Irodov Solutions: Kinematics - 3 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
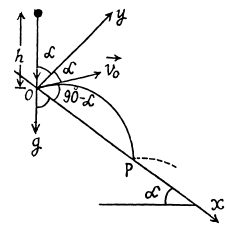
Q. 31. A ball starts falling with zero initial velocity on a smooth inclined plane forming an angle a with the horizontal. Having fallen the distance h, the ball rebounds elastically off the inclined plane. At what distance from the impact point will the -ball rebound for the second time?
Ans. The ball strikes the inclined plane (Ox) at point O (origin) with velocity 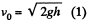 As the ball elastically rebounds, it recalls with same velocity v0, at the same angle a from the normal or y axis (Fig.). Let the ball strikes the incline second time at P, which is at a distance l (say) from the point O, along the incline. From the equation
As the ball elastically rebounds, it recalls with same velocity v0, at the same angle a from the normal or y axis (Fig.). Let the ball strikes the incline second time at P, which is at a distance l (say) from the point O, along the incline. From the equation 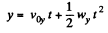
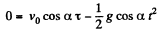
where τ is the time of motion of ball in air while moving from O to P.
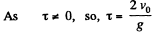 (2)
(2)
Now from me equation.
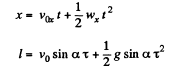
so, 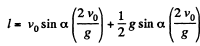
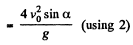
Hence the sought distance, 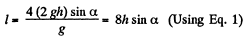
Q. 32. A cannon and a target are 5.10 km apart and located at the same level. How soon will the shell launched with the initial velocity 240 m/s reach the target in the absence of air drag?
Ans. Total time of motion
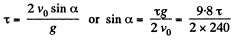 (1)
(1)
and horizontal range
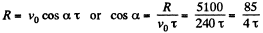 (2)
(2)
From Eqs. (1) and (2)
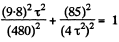
On simplifying 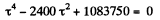
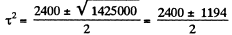
Solving for τ2 wc get :
Thus
τ = 42.39 s = 0.71 min and
τ = 24-55 s = 0.41 min depending on the angle α.
Q. 33. A cannon fires successively two shells with velocity v0 = 250 m/s; the first at the angle θ1 = 60° and the second at the angle θ2 = 45° to the horizontal, the azimuth being the same. Neglecting the air drag, find the time interval between firings leading to the collision of the shells.
Ans. Let the shells collide at the point P (x, y). If the first shell takes t s to collide with second and Δt be the time interval between the firings, then
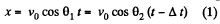
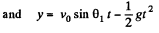
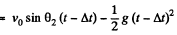
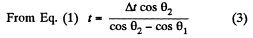
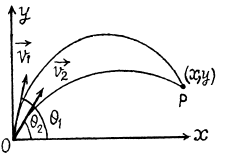
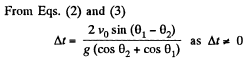
Q. 34. A balloon starts rising from the surface of the Earth. The ascension rate is constant and equal to v0. Due to the wind the balloon gathers the horizontal velocity component vx = ay, where a is a constant and y is the height of ascent. Find how the following quantities depend on the height of ascent:
(a) the horizontal drift of the balloon x (y);
(b) the total, tangential, and normal accelerations of the balloon.
Ans. According to the problem
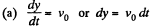
Integrating 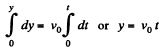 (1)
(1)
And also we have 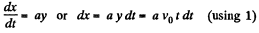
So, 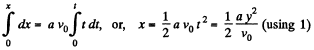
(b) According to the problem
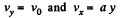 (2)
(2)
So, 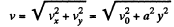
Therefore 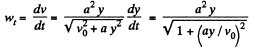
Diff. Eq. (2) with respect to time.
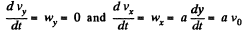
So, 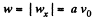
Hence 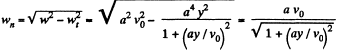
Q. 35. A particle moves in the plane xy with velocity v = ai + bxj, where i and j are the unit vectors of the x and y axes, and a and b are constants. At the initial moment of time the particle was located at the point x = y = 0. Find:
(a) the equation of the particle's trajectory y (x);
(b) the curvature radius of trajectory as a function of x.
Ans. (a) The velocity vector of the particle
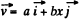
So, 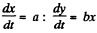 (1)
(1)
From (1) 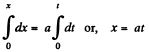 (2)
(2)
And 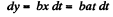
Integrating 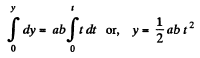 (3)
(3)
From Eqs. (2) and (3) , we get, 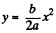 (4)
(4)
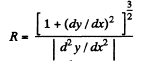
Let us differentiate the path Eq. 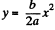 w ith resp ect to x,
w ith resp ect to x,
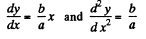
From Eqs. (5) and (6), the sought curvature radius :
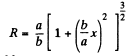
Q. 36. A particle A moves in one direction along a given trajectory with a tangential acceleration wτ = aτ, where a is a constant vector coinciding in direction with the x axis (Fig. 1.4), and τ is a unit vector coinciding in direction with the velocity vector at a given point. Find how the velocity of the particle depends on x provided that its velocity is negligible at the point x = 0.
