NEET Exam > NEET Notes > NCERT Exemplar & Revision Notes for NEET > Revision Notes: Heat Phenomena
Heat Phenomena Class 11 Notes Physics
- Heat:- Heat is the agent which produces in us the sensation of warmth and makes bodies hot. It is form of energy. The part of thermal energy which flows from one body to the other due to temperature difference is called heat.
- Nature of heat:-
(a) The weight of a body remains the same weather it is heated or cooled.
(b) Heat flows from higher to lower temperature
(c) In any exchange of heat, heat lost by the hot body is equal to the heat gained by the cold body.
(d) Substances generally expand when heated
(e) A certain amount of heat known as latent heat is required to change the state of a body from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas without any change in temperature. - Thermal Energy:- In accordance to dynamical theory of heat the sum total of translational, vibrational and rotational energies of the molecules of a system is called the thermal energy of the system .
- Unit of Heat:-
(a) Calorie (cal):- It is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water through 1ºC.
(b) Kilocalorie (kcal):- It is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kilo gram of water through 1ºC. - Temperature:- It is defined as the degree of hotness of a body.
- Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics:-
It states that the two systems (A and B) which are separately in equilibrium with a third system (C) must also be in equilibrium with each other.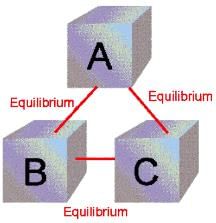
- Absoluter Zero of Temperature:-
(a) Charle’s law:- Vt = V0(1+ t/273)
(b) Gay Lussac’s law:- Pt = P0(1+ t/273)
(c) Absolute zero of temperature is defined as the temperature at which a gas has zero volume and exerts zero pressure. It is that temperature at which molecular motion ceases.
(d) C∝√T, C = √[c12 + c22 +…….+ cn2]/n - Absolute gas scale or absolute scale of temperature:- It is that scale of temperature whose zero (i.e. 0ºK) = -273ºC
A centigrade degree is exactly equal to the absolute or Kelvin’s degree. - Conversion of temperature from one scale to another:-
C/100 = (K-273)/100 = (F-32)/180 = Re/80 = (Rα-492)/180
Here C, K, F, Re and Rα are respectively, the temperatures of same both on centigrade, Kelvin, Fahrenheit, Reaumer and Rankin scale, respectively. - F = [(9/5)C ]+32
- K = C+273
- Linear Expansion (longitudinal expansion):-
When the expansion due to heating takes place only along one direction, the expansion is said to be one dimensional and linear.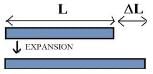
- Coefficient of linear expansion (α):- Coefficient of linear expansion of the material of a rod is defined as the change in length per unit length, at 0ºC, per degree centigrade rise of temperature.
α = lt-l0/l0t - Expansion in two dimensions (Superficial expansion):-
When the thermal expansion of a body is confined to a plane, it is to be two dimensional expansion or superficial expansion.
- Coefficient of superficial expansion (β):- It is defined as the change in area of the surface per unit area at 0ºC, per degree centigrade rise of temperature.
β = St-S0/S0t - Expansion in three dimensions (Cubical expansion/volume expansion):- When thermal expansion of the body takes place in space, it is said to be three dimensional expansion or cubical expansion.
- Coefficient of cubical expansion (γ):- Coefficient of cubical expansion is defined as the change in volume per unit volume, at 0ºC, per degree celsius rise of temperature .
γ = Vt-V0/V0t - Relation between expansion coefficients:-
(a) Relation between α and β:-
β = 2α
(b) Relation between α and γ:-
γ= 3α
(c) Relation between β and γ:-
γ = 3/2 β
(d) α : β : γ = 1:2:3 - Thermal expansion of liquids:-
(a) Co-efficient of apparent expansion (γa):- The coefficient of apparent expansion of a liquid is defined as the apparent (or observed) increase in volume, per unit volume of the liquid at 0ºC per degree celcius rise of temperature.
γa = apparent increase in volume/(original volume at 0ºC) × (rise of temperature)
(b) Co-efficient of real expansion (γr):- The coefficient of real expansion of a liquid is defined as the real increase in volume, per unit volume of the liquid at 0ºC per degree centigrade rise of temperature.
