Theory & Procedure, Potentiometer (Internal Resistance of a Cell) | Physics Class 12 PDF Download
Objective
To measure the internal resistance of a given primary cell using potentiometer.
Theory
Potentiometer
Potentiometer is a device used to measure the internal resistance of a cell, to compare the e.m.f. of two cells and potential difference across a resistor. It consists of a long wire of uniform cross sectional area and of 10 m in length. The material of wire should have a high resistivity and low temperature coefficient. The wires are stretched parallel to each other on a wooden board. The wires are joined in series by using thick copper strips. A metre scale is also attached on the wooden board.
It works on the principle that when a constant current flows through a wire of uniform cross sectional area, potential difference between its two points is directly proportional to the length of the wire between the two points.
Relation between e.m.f., potential difference, and internal resistance of a cell
If a cell of emf E and internal resistance r, connected to an external resistance R, then the circuit has the total resistance (R+r). The current I in the circuit is given by,
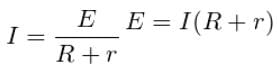
or
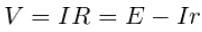
Hence,
This means, V is less than E by an amount equal to the fall of potential inside the cell due to its internal resistance.
From the above equation,
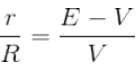
Or; The internal resistance of the cell,
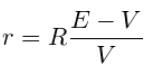
Using a potentiometer, we can adjust the rheostat to obtain the balancing lengths l1 and l2 of the potentiometer for open and closed circuits respectively.
Then, E= k l1 and V = k l2 ; where k is the potential gradient along the wire.
Now we can modify the equation for getting the internal resistance of the given cell, by using the above relations as;
Learning Outcomes
- Students get the idea of potentiometer apparatus and its parts.
- Students are able to construct circuits based on circuit diagrams.
- Students understand the different component used in the experiment.
Materials Required:
- Potentiometer
- Battery eliminator
- Two one way keys
- Rheostat of low resistance
- Galvanometer
- Two resistance boxes
- Leclanche cell
- Jockey
- Ammeter
- Connecting wires
Real lab Procedure
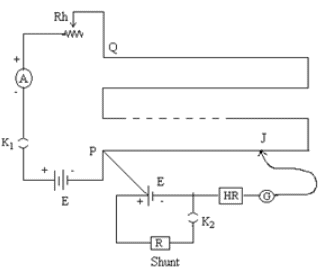
- Arrange the required materials on a table and make the connections as per the connection diagram.
- Tight the plugs of the resistance box.
- To test the connection, insert the key k1 and note the ammeter reading. Introduce a sufficiently high resistance on the resistance box (H.R). Place the jockey at the two end points of the wire. If the galvanometer shows opposite deflection, then the connections are correct.
- Without inserting the key k2, slide the jockey along the potentiometer wire and stops when null point is obtained.
- Measure the balancing length l1 between this point and the end P of the potentiometer.
- Now, introduce plugs in keys k1 and k2. Take out a small resistance from the resistance box R connected in parallel with the cell.
- Again slide the jockey along the potentiometer wire to obtain the null point. Measure the new balancing length l2 based on this point.
- Reduce the value of R successively and in each time, measure the balancing length.
- Keep the reading on the ammeter constant throughout the observation.
Simulator Procedure (as performed through the Online Labs)
- Select the primary cell form the drop down list.
- Select the rheostat resistance using the slider.
- To see the circuit diagram, click on the ‘Show circuit diagram’ check box seen inside the simulator window.
- Connections can be made as seen in the circuit diagram by clicking and dragging the mouse form one connecting terminal to the other connecting terminal of the devices to be connected.
- Once all connections are made, click and drag the key 1 to insert it into the switch.
- The ammeter shows a deflection.
- To check whether the connections are correct or not, drag the jockey and place it at the two end points of the wire. If the galvanometer shows opposite deflections, the connections are correct.
- To obtain the null point slide the jockey along the potentiometer wire.
- You can see the first balancing length in the popup.
- Select the desired shunt resistance from the resistance box.
- Click and drag the key 2 to insert it into the switch.
- Again slide the jockey along the potentiometer wire to obtain the null point.
- You can see the second balancing length in the popup.
- You can calculate the internal resistance for each set of balancing lengths.
- To verify your result click on the ‘Show result’ check box.
- To redo the experiment, click on the ‘Reset’ button.
|
127 videos|452 docs|99 tests
|
FAQs on Theory & Procedure, Potentiometer (Internal Resistance of a Cell) - Physics Class 12
| 1. What is a potentiometer and how is it used to measure internal resistance of a cell? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of using a potentiometer over other methods for measuring internal resistance of a cell? |  |
| 3. What factors can affect the accuracy of the measurement obtained using a potentiometer? |  |
| 4. How can one determine the precision of the measurement obtained using a potentiometer? |  |
| 5. What are some practical applications of measuring internal resistance of cells using a potentiometer? |  |

