Ans. In accordance with the problem 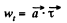
But 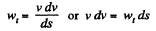
So, 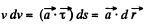
or, 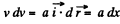 (because
(because 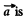 directed towards the jc-axis)
directed towards the jc-axis)
So, 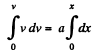
Hence 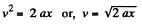
Q. 37. A point moves along a circle with a velocity v = at, where a = 0.50 m/s2. Find the total acceleration of the point at the mo- merit when it covered the n-th (n = 0.10) fraction of the circle after the beginning of motion.
Ans. The velocity of the particle v = at
So, 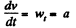 (1)
(1)
And 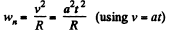 (2)
(2)
From 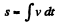
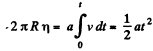
So, 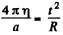 (3)
(3)
From Eqs. (2) and (3) wn = 4πaη
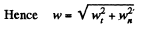
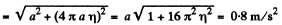
Q. 38. A point moves with deceleration along the circle of radius R so that at any moment of time its tangential and normal accelerations are equal in moduli. At the initial moment t = 0 the velocity of the point equals v0. Find:
(a) the velocity of the point as a function of time and as a function of the distance covered s;
(b) the total acceleration of the point as a function of velocity and the distance covered.
Ans. (a) According to the problem
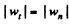
For v (t), 
Integrating this equation from 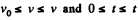
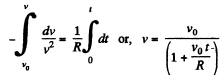
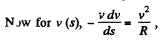 Integrating this equation from
Integrating this equation from 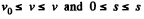
So, 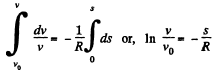
Hence 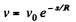
(b) The normal acceleration of the point
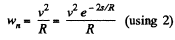
And as accordance with the problem
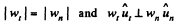
so, 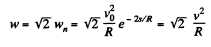
Q. 39. A point moves along an arc of a circle of radius R. Its velocity depends on the distance covered 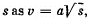 where a is a constant. Find the angle α between the vector of the total acceleration and the vector of velocity as a function of s.
where a is a constant. Find the angle α between the vector of the total acceleration and the vector of velocity as a function of s.
Ans. From the equation 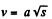
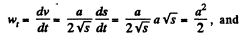
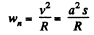
As w, is a positive constant, the speed of the particle increases with time, and the tangential acceleration vector and velocity vector coincides in direction.
Hence the angle between 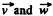 is equal to between
is equal to between 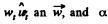 can be found by means of the formula
can be found by means of the formula 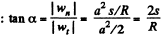
Q. 40. A particle moves along an arc of a circle of radius R according to the law l = a sin ωt, where l is the displacement from the initial position measured along the arc, and a and ω are constants. Assuming R = 1.00 m, a = 0.80 m, and co = 2.00 rad/s, find:
(a) the magnitude of the total acceleration of the particle at the points l = 0 and l = ±a;
(b) the minimum value of the total acceleration wmin and the corresponding displacement lm.
Ans. From the equation 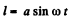
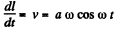
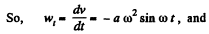 (1)
(1)
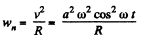 (2)
(2)
(a) At the point 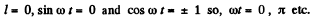
Hence 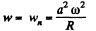
Similarly 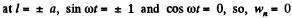
Hence 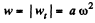
Q. 41. A point moves in the plane so that its tangential acceleration wτ = a, and its normal acceleration wn = bt4, where a and b are positive constants, and t is time. At the moment t = 0 the point was at rest. Find how the curvature radius R of the point's trajectory and the total acceleration w depend on the distance covered s.
Ans. As wt = a and at t = 0, the point is at rest
So, 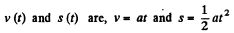 (1)
(1)
Let R be the curvature radius, then
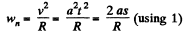
But according to the problem
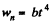
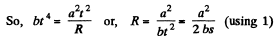
Therefore 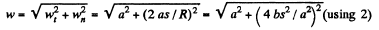
Hence 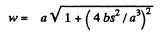
Q. 42. A particle moves along the plane trajectory y (x) with velocity v whose modulus is constant. Find the acceleration of the particle at the point x = 0 and the curvature radius of the trajectory at that point if the trajectory has the form
(a) of a parabola y = ax2;
(b) of an ellipse (xla)2 (y/b)2 = 1; a and b are constants here.
Ans. (a) Let us differentiate twice the path equation y (x) with respect to time.
