Natural Vegetation and Wildlife | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
What is the region we have lost our natural vegetation and wildlife resources ?
Ref: https://edurev.in/question/547160/What-is-the-region-we-have-lost-our-natural-vegetation-and-wildlife-resources-
Natural Vegetation
- Natural vegetation means plants that grow on their own without human help and have not been disturbed by people for a long time. This untouched plant community is called virgin vegetation.
- The word "flora" refers to the plants in a certain place or time, while "fauna" means the animals in that area. The variety of plants and animals is affected by factors like the land's shape and the soil.

Relief
Land
Land has a direct and indirect effect on natural vegetation.
- Fertile Level Land: This kind of land is good for farming because it has lots of nutrients and is great for growing crops.
- Undulating and Rough Terrains: These areas have bumpy surfaces and rough landscapes where grasslands and woodlands usually form. Such terrains are homes to many different kinds of animals.
Soil
Different types of soils support different types of vegetation.
- Sandy Soils of the Desert: These soils are found in dry regions and can support plants like cacti and thorny bushes that thrive in dry conditions.
- Wet, Marshy, Deltaic Soils: These soils are located in wet and marshy areas, often in deltas, and provide a habitat for vegetation such as mangroves and other plants typical of deltas.
- Soil on Hill Slopes: The soil on hillsides is suitable for the growth of cone-shaped trees that are well-suited to sloping terrain, commonly found in mountainous regions.
This variety in soil and land types across different regions of India leads to a diverse range of natural vegetation and wildlife, contributing to the rich biodiversity of the country.
Climate
Temperature
Temperature has a big role in deciding what kinds of plants can grow somewhere and how many can grow there.
- High Temperatures: Places that are really hot usually have plants that like heat, like tropical and subtropical plants.
- Low Temperatures: Areas that are very cold, especially those with frost, usually have plants that can handle cold, like coniferous forests.
- Temperature not only decides what plants can grow but also how fast they grow. For example, in colder places, plants often grow slower.

Photoperiod (Sunlight)
- More Sunlight in Summer: During summer, there is more daylight time, so plants and trees can do more photosynthesis, which helps them grow quicker.
- Less Sunlight in Winter: In winter, days are shorter, which slows down plant growth because there is less photosynthesis happening.
Precipitation
The amount of rainfall in an area is directly connected to the density and types of plants found there.
- Heavy Rainfall: Places with lots of rain support thick forests like tropical rainforests, where many different plant types grow well.
- Low Rainfall: Areas with little rain usually have sparse vegetation like grasslands and deserts, where plants are adapted to dry conditions and can survive with very little water.
- Temperature, sunlight, and precipitation work together to create various climates that influence the natural plants and animals in different regions, contributing to the diverse biodiversity seen across different landscapes.
Types of Vegetation in India
In India, there are several major types of vegetation, each adapted to specific climatic and geographic conditions:
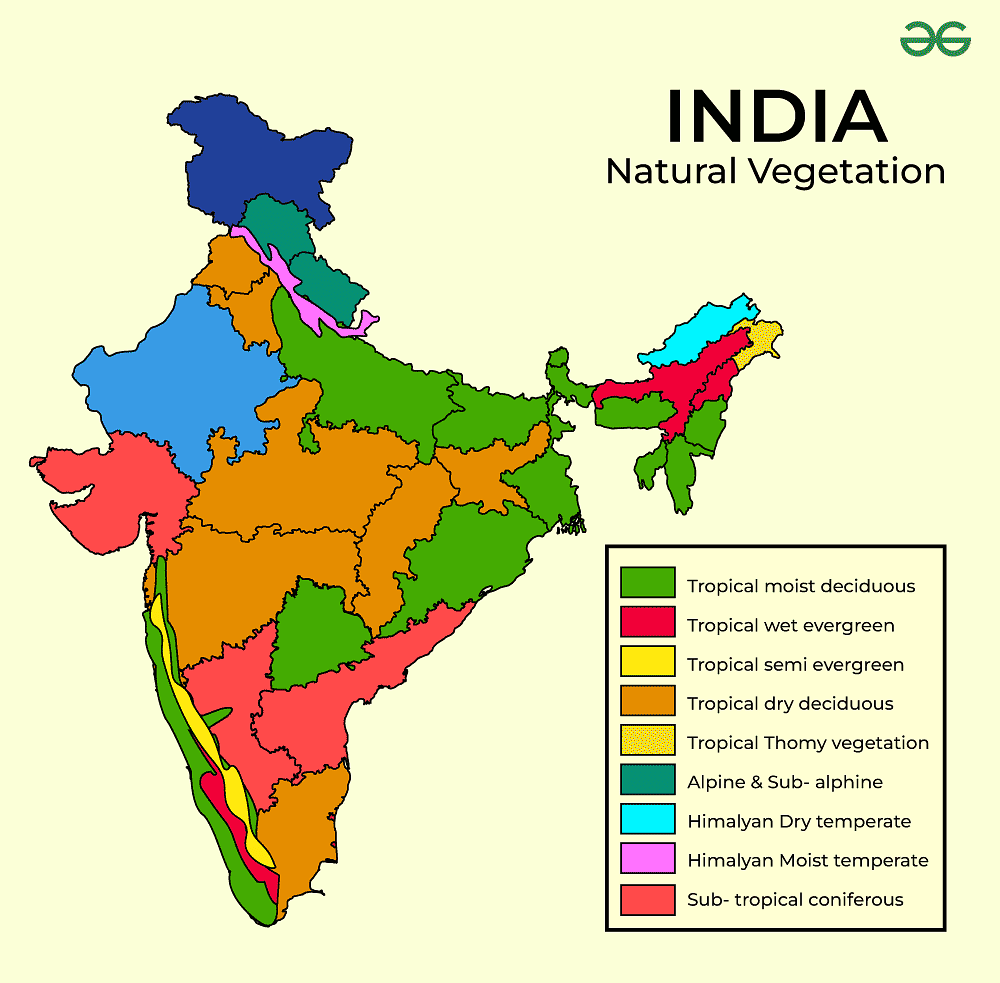
Tropical Evergreen Forests
- Location: Found in the Western Ghats, Lakshadweep Islands, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, upper Assam, and Tamil Nadu coast.
