Theory & Procedure, Role of Carbon Dioxide During Respiration | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Objective
Our objective is to show experimentally that carbon dioxide is given out during respiration.
Theory
Respiration is a biochemical process during which simple carbohydrates, like glucose, are broken down to release energy. Every cell of a living organism- man, animal and plant, respires.
Respiration in plants can be studied in moist germinating seeds that release carbon dioxide (CO2) during respiration. The seeds are kept in an air tight conical flask. A small test tube containing potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution is placed in the flask. Potassium hydroxide absorbs carbon dioxide released by the seeds and a partial vacuum is created in the flask as a result. This causes the water level in the delivery tube to rise.
Respiration in humans can be studied with lime water. Carbon dioxide reacts with lime water on respiration to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3) that turns lime water milky. Freshly prepared lime water is taken in a boiling tube and a cork with two glass tubes is inserted into the cork. The tip of one of the glass tube dips in the lime water and air is blown with full force through this glass tube. The bubbles of the air breathed out gradually turn lime water milky, showing that carbon dioxide is produced in human respiration.
Respiration
Respiration is the process during which organic food, mainly glucose that is present in the cell, breaks down into simpler substances and liberates carbon dioxide and energy. The energy released during respiration is chemical energy. There are two types of respiration- aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic means ‘with air’. This type of respiration requires oxygen, so it is called aerobic respiration. During aerobic respiration, complete oxidation of carbohydrates takes place. Glucose is broken down by oxygen to release energy, while carbon dioxide and water are the by-products of the reaction. The released energy is used to make a special energy molecule called Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is where the energy is stored for later use by the body. Aerobic respiration occurs in plants as well as animals and takes place in the mitochondria.
The word equation for aerobic respiration is:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
The chemical equation is:
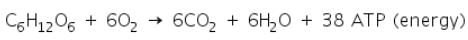
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic means without air. Sometimes there is not enough oxygen around for animals and plants to respire, but they still need energy to survive, so they carry out respiration in the absence of oxygen to produce the energy they require. As the respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen, incomplete oxidation of food occurs and much less energy is released. However, carbon dioxide is still produced. This is called anaerobic respiration and the process occurs in the cytoplasm.
The word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants is:

The chemical equation is:
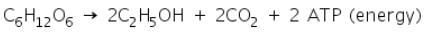
The word equation for anaerobic respiration in animals is:

The chemical equation is:
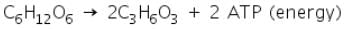
Factors Effecting Respiration
Here are some of the few factors that affect the rate of respiration.
- Temperature- At a very high temperature, the rate of respiration decreases with time and at very low temperature, the respiration rate is insignificant. Optimum temperature for respiration is 20 - 30oC.
- Carbon dioxide concentration - Increase in CO2 concentration and absence of O2 adversely affects the rate of aerobic respiration.
- Light- Light controls respiration by raising the temperature of an organism.
- Water- The respiratory rate increases with the increase in water content of the respiring organism.
Learning Outcomes
- Students understand the terms respiration, aerobic and anaerobic respiration and ATP.
- Students understand the two types of respiration.
- Students understand the factors affecting the rate of respiration.
- Students do the experiment better in the real lab having gone through the animation and simulation.
Respiration in Plants
Materials Required:

Real Lab Procedure
- Using a spatula, place about 30 germinating bean seeds in a conical flask.
- Pour 4ml of potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution into a measuring cylinder.
- Transfer the KOH solution from the measuring cylinder into a small test tube.
- Tie a cotton thread around the neck of the test tube.
- Suspend the test tube in the conical flask above the germinating seeds.
- Close the mouth of the conical flask with a cork.
- Insert one end of a delivery tube into the conical flask through the cork and dip the other in a beaker containing water.
- Take some Vaseline with your finger and apply this on the cork to make the apparatus air tight.
- Keep the apparatus undisturbed for two hours.
Observation
After two hours, you will see that the level of water has risen in the delivery tube at the end dipped in the beaker of water.
Conclusion
The germinating seeds in the conical flask release CO2 during respiration, which is absorbed by the KOH solution kept in the small test tube. This creates a partial vacuum in the flask that forces the water up the delivery tube. Thus, it proves that germinating seeds produce carbon dioxide during respiration.
Precautions:
- Germination in seeds can be done by soaking them overnight and then keeping them in moist cotton wool for 1-2 days.
- Freshly prepared potassium hydroxide should be used.
- The apparatus should be air tight to prevent escape of CO2.
Respiration in animals
Materials Required:
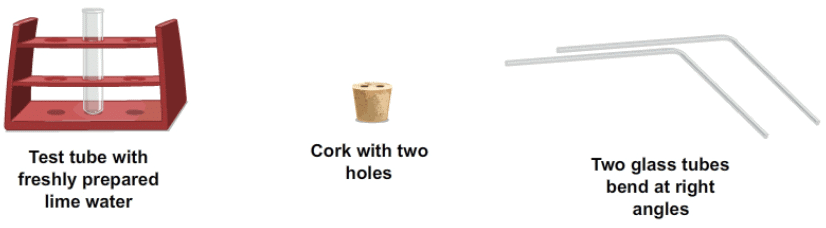
Real Lab Procedure
- Pour freshly prepared lime water into a test tube so that it is 3/4 full.
- Take a cork with two holes and fix it into the mouth of the test tube.
- Insert the glass tubes, let us name them A and B, into the test tube through the cork, such that end of the glass tube A dips in the lime water.
- Breathe out air with full force by putting your mouth at the end of tube A.
- Continue doing this vigorously for at least 1 minute.
Observation
The bubbles of the air breathed out gradually turn the lime water milky.
Conclusion
The only gas that can turn lime water milky is carbon dioxide. When carbon dioxide reacts with lime water, it forms calcium carbonate (CaCO3), thus giving lime water its milky appearance. So, we can conclude that humans and animals give out CO2 during respiration.
Precautions
- Use freshly prepared calcium carbonate solution.
- Breathe out air vigorously for at least 1 minute.
Simulator Procedure (as performed through the Online Labs)
You can select the test - respiration in animals or plants, by clicking on the corresponding icon - ‘Animals’ or ‘Plants’.
Respiration in Plants
- You can increase or decrease the number of seeds inside the beaker by moving the ‘Number of seeds’ slider to the right and left respectively.
- The same way, you can increase or decrease the temperature by moving the ‘Temperature’ slider to the right and left respectively.
- Click on the ‘Start’ button to start the experiment.
- You can observe that the level of water in the delivery tube rises at the end dipped in the beaker.
- A timer is shown and you need to wait till the timer stops.
- Click on the information icon to see the inference.
- You can redo the experiment by clicking on the ‘Reset’ button.
Respiration in Animals
To study respiration in a human being or a grasshopper, select your choice from the ‘Select the animal’ drop down list.
Respiration in the Grasshopper:
- You can increase or decrease the number of grasshoppers inside the beaker by moving the ‘Number of grasshoppers’ slider to the right and left respectively.
- The same way, you can increase or decrease the temperature by moving the ‘Temperature’ slider to the right and left respectively.
- Click on the ‘Start’ button to start the experiment.
- You can observe that the level of water in the delivery tube rises at the end dipped in the beaker.
- A timer is shown and you need to wait till the timer stops.
- Click on the information icon to see the inference.
- You can redo the experiment by clicking on the ‘Reset’ button.
Respiration in Human Beings:
- You can select the indicator - Lime water or BTB (Bromothymol Blue) from the ‘Select the indicator’ drop down list
- Click on the ‘Start’ button to start the experiment.
- A timer is shown and you need to wait till the timer stops.
- Observe the solution (indicator) in the test as the bubbles of air pass through the delivery tube.
- If the indicator chosen was lime water, it gradually turns milky, and if the chosen indicator was BTB (Bromothymol Blue), it turns green.
- You can redo the experiment by clicking on the ‘Reset’ button.
|
83 videos|438 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Theory & Procedure, Role of Carbon Dioxide During Respiration - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the role of carbon dioxide during respiration? |  |
| 2. How does carbon dioxide affect the pH of the blood during respiration? |  |
| 3. How is carbon dioxide transported in the blood during respiration? |  |
| 4. How does carbon dioxide regulate the rate of respiration? |  |
| 5. Can the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the body have harmful effects? |  |


