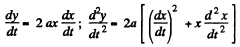
Since the particle moves uniformly, its acceleration at all points of the path is normal and at the point x = 0 it coincides with the direction of derivative 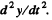 Keeping in mind that at the point
Keeping in mind that at the point 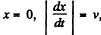
We get 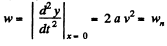
So, 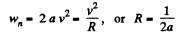
Note that we can also calculate it from the formula of problem (1.35 b)
(b) Differentiating the equation of the trajectory with respect to time we see that
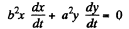 (1)
(1)
which implies that the vector 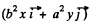 is normal to the velocity vector
is normal to the velocity vector 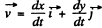 which, of course, is along the tangent. Thus the former vactor is along the normal and the normal component of acceleration is clearly
which, of course, is along the tangent. Thus the former vactor is along the normal and the normal component of acceleration is clearly
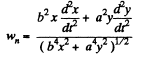
on using 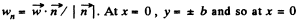
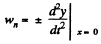
Differentiating (1)
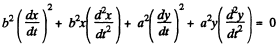
Also from (1) 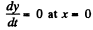
So, 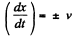 (since tangential velocity is constant = v)
(since tangential velocity is constant = v)
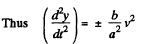
and 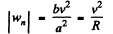
This gives R = a2/ b .
Q. 43. A particle A moves along a circle of radius R = 50 cm so that its radius vector r relative to the point O (Fig. 1.5) rotates with the constant angular velocity ω = 0.40 rad/s. Find the modulus of the velocity of the particle, and the modulus and direction of its total acceleration.
Ans. Let us fix the co-ordinate system at the point O as shown in the figure, such that the radius vector 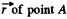 makes an angle θ with x axis at the moment shown.
makes an angle θ with x axis at the moment shown.
Note that the radius vector of the particle A rotates clockwise and we here take line ox as reference line, so in this case obviously the angular velocity 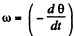 taking anticlockwise sense of angular displacement as positive.
taking anticlockwise sense of angular displacement as positive.
Also from the geometry of the triangle OAC 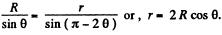
Let us write,
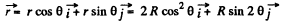
Differentiating with respect to time.
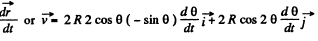
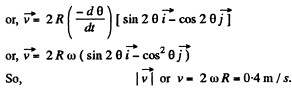
As ω is constant, v is also constant and 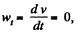
So, 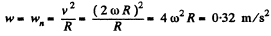
Alternate : From the Fig. the angular velocity of the point A, with respect to centre of the circle C becomes
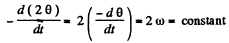
Thus we have the problem of finding the velocity and acceleration of a particle moving along a circle of radius R with constant angular velocity 2 ω
Hence
. 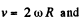
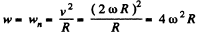
Q. 44. A wheel rotates around a stationary axis so that the rotation angle φ varies with time as φ = at2, where a = 0.20 rad/s2. Find the total acceleration w of the point A at the rim at the moment t = 2.5 s if the linear velocity of the point A at this moment v = 0.65 m/s.
Ans. Differentiating φ (t) with respect to time
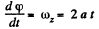 (1)
(1)
For fixed axis rotation, the speed of the point A:
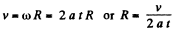 (2)
(2)
Differentiating with respect to time
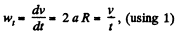
But 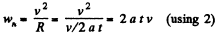
So, 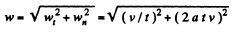
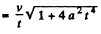
Q. 45. A shell acquires the initial velocity v = 320 m/s, having made n = 2.0 turns inside the barrel whose length is equal to l = 2.0 m. Assuming that the shell moves inside the barrel with a uniform acceleration, find the angular velocity of its axial rotation at the moment when the shell escapes the barrel.
Ans. The shell acquires a constant angular acceleration at the same time as it accelerates linearly. The two are related by (assuming both are constant)

Where w = linear acceleration and β = angular acceleration
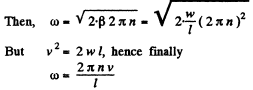
Q. 46. A solid body rotates about a stationary axis according to the law φ = at - bt3, where a = 6.0 rad/s and b = 2.0 rad/s3. Find:
(a) the mean values of the angular velocity and angular acceleration averaged over the time interval between t = 0 and the complete stop;
(b) the angular acceleration at the moment when the body stops.
Ans. Let us take the rotation axis as z-axis whose positive direction is associated with the positive direction o f the cordinate <p, the rotation angle, in accordance w ith the right-hand screw rule (Fig.)
(a) Defferentiating φ (t) with respect to time.
