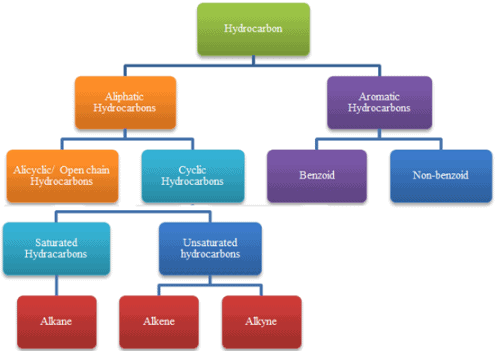
Hydrocarbons Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 9
- Compounds of carbon and hydrogen.
- Classification of Hydrocarbons:
Alkane
- Open chain saturated hydrocarbon with general formula (CnH2n+2).
- All the C atoms are single bonded i.e. sp3 hybridised.
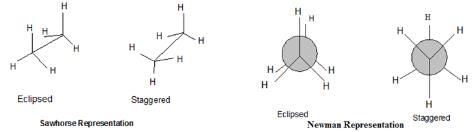
Conformations of Alkane
- Conformations are the different arrangement of atoms that can be converted into one another by rotation about single bonds.
- Eclipsed Conformation: H atoms on two adjacent carbon atoms are closest to each other i.e. dihedral angle is 0.
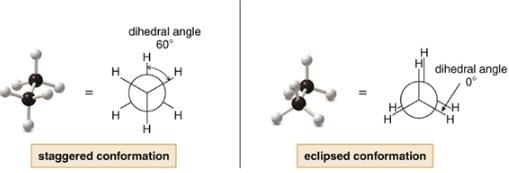
- Staggered Conformation: H atoms on two adjacent carbon atoms are farthest to each other i.e. dihedral angle is 60.
Preparation of Alkanes:
- Reduction of Alkyl Halides:
RX + Zn: + H+ → RH + Zn2+ + X-
4RX + LiAlH4 → 4RH + LiX + AlX3 (X≠ F)
RX + (n - C4H9)3 SnH → R-H + (n - C4H9)3 SnX - Grignard Reagent:
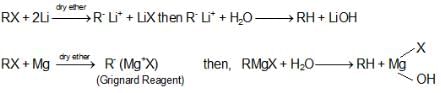
- Hydrogenation of Alkenes:
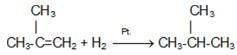
- Wurtz Reaction:
2RX + 2Na → R-R + 2NaX
2Na + 2CH3CH2CH2Cl → CH3CH2CH2CH2-CH2CH3 + 2NaCl - Corey House Reaction:
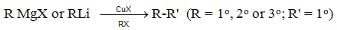
- Decarboxylation of a mixture of the sodium salt of a carboxylic acid:
RCOONa +NaOH(CaO) → RH + Na2CO3 - Kolbe's electrolytic method:
2 RCOOK + 2H2O → R-R + 2CO2 + H2+ 2KOH
Chemical Properties of Alkane
- Direct Halogenation
RH + X2→ RX + HX
Order of Reactivity of X2: F2 > Cl2 > Br2; I2 does not react
a. Initiation Step
Cl-Cl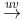 2Cl.
2Cl.
b. Propagation Step
H3C-H +Cl• → H3C• + H-Cl
H3C• + Cl-Cl → H3C-Cl +Cl•
c. Termination Step
Cl• + Cl• →Cl-Cl
H3C• + H3C• → H3C-CH3
Cl• + H3C• → Cl-CH3 - Nitration
Nitration of alkane is made by heating vapours of alkanes and HNO3 at about 400oC to give nitroalkanes.
This is also known as vapour phase nitration.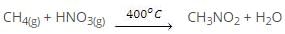
- Combustion:
Alkanes burn readily with non luminous flame in presence of air or oxygen to give CO2 & water along with evolution of heat.
C2H6 + 7O2 → CO2 +6H2O + heat - Aromatization
Alkanes having six to 10 carbon atoms are converted into benzene and its homologues at high pressure and temperature in presence of catalyst.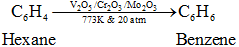
- Oxidization of 30 alkane:
Tertiary alkanes are oxidized to tertiary alcohols by KMnO4
R3CH + KMnO4 → R3COH
Alkene (olefins)
- Open chain, Unsaturated hydrocarbons with general formula (CnH2n).
