Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7
ALCOHOLS
Preparation of Alcohols:
- By hydrolysis of haloalkanes : R-X + aq. KOH →ROH +KX
- By reduction of Carbonyl compounds
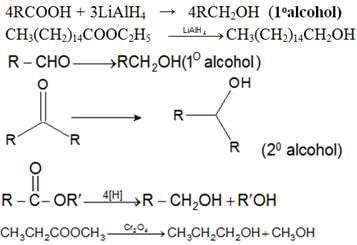
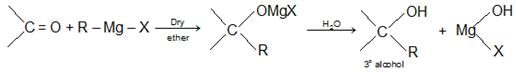
- By the action of Grignard’s Reagent on aldehydes, ketones and esters
- By Aliphatic Primary Amines: RCH2NH2 + HNO2 → RCH2OH + N2 + H2O
- Hydration of alkenes:
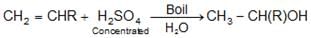
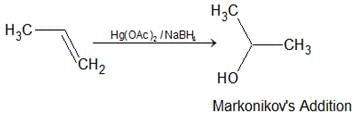
- Oxymercuration-demercuration:
- Hydroboration-oxidation:
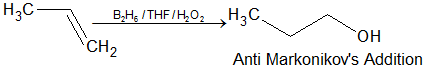
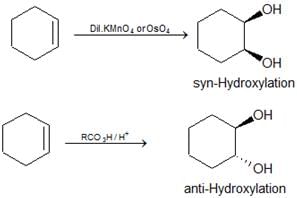
- Hydroxylation of alkenes:
Physical Properties of Alcohol:
- Lower alcohols are liquid at room temperature while higher ones are solid.
- High boiling point due to presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Order of Boiling Point: primary > secondary > tertiary
- Solubility in water decreases with increase in molecular mass due to decrease in extent of intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Chemical Properties of Alcohol:
- Alcohol's reaction with metal: ROH + Na→2RO+Na– + H2
- Formation of Halides:
- 3ROH + P+I2→3RI + H3PO3
- ROH + SOCl2/PCl3/PCl5→ RCl
- ROH+HX→ RX
- ROH+ NaBr,H2SO4→R-Br
- ROH+ Zn+HCl→R-Cl
- R2C-OH alcohol + HCl→ R2CCl
- Reaction with HNO3: R-OH + HO-NO2→ R-O-NO2
- Reaction with carboxylic acid (Esterification) : R-OH +R’-COOH +H+↔ R’-COOR
- Reaction with Grignard reagent: R'OH + RMgX → RH + R'OMgX
- Reduction of alcohol : ROH + 2HI + Red P→ RH +I2+H2O
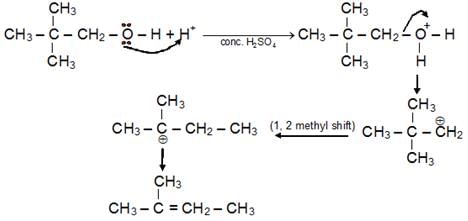
- Dehydration of Alcohol: Dehydration of alcohols takes place in acidic medium. Intra-molecular dehydration leads to the formation of alkene while inter molecular dehydration which forms ether. Ease of dehydration: 3° > 2° > 1
- Satyzeff’s Rule : Elimination through b carbon containing minimum b hydrogen
- Oxidation of Alcohol:
RCH2-OH + [O] → RCHO → RCOOH
RCH2-OH + [O] +PCC → RCHO - Haloform Reaction: Compound containing CH3CO- group (or compound on oxidation gives CH3CO – group) which is attached with a C or H, in presence of halogen and mild alkali gives haloform.CH3-CH2-COCH2-CH3, CH3-CO-Cl, CH3COOH will not respond to haloform reaction wile CH3CH2OH will respond to haloform Reaction.
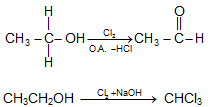
Test for Alcohols:
1. Lucas Test:
Alcohols + ZnCl2 + HCl
- 1o Alcohol: RCH2OH + ZnCl2 +HCl → No reaction at room temperature
- 20 Alcohol: R2CHOH + ZnCl2 +HCl → R2CHCl White turbidity after 5-10 min.
- 30 Alcohol: R3CHOH + ZnCl2 +HCl → R3CHCl white turbidity instantaneously.
