Law of Demand - Market Demand Analysis, Business Economics & Finance | Business Economics & Finance - B Com PDF Download
Introduction to the Law of Demand:
The law of demand expresses a relationship between the quantity demanded and its price. It may be defined in Marshall’s words as “the amount demanded increases with a fall in price, and diminishes with a rise in price”. Thus it expresses an inverse relation between price and demand. The law refers to the direction in which quantity demanded changes with a change in price.
On the figure, it is represented by the slope of the demand curve which is normally negative throughout its length. The inverse price- demand relationship is based on other things remaining equal. This phrase points towards certain important assumptions on which this law is based.
Assumptions of the Law of Demand:
These assumptions are:
(i) There is no change in the tastes and preferences of the consumer;
(ii) The income of the consumer remains constant;
(iii) There is no change in customs;
(iv) The commodity to be used should not confer distinction on the consumer;
(v) There should not be any substitutes of the commodity;
(vi) There should not be any change in the prices of other products;
(vii) There should not be any possibility of change in the price of the product being used;
(viii) There should not be any change in the quality of the product; and
(ix) The habits of the consumers should remain unchanged. Given these conditions, the law of demand operates. If there is change even in one of these conditions, it will stop operating.
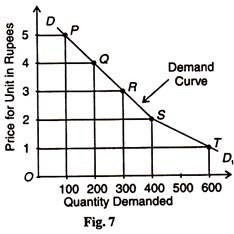
Given these assumptions, the law of demand is explained in terms of Table 3 and Figure 7.
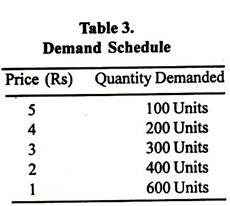
The above table shows that when the price of say, orange, is Rs. 5 per unit, 100 units are demanded. If the price falls to Rs.4, the demand increases to 200 units. Similarly, when the price declines to Re.1, the demand increases to 600 units. On the contrary, as the price increases from Re. 1, the demand continues to decline from 600 units.
In the figure, point P of the demand curve DD1 shows demand for 100 units at the Rs. 5. As the price falls to Rs. 4, Rs. 3, Rs. 2 and Re. 1, the demand rises to 200, 300, 400 and 600 units respectively. This is clear from points Q, R, S, and T. Thus, the demand curve DD1 shows increase in demand of orange when its price falls. This indicates the inverse relation between price and demand.
Exceptions to the Law of Demand:
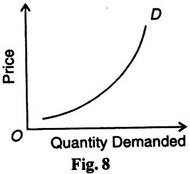
In certain cases, the demand curve slopes up from left to right, i.e., it has a positive slope. Under certain circumstances, consumers buy more when the price of a commodity rises, and less when price falls, as shown by the D curve in Figure 8. Many causes are attributed to an upward sloping demand curve.
(i) War:
If shortage is feared in anticipation of war, people may start buying for building stocks or for hoarding even when the price rises.
(ii) Depression:
During a depression, the prices of commodities are very low and the demand for them is also less. This is because of the lack of purchasing power with consumers.
(iii) Giffen Paradox:
If a commodity happens to be a necessity of life like wheat and its price goes up, consumers are forced to curtail the consumption of more expensive foods like meat and fish, and wheat being still the cheapest food they will consume more of it. The Marshallian example is applicable to developed economies.
In the case of an underdeveloped economy, with the fall in the price of an inferior commodity like maize, consumers will start consuming more of the superior commodity like wheat. As a result, the demand for maize will fall. This is what Marshall called the Giffen Paradox which makes the demand curve to have a positive slope.
(iv) Demonstration Effect:
If consumers are affected by the principle of conspicuous consumption or demonstration effect, they will like to buy more of those commodities which confer distinction on the possessor, when their prices rise. On the other hand, with the fall in the prices of such articles, their demand falls, as is the case with diamonds.
(v) Ignorance Effect:
Consumers buy more at a higher price under the influence of the “ignorance effect”, where a commodity may be mistaken for some other commodity, due to deceptive packing, label, etc.
(vi) Speculation:
Marshall mentions speculation as one of the important exceptions to the downward sloping demand curve. According to him, the law of demand does not apply to the demand in a campaign between groups of speculators. When a group unloads a great quantity of a thing on to the market, the price falls and the other group begins buying it. When it has raised the price of the thing, it arranges to sell a great deal quietly. Thus when price rises, demand also increases.
(vii) Necessities of Life:
Normally, the law of demand does not apply on necessities of life such as food, cloth etc. Even the price of these goods increases, the consumer does not reduce their demand. Rather, he purchases them even the prices of these goods increase often by reducing the demand for comfortable goods. This is also a reason that the demand curve slopes upwards to the right.
|
69 videos|101 docs|23 tests
|
FAQs on Law of Demand - Market Demand Analysis, Business Economics & Finance - Business Economics & Finance - B Com
| 1. What is the law of demand in economics? |  |
| 2. How is market demand analyzed in business economics? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of market demand analysis for businesses? |  |
| 4. How does the law of demand impact the pricing strategy of businesses? |  |
| 5. What are some factors that can influence market demand? |  |





