- At least one >c=c< (double bond) group i.e. sp2 hybridisation, is present throughout the chain.
- Allene: alkene molecule in which at least one C has double bonds with each of the adjacent carbon i.e. -c=c=c- group.
- Isomeric with saturated cycloalkanes.
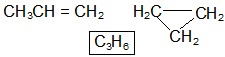
Geometric Isomers: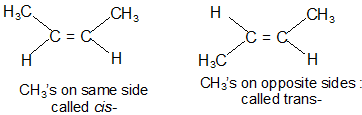
Z is used if the higher - priority substituents on each C are on the same side of the double bond. letter E is used if they are on opposite sides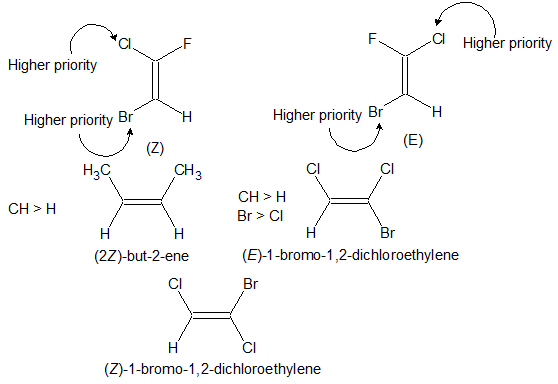
Heats of Hydrogenation: Heat of hydrogenation increases with increase in stability of alkene.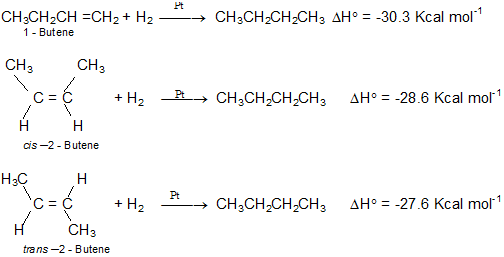
Order of heat of hydrogenation: 1-Butene> cis-2-Butene > trans-2-Butene
Order of stability: 1-Butene> cis-2-Butene > trans-2-Butene
Preparation of Alkenes:
1. Cracking of petroleum:
2. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: RCH2CH2X + alc.KOH → RCH = CH2
3. Dehydration of Alcohols:
Saytzeff Rule: In dehydration and dehydrohalogenation the preferential order for removal of an H is 3° > 2° > 1°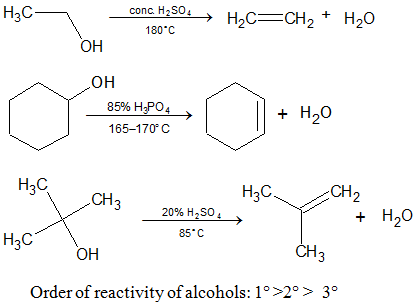
4. Reduction of alkynes: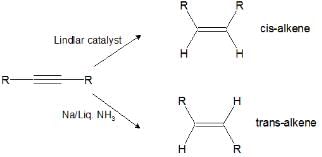
Chemical Properties:
1. Electrophilic Polar Addition Reactions
Reagent | Product | ||
Name | Structure | Name | Structure |
Halogens (Cl2, Br2 only) | X:X | Ethylene dihalide | CH2XCH2X |
Hydrohalic acids | H:X | Ethyl halide | CH3CH2X |
Hypohalous acids | X:OH | Ethylene halohydrin | CH2XCH2OH |
