Biomolecules Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 9
Carbohydrates
Classification of carbohydrates:
- Monosaccharides: Polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to give simpler carbohydrates.Examples: Glucose, Fructose, Ribose, Arabinose, Mannose, Gulose etc..
- Oligosaccharides: The oligosaccharides (Greek, oligo, few) are carbohydrates which yield a definite number (2-9) of monosaccharide molecules on hydrolysis.
- Trisaccharides: yield three monosaccharide molecules on hydrolysis.
Examples: raffinose, which has molecular formula, C18H32O16 - Polysaccharides: The polysaccahrides are carbohydrates of high molecular weight which yield many monosaccharide molecules on hydrolysis. Examples are starch and cellulose, both of which have molecular formula, (C6H10O5)n.
Monosaccharides and oligosaccharides are crystalline solids, soluble in water and sweet to taste. They are collectively known as sugars. The polysaccharides, on the other hand, are amorphous, insoluble in water and tasteless. They are called non-sugars carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides
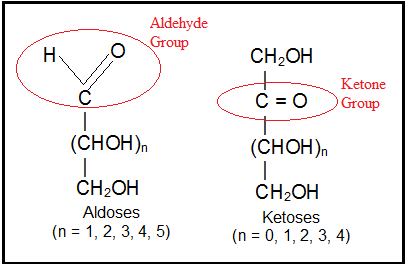
- The Aldoses, which contain an aldehyde group (-CHO).
- The Ketoses, which contain a ketone group (>C=O).
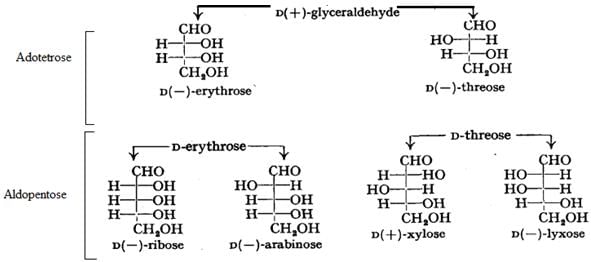
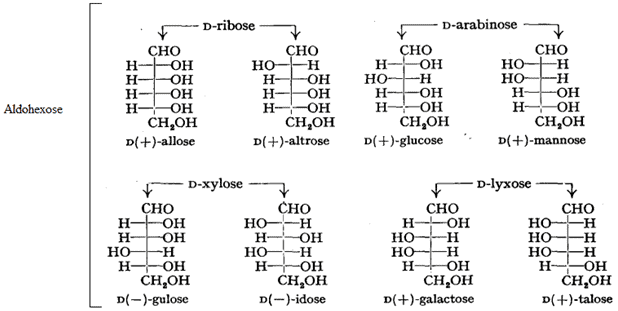
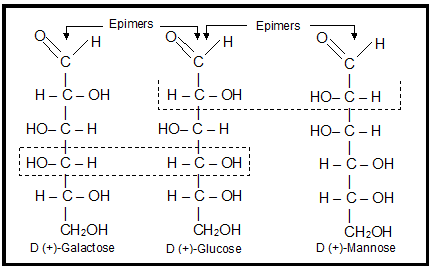
Stereo Isomerism in Carbohydrates:
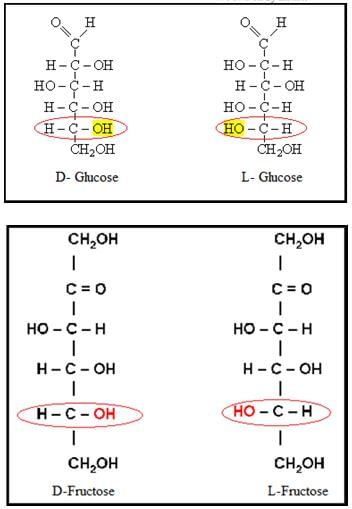
- If the hydroxyl group on the asymmetric carbon atom farthest from aldehyde or ketone group projects to the right, the compound is a member of the D-family.
- If the hydroxyl group on the farthest asymmetric carbon projects to the left, the compound is a member of the L-family.