2. Victor Meyer Test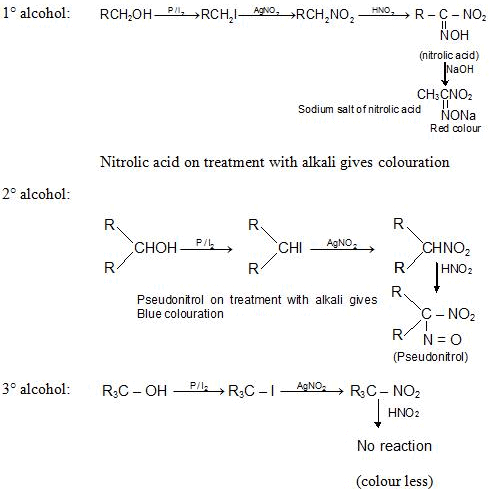
Phenols:
Preparation: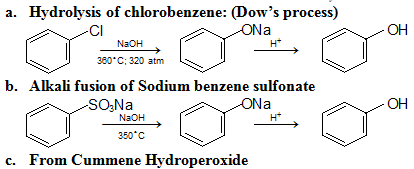
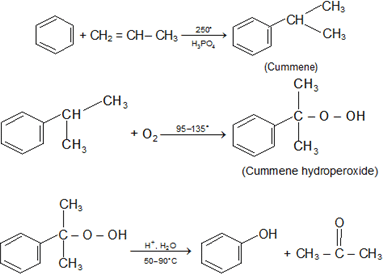
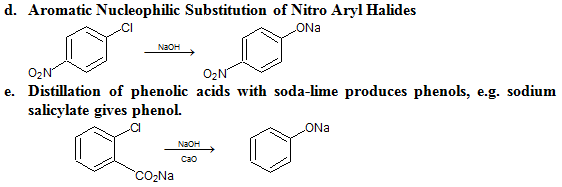
Physical Properties of Phenols
- Phenol is a colorless, toxic, corrosive, needle shaped solid.
- Phenol soon liquifies due to high hygroscopic nature.
- Phenol is less soluble in water, but readily soluble in organic solvents.
- Simplest phenols, because of hydrogen bonding have quite high boiling points.
- o-nitrophenol is, steam volatile and also is less soluble in water because of intramolecular hydrogen bonding
Chemical Properties of Phenols
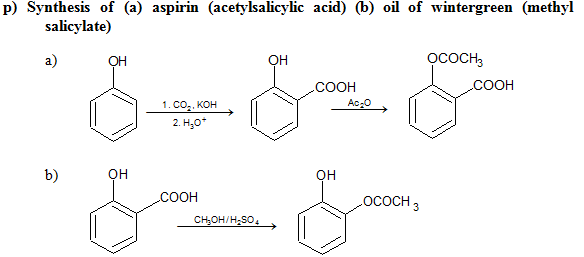
a) Formation of Esters
Phenyl esters (RCOOAr) are not formed directly from RCOOH. Instead, acid chlorides or anhydrides are reacted with ArOH in the presence of strong base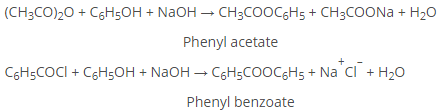
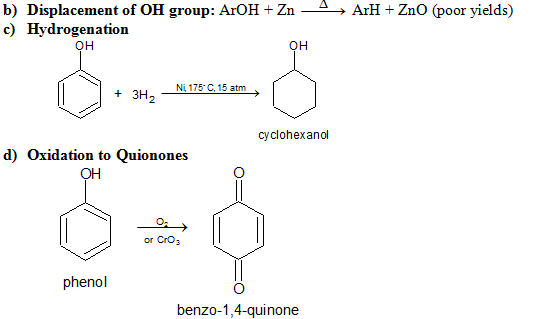
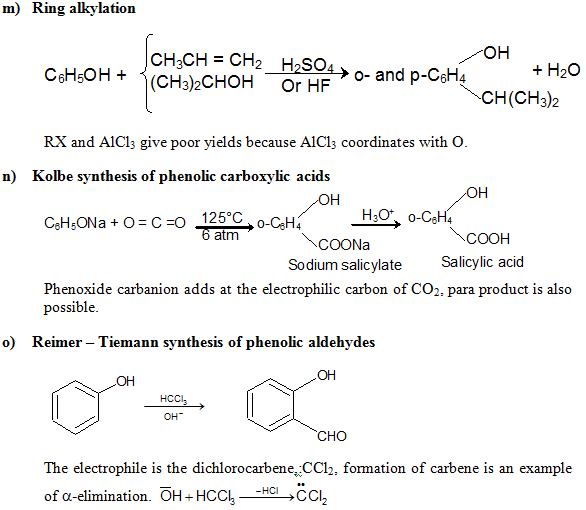
e) Electrophilic Substitution The —OH and even more so the —O(phenoxide) are strongly activating ortho ,para - directing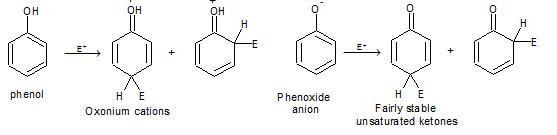