Sulfuric acid (cold) | H:OSO2OH | Ethyl bisulfate | CH3CH2OSO3H |
Water (dil. H3O+) | H:OH | Ethyl alcohol | CH3CH2OH |
Borane | H2B:H | Ethyl borane | (CH3CH2BH2) → (CH3CH2)3B |
Peroxyformic acid | H:O-OCH=O (HCO3H) | Ethylene glycol | CH2OHCH2OH |
2. Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes: Markovnikov’s Addition:
R - CH = CH2 + HBr → R – CHBr – CH3
Mechanism:
R - CH = CH2 + HBr → R – CH+ - CH3 +Br-
R – CH+ - CH3 + Br- → R – CHBr - CH3
Anit- Markovnikov’s Addition (Peroxide Effect):
R - CH = CH2 + HBr + (C6H5CO)2O2 → R – CHBr – CH3
Mechanism
Initiation:
R - O - O - R → 2RO•
RO. + HBr → Br. + ROH
Propagation
CH3CH = CH2 + Br• → CH3•CH - CH2Br
CH3•CHCH2Br + HBr→ CH3CH2CH2Br + Br•
Termination:
2RO• → R - O - O - R
Br• + Br•→Br2
3. Addition of Water to Alkenes: Acid Catalyzed Hydration: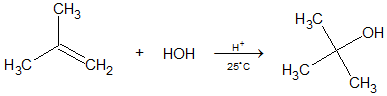
4. Oxymercuration-Demercuration: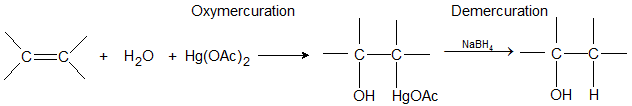
Examples: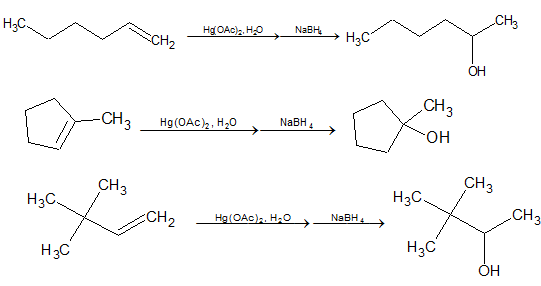
5. Hydroboration-Oxidation: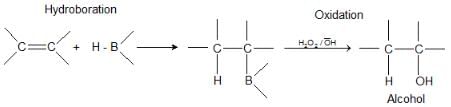
Examples: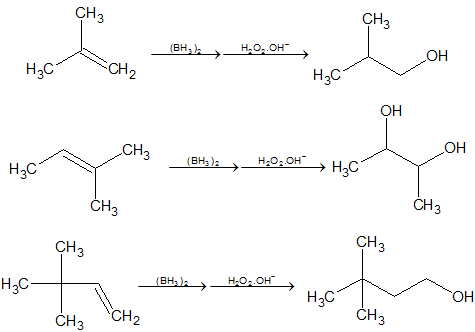
6. Halogen Addition in Non-polar Solvent: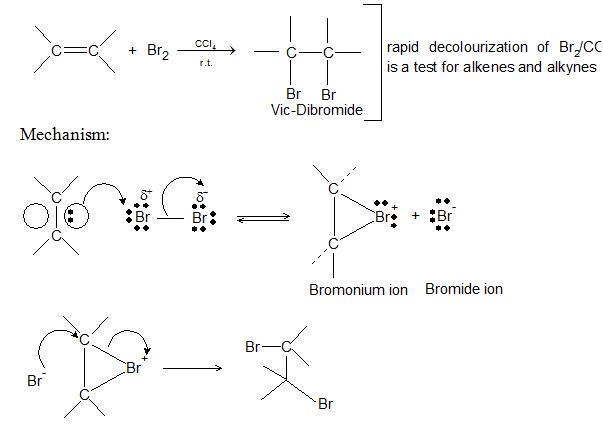
7. Halogen Addition in Aqueous Medium: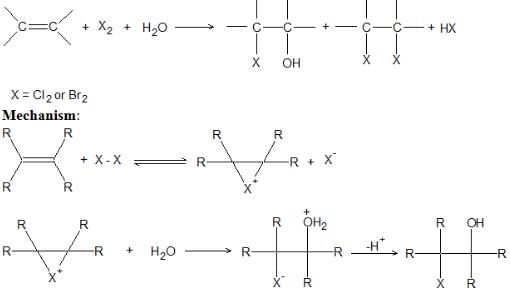
8. Syn – Hydroxylation: Formation of di-oles.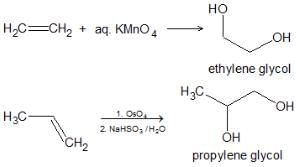
9. Ozonolysis of Alkenes: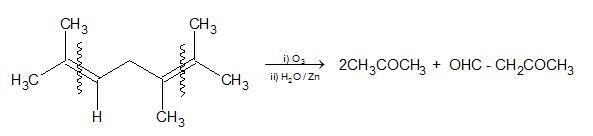
Alkyne
- Saturated open chain hydrocarbon with general formula (CnH2n-2).
