Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Notes > The MOT diagram of F2
The MOT diagram of F2 - Class 12 PDF Download
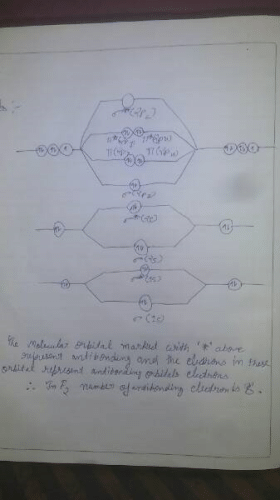
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Ref: https://edurev.in/question/496513/In-the-MOT-of-F2-molecule-number-of-electrons-occupying-antibonding-orbitals-areCorrect-answer-is-
 😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊☝☝☝☝☝☝☝☝☝👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆
😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃😃👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺☺😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊☝☝☝☝☝☝☝☝☝👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆FAQs on The MOT diagram of F2 - Class 12
| 1. What is the MOT diagram of F2 Class 12? |  |
| 2. How does the MOT diagram of F2 Class 12 explain the bonding in fluorine? |  |
In the MOT diagram of F2, the atomic orbitals of each fluorine atom, called 2p orbitals, combine to form molecular orbitals. The lower energy bonding molecular orbital (σ) is formed by constructive interference, resulting in a stable bond between the fluorine atoms. The higher energy anti-bonding molecular orbital (σ*) is formed by destructive interference, which weakens the bond. The electrons populate the bonding orbital first, making the molecule stable.
| 3. What are the energy levels represented in the MOT diagram of F2 Class 12? |  |
The MOT diagram of F2 Class 12 represents two energy levels: the bonding molecular orbital (σ) and the anti-bonding molecular orbital (σ*). The bonding orbital is lower in energy and contains the electrons that contribute to the stability and bonding between the fluorine atoms. The anti-bonding orbital is higher in energy and contains electrons that weaken the bond.
| 4. How does the MOT diagram of F2 Class 12 explain the stability of the molecule? |  |
The MOT diagram of F2 Class 12 explains the stability of the molecule by showing the population of electrons in the bonding molecular orbital. The electrons occupy the bonding orbital first, resulting in a stable bond between the fluorine atoms. The filling of the bonding orbital lowers the overall energy of the molecule and makes it more stable.
| 5. What is the significance of the MOT diagram of F2 Class 12 in understanding chemical reactions involving fluorine? |  |
The MOT diagram of F2 Class 12 is significant in understanding chemical reactions involving fluorine as it provides insights into the bonding and stability of the molecule. It helps in predicting the reactivity and behavior of fluorine in various reactions. By analyzing the energy levels and electron distribution, the MOT diagram allows us to understand how fluorine interacts with other atoms and molecules, leading to chemical reactions.
Related Searches




