- Climate: Flourish in areas with more than 200 cm of rainfall each year and a brief dry period.
- Characteristics: Trees grow up to 60 meters tall with a thick, layered mix of trees, shrubs, and vines.
- Flora: Contains ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber, and cinchona trees.
- Fauna: Habitat for elephants, monkeys, lemurs, and various types of deer.
Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Also Known As: Rainforests occurring in regions with annual rainfall between 200 cm and 70 cm.
- Distribution: Found in areas that receive rainfall ranging from 200 cm to 70 cm every year.
- Seasonal Shedding: Trees drop their leaves in the dry summer season.
- Animals: Home to various animals like lions, tigers, pigs, deer, and elephants.
Moist Deciduous:
- Rainfall: Found in regions with rainfall ranging from 200 cm to 100 cm.
- Dominant Species: Teak; other species comprise bamboos, sal, shisham, sandalwood, and khair.
Dry Deciduous:
- Rainfall: Found in regions receiving rainfall ranging from 100 cm to 70 cm.
- Flora: Comprises teak, sal, peepal, and neem trees.
Thorn Forests and Scrubs
- Location: Found in the north-western parts of India, including semi-arid regions of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, and Haryana.
- Adaptations: Trees and bushes have sharp thorns and deep roots to find water.
- Characteristics: Stems with moisture and small, thick leaves to keep water.
- Flora: Types of trees like Acacias, palms, euphorbias, and cacti.
- Fauna: Animals include rodents, rabbits, foxes, wolves, tigers, lions, wild donkeys, horses, and camels.
Montane Forests
- Location: Found in mountainous regions.
- Types:
- Wet Temperate: Situated at elevations between 1000 and 2000 meters.
- Alpine: Located above 3600 meters, transitioning to grasslands and alpine vegetation.
- Flora: Consists of various trees and grasses that are suited to colder temperatures.
- Fauna: Includes a range of animals like the Kashmir stag, spotted deer, wild sheep, jackrabbit, Tibetan antelope, yak, snow leopard, squirrels, shaggy horn wild ibex, bears, red pandas, and different types of sheep and goats.
Mangrove Forests
- Location: Found in coastal regions affected by tides like the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta.
- Adaptations: Trees growing in salty soil and covered by water.
- Flora: Sundari trees stand out, offering tough wood.
- Fauna: Famous for the Royal Bengal Tiger and various water creatures adapted to salty water conditions.
Each type of vegetation in India is uniquely adapted to its specific environment, contributing to the country’s rich biodiversity and ecosystem diversity.
Wildlife in India
 India boasts a diverse array of wildlife across its varied landscapes:
India boasts a diverse array of wildlife across its varied landscapes:
- Elephants: These large animals are typically found in the hot and wet forests of Assam, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- One-horned Rhinoceroses: These unique creatures are native to Assam and West Bengal.
- Wild Donkeys: These animals live in the Rann of Kachchh, while camels thrive in the Thar Desert.
- Indian Lions: These majestic creatures are naturally found in the Gir forest of Gujarat.
- Tigers: These big cats can be spotted in various regions like Madhya Pradesh, the Sundarbans of West Bengal, and the Himalayan region.
- High Altitude Wildlife: In Ladakh, you can find yak, shaggy horned wild oxen, Tibetan antelope, bharal (blue sheep), wild sheep, and kiang (Tibetan wild donkey).
- Aquatic Life: Turtles, crocodiles, and gharials make their homes in rivers, lakes, and coastal areas.
- Birds: Forests and wetlands are home to peacocks, pheasants, ducks, parakeets, cranes, and pigeons.
Threats to Flora and Fauna
Conservation efforts are crucial due to the significant threats faced by wildlife and plant species:
- Causes: Major dangers involve hunting for business reasons, contamination from chemicals and industrial garbage, and fast clearing of forests for farming and city development.
- Endangered Species: Around 1,300 plant kinds are at risk, with 20 types already vanished.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to protect its flora and fauna:
- Biosphere Reserves: India has set up 18 special areas to protect nature, with 10 being part of a global network.
- Botanical Gardens: Since 1992, financial and technical support has helped various botanical gardens.
- Conservation Projects: Programs like Project Tiger, Project Rhino, and others work to save endangered animals and their homes.
- Protected Areas: India takes care of its natural treasures through 103 National Parks, 535 Wildlife Sanctuaries, and Zoological Gardens.
These efforts underscore India’s commitment to biodiversity conservation, ensuring the survival and well-being of its unique flora and fauna for future generations.
|
365 videos|701 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on Natural Vegetation and Wildlife - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What are the different types of natural vegetation? |  |
| 2. How does natural vegetation support wildlife? |  |
| 3. What are some threats to natural vegetation and wildlife? |  |
| 4. How do different types of natural vegetation vary based on climate and geography? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to conserve natural vegetation and wildlife? |  |

