- At least one -c≡c- (triple bond) group i.e. sp hybridisation, is present throughout the chain.
- Physical properties of alkynes are similar to those of the corresponding alkenes
Preparation
1. Dehydrohalogenation of vic-Dihalides or gem-Dihalides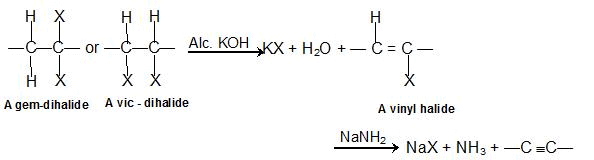
2. Dehalogenation of vic-Tetrahalogen Compounds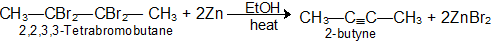
3. Alkyl Substitution in Acetylene; Acidity of º C-H
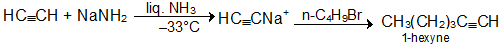
4. From Calcium Carbide:
CaC2 +2H2O → Ca(OH)2+ C2H2
5. Kolbe’s Electrolysis: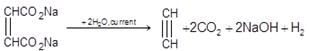
Chemical Properties
1. Hydrogenation: RC ≡ CCH2CH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
2. Hydro-halogenation:
Markovnikov addition: RC≡CH +HBr → RCBr=CH2 +HBr→ RCBr2-CH3
Anti-markovnikov addition: RC≡CH +HBr +peroxide → RCH=CHBr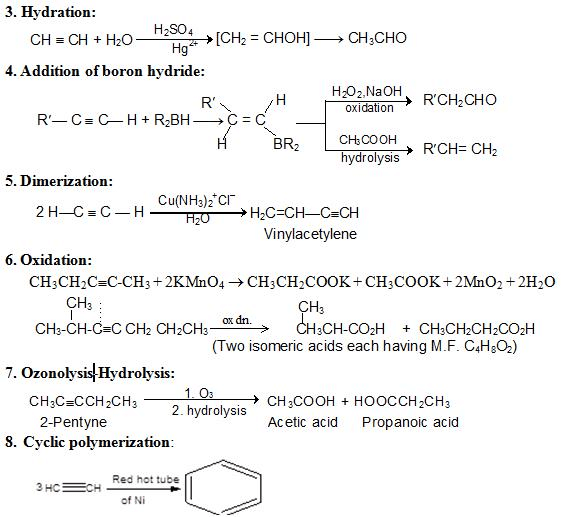
Aromatic Hydrocarbons:
For being aromatic a hydrocarbon should
- be a cyclic compounds.
- have planarity in geometry.
- have complete delocalization of electrons over ring.
- follow Huckel Rule i.e. number of ?? electrons in ring = (4n+2).
Benzene (C6H6)
1. Structure: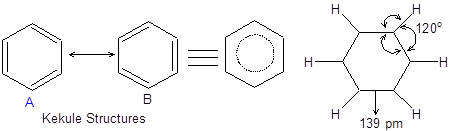
2. Chemical Reactions of Benzene: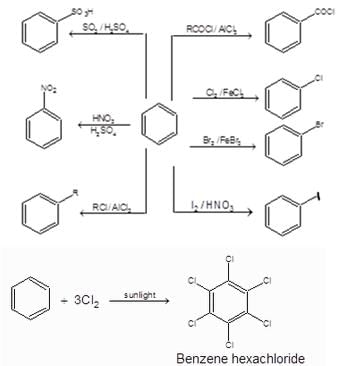
Anti-aromatic Hydrocarbons:
Highly unstable compounds.
Number of π electrons in ring = 4n.
Example: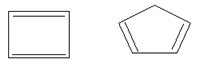
FAQs on Hydrocarbons Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 9
| 1. What are hydrocarbons? |  |
| 2. How are hydrocarbons classified? |  |
| 3. What are the common uses of hydrocarbons? |  |
| 4. How are hydrocarbons extracted from the Earth? |  |
| 5. Are hydrocarbons harmful to the environment? |  |

