Special mild conditions are needed to achieve electrophilic monosubstituion in phenols because their high reactivity favors both polysubstitution and oxidation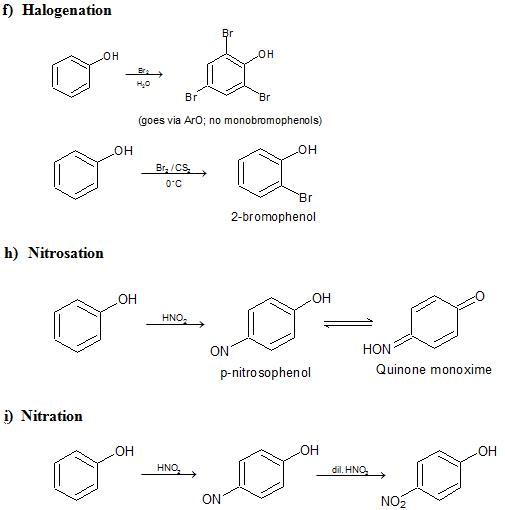
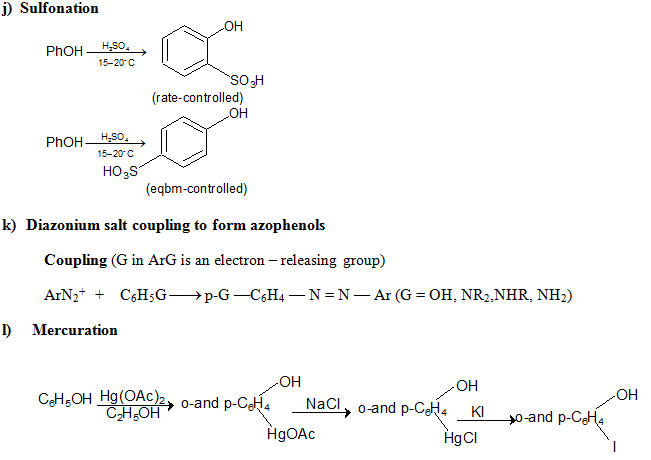
Ethers:
Physical Properties of Ethers
- Physical state, colour and odour: Dimethyl ether and ethyl methyl ether is gas at ordinary temperature while the other lower homologues of ethers are colourless liquid with characteristic 'ether smell'.
- Dipole nature: Ethers have a tetrahedral geometry i.e., oxygen is sp3 hybridized. The C— O—C angle in ethers is 110°. Because of the greater electronegativity of oxygen than carbon, the C—O bonds are slightly polar and are inclined to each other at an angle of 110°, resulting in a net dipole moment.
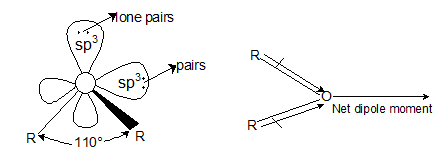
Bond angle of ether is greater than that of tetrahedral bond angle of 109°28'. - Solubility and boiling point: Due to the formation of less degree of hydrogen bonding, ethers have lower boiling point than their corresponding isomeric alcohols and are slightly soluble in water.