γa= real increase in volume/(original volume at 0ºC) × (rise of temperature) - Work and Heat:-
Whenever heat is conserved into work or work into heat, the quantity of energy disappearing in one form is equivalent to the quantity of energy appearing in the order.
W∝H or W = JH
Joule’s mechanical equivalent of heat is defined as the amount of work required to produce a unit quantity of heat.
J = W/H
Value of J:- J = 4.2×107 erg cal-1 = 4.2 J cal-1 - Specific heat capacity or specific heat (c):-
Specific heat capacity of a material is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of material through 1ºC.
c = Q/mΔT
Unit:- kcal kg-1K-1 or J kg-1K-1
Dimension:- M0L2T-2K-1 - Molar specific heat capacity(C):-
Molar specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram molecule of the substance through one degree centigrade.
(a) C = Mc (Here M is the molecular weight of the substance)
(b) C = 1/n (dQ/dT) - Heat Capacity or Thermal Capacity:-
It is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of body through 1ºC.
Q = mcΔT
If ΔT = 1ºC, Q = heat capacity = mc
Unit:- kcal K-1 or JK-1 - Water Equivalent:-
Water equivalent of a body is defined as the mass of water which gets heated through certain range of temperature by the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of body through same range of temperature.
w = mc
Water equivalent of a body is equal to the product of its mass and its specific heat. - Latent Heat:- When the state of matter changes, the heat absorbed or evolved is given by: Q = mL. Here L is called the latent heat.
(a) Specific latent heat of fusion (Lf):-
Specific latent heat of fusion of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to convert 1 gram of substance from solid to liquid state, at the melting point, without any change of temperature.
(b) Specific latent heat of vaporization (Lv):-
Specific latent heat of vaporization of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to convert 1 gram of liquid into its vapours at its boiling point without any rise of temperature.
Dimensional formula:- M0L2T-2
Unit:- kg cal kg-1 or J kg-1 - Triple point of water = 273.16 K
- Absolute zero = 0 K = -273.15ºC
- For a gas thermometer, T = (273.15) P/Ptriple (Kelvin)
- For a resistance thermometer, Re = R0[1+αθ]
S. No. | Physical quantity | Symbol | Dimensions | Units | |
SI | CGS | ||||
1. | Heat | Q | [ML2T–2] | Joule | calorie |
2. | Specific–heat | c | [L2T–2q–1] | J/kg K | cal/gm C° |
3. | Molar sp. heat | C | [ML2T–2q–1m–1] | J/mol K | cal/mol C° |
4. | Latent heat | L | [L2T–2] | J/kg | cal/gm |
5. | Thermal capacity | Tc | [ML2T–2q–1] | J/K | cal/C° |
6. | Water–equivalent | W | [M] | kg | gm |
The document Heat Phenomena Class 11 Notes Physics is a part of the NEET Course NCERT Exemplar & Revision Notes for NEET.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
FAQs on Heat Phenomena Class 11 Notes Physics
| 1. What is heat? |  |
Ans. Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between objects or regions of different temperatures. It is the energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules within a substance.
| 2. How is heat transferred? |  |
Ans. Heat can be transferred through three main mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects, convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids, and radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves.
| 3. What is specific heat capacity? |  |
Ans. Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by a certain amount. It is a property that is unique to each substance and is measured in J/kg·°C or J/g·°C.
| 4. What is the difference between heat and temperature? |  |
Ans. Heat and temperature are related but distinct concepts. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance, while heat is the transfer of energy from a hotter object to a cooler object. In other words, temperature is a measure of the intensity of heat.
| 5. How does heat affect the state of matter? |  |
Ans. Heat can cause changes in the state of matter. When heat is added to a substance, its particles gain energy and move more rapidly, causing the substance to change from a solid to a liquid (melting) or from a liquid to a gas (evaporation). Conversely, when heat is removed, the substance may change from a gas to a liquid (condensation) or from a liquid to a solid (freezing).
Related Searches
