- Maximum Number of Optical Isomers = 2n, where n = the number of asymmetric carbon atoms.
- Epimer: A pair of diastereomers that differ only in the configuration about of a single carbon atom are said to be epimers.
Cyclic Form of Monosaccharide:
• Pyranose and Furanose Forms: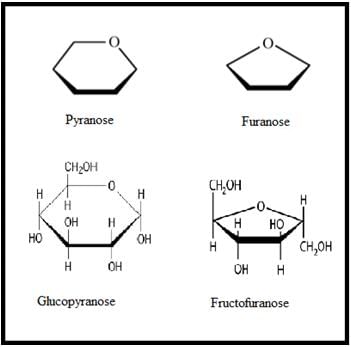
- Anomers: Pair of stereoisomers which differ in configuration only around C1 are called anomers and the C1 carbon is called Anomeric carbon.
In a- anomer-, the OH group at C1 is towards right while in b-anomer, the OH group at C1 is towards left.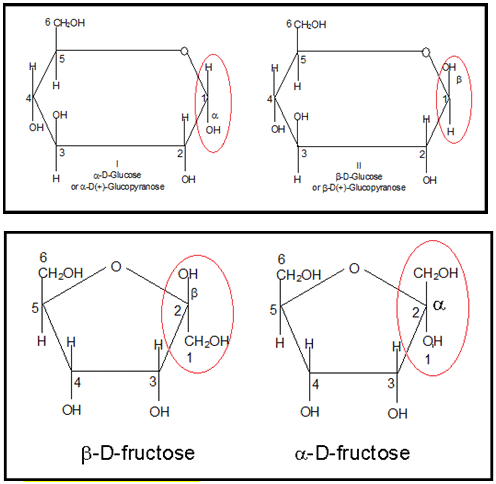
Mutarotation:
Change in rotation of an optically active sugar in solution with time, to an equilibrium value, is called mutarotation. During mutarotation, the ring opens and then recloses either in the inverted position or in the original position giving a mixture of a-and-b-forms.
Reactions of Glucose:
a) With HI/P: It undergoes reduction to form n-hexane while with sodium amalgam it forms sorbitol.
e) Oxidation: Glucose on oxidation with Br2 gives gluconic acid which on further oxidation with HNO3 gives glucaric acid
f) With Tollen reagent and Fehling solution. Glucose forms silver mirror and red ppt. of Cu2O respectively.
g) With acetic anhydride. In presence of pyridine glucose forms pentaacetate.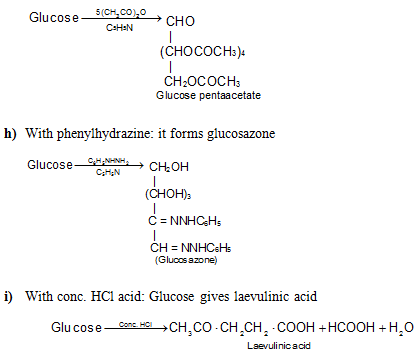
j) Glycoside formation: When a small amount of gaseous HCl is passed into a solution of D (+) glucose in methanol, a reaction takes place that results in the formation of amomeric methyl acetals.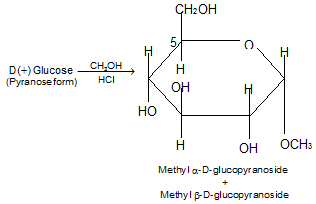
Carbohydrate acetals, genrally are called glycosides and an acetal of glucose is called glucoside.
k) Kiliani - Fischer Synthesis: This is a method of lengthening the carbon chain of an aldose.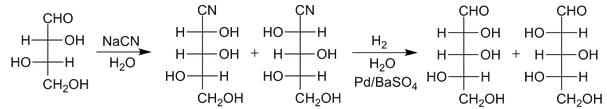
l) Ruff Degradation: It is opposite to Kiliani Fischer synthesis that can be used to shorten the chain by a similar unit.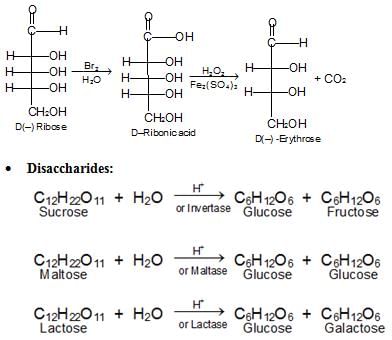
a) Sucrose:
Non-reducing sugar.