Preparation of Ethers:
a) From alcohols: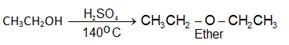
Order of dehydration of alcohol leading to formation of ethers: 1° > 2° > 3°
b) Williamson's synthesis:
R-X + Na+ -O-R' → R-O-R' + Na+ X-
In case of tertiary substrate elimination occurs giving alkenes.
c) From alkenes: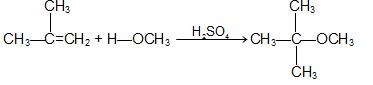
d) From Grignard reagent: Treating a - halo ethers with suitable Grignard reagents.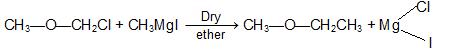
e) On standing in contact with air, most aliphatic ethers are converted slowly into unstable peroxides. The presence of peroxides is indicated by formation of a red colour when the ether is shaken with an aqueous solution of ferrous ammonium sulfate and potassium thiocyanate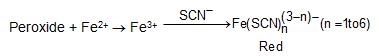
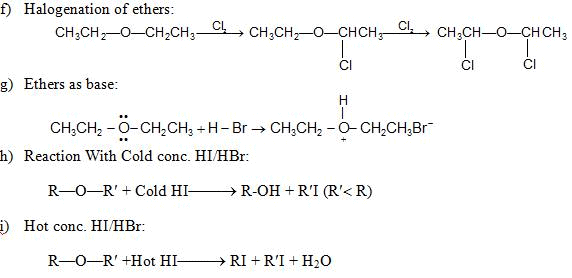
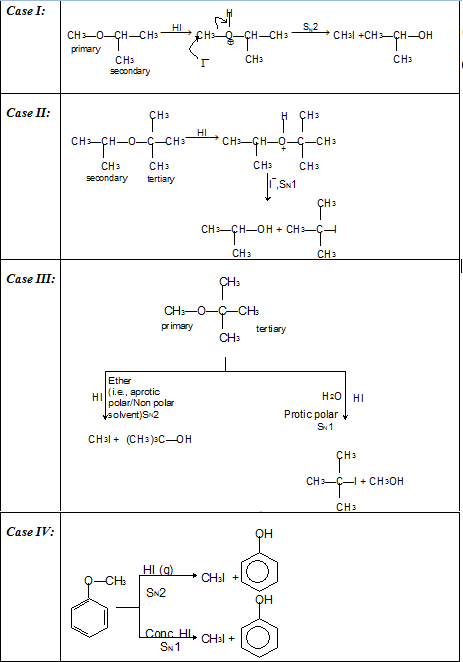
(i) Reaction with acid chlorides and anhydrides: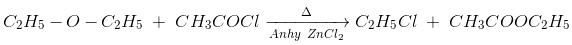
(j) Electrophilic substitution reactions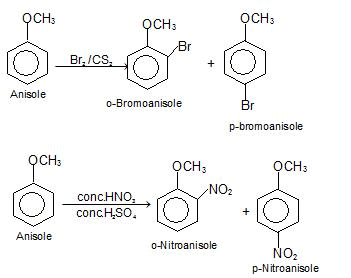
Epoxides or Oxiranes:
Preparation
(a) Oxidation of ethylene: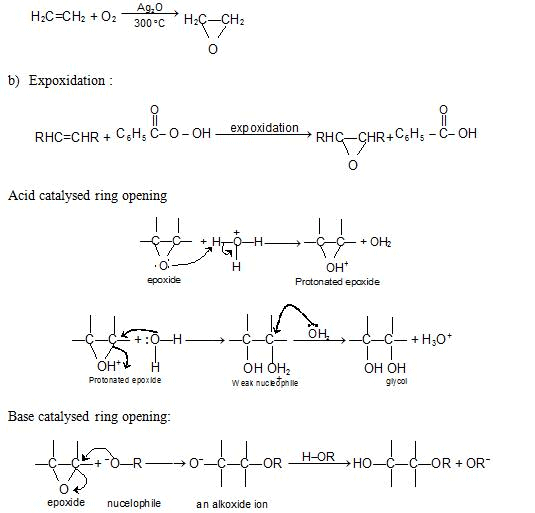
FAQs on Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7
| 1. What are alcohols, phenols, and ethers? |  |
| 2. What are the properties of alcohols? |  |
| 3. How are phenols different from alcohols? |  |
| 4. What are the uses of ethers? |  |
| 5. Can alcohols, phenols, and ethers be used as fuels? |  |
















