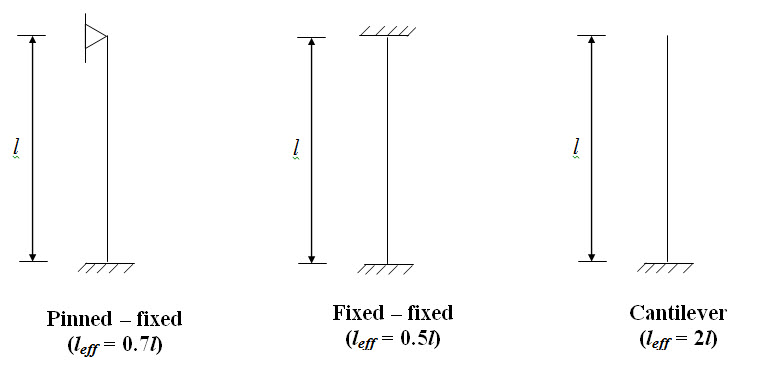 Fig. 22.3.
Fig. 22.3.
FAQs on Buckling and Stability & Euler Load - Columns and Struts, Strength of Materials - Strength of Material Notes - Agricultural Engg - Agricultural Engineering
| 1. What is buckling and stability in the context of columns and struts? |  |
| 2. How is Euler's load related to columns and struts? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the buckling and stability of columns and struts? |  |
| 4. What are the consequences of column or strut buckling? |  |
| 5. How can the strength of columns and struts be improved to prevent buckling? |  |

