Formed by condensation of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose.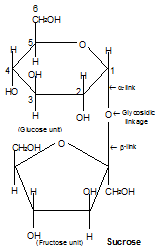
Hydrolysis: (Invert Sugar or Invertose). Hydrolysis of sucrose with hot dilute acid yields D-glucose and D-fructose.
Polysaccharides
a. Starch:
i. A polymer of glucose.
ii. Mixture of two components – a water soluble component called amylose (20%) and a water insoluble component called amylopectin (80%).
iii. Both amylose and amylopectin are polymers of a-D-glucose.
iv. Amylose is a linear polymer of a-D-glucose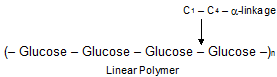
vi. Amylopectin, is a highly branched polymer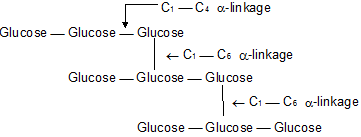
Amino Acids,
Amino acids are molecules, which contain two functional groups, one is carboxylic group and another is amino group
H2N CH2 COOH : Amino acetic acid, or Glycine
CH3 CH (NH2) COOH : a - Amino propionic acid or Alanine
H2N CH2 CH2COOH : b - Amino propionic acid
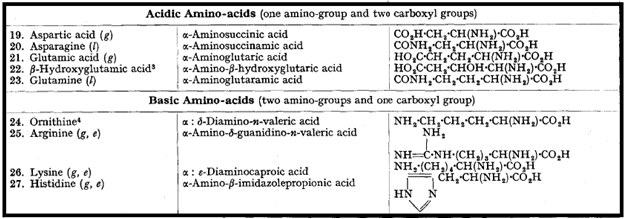
Acidic Amino Acid: These amino acids contain a second carboxyl group or a potential carboxyl group in the form of carboxamide.
Basic Amino Acids: These contain a second basic group which may be an amino group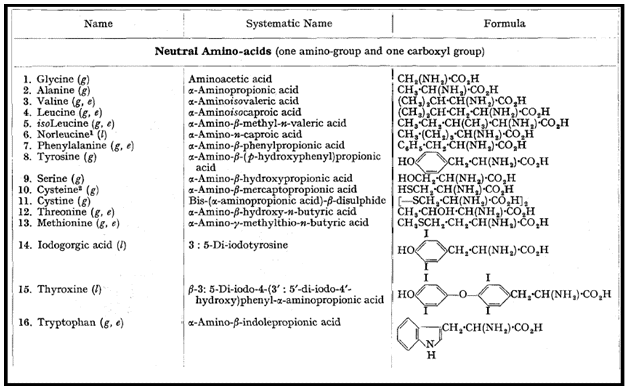
Iso Electric Point:
The hydrogen ion concentration of the solution in which a particular amino acid does not migrate under the influence of an electric field is called the isoelectric point of that amino acid.
Peptides
A peptides as the amides formed by interaction between amino groups and carboxyl groups of amino acids.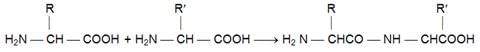
Depending upon the number of amino acid residues per molecule, they are known as dipeptides, tripeptides and so on and finally polypeptides.
Every two amino acids are linked by means of a –CO-NH group, which is commonly referred as peptide bond.
FAQs on Biomolecules Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 9
| 1. What are biomolecules? |  |
| 2. How do carbohydrates function in biomolecules? |  |
| 3. What is the role of lipids in biomolecules? |  |
| 4. What are proteins and their significance in biomolecules? |  |
| 5. How do nucleic acids contribute to biomolecules? |  |

