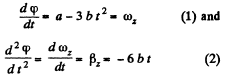
From (1) the solid comes to stop at 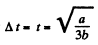
The angular velocity 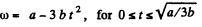

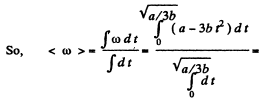
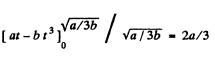
Sim ilarly 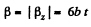 for all values of t.
for all values of t.
So, 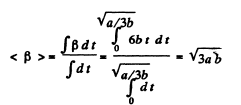
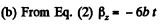
So, 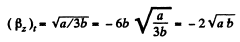
Hence 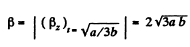
Q. 47. A solid body starts rotating about a stationary axis with an angular acceleration β = at, where a = 2.0.10-2 rad/s3. How soon after the beginning of rotation will the total acceleration vector of an arbitrary point of the body form an angle α = 60° with its velocity vector?
Ans. Angle a is related with |wt| and wn by means of the fomula :
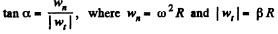 (1)
(1)
where R is die radius of die circle which an arbitrary point of the body circumscribes. From die given equation 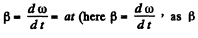 is positive for all values of t)
is positive for all values of t)
Integrating within the limit 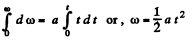
So, 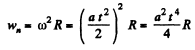
and 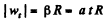
Putting the values of |wt| and wn in Eq. (1), we get,
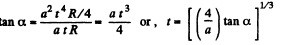
Q. 48. A solid body rotates with deceleration about a stationary axis with an angular deceleration 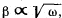 where ω is its angular velocity. Find the mean angular velocity of the body averaged over the whole time of rotation if at the initial moment of time its angular velocity was equal to ω0.
where ω is its angular velocity. Find the mean angular velocity of the body averaged over the whole time of rotation if at the initial moment of time its angular velocity was equal to ω0.
Ans. In accordance with the problem, βz < 0
Thus 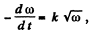 where A: is proportionality constant
where A: is proportionality constant
or, 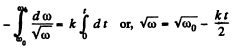 (1)
(1)
When ω = 0 , total time o f rotation 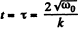
Average angular velocity 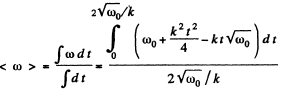
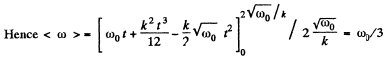
Q.49. A solid body rotates about a stationary axis so that its angular velocity depends on the rotation angle φ as ω = ω0 — aφ, where ω0 and a are positive constants. At the moment t = 0 the angle = 0. Find the time dependence of
(a) the rotation angle;
(b) the angular velocity.
Ans. We have 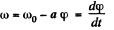
Integratin this Eq. within its limit for (φ) f
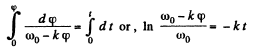
Hence 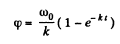 (1)
(1)
(b) From the 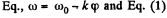 or by differentiating Eq. (1)
or by differentiating Eq. (1)
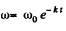
Q.50. A solid body starts rotating about a stationary axis with an angular acceleration β = β0 cos φ, where β0 is a constant vector and φ is an angle of rotation from the initial position. Find the angular velocity of the body as a function of the angle φ. Draw the plot of this dependence.
Ans. Let us choose the positive direction of z-axis (stationary rotation axis) along the vector 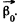
In accordance with the equation 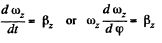
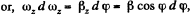
Integrating this Eq. within its limit for
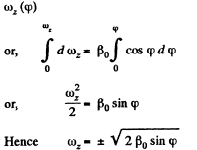
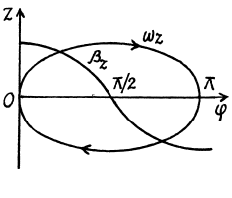
The plot 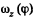 is shown in the Fig. It can be seen that as the angle qp grows, the vector
is shown in the Fig. It can be seen that as the angle qp grows, the vector 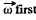 increases, coinciding with the direction of the vector
increases, coinciding with the direction of the vector 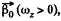 reaches the maximum at
reaches the maximum at 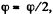 then starts decreasing and finally turns into zero at φ = π. After that the body starts rotating in the opposite direction in a similar fashion (ωz < 0). As a result, the body will oscillate about the position
then starts decreasing and finally turns into zero at φ = π. After that the body starts rotating in the opposite direction in a similar fashion (ωz < 0). As a result, the body will oscillate about the position 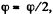 with an amplitude equal to π/2.
with an amplitude equal to π/2.
Q. 51. A rotating disc (Fig. 1.6) moves in the positive direction of the x axis. Find the equation y (x) describing the position of the instantaneous axis of rotation, if at the initial moment the axis C of the disc was located at the point O after which it moved
(a) with a constant velocity v, while the disc started rotating counterclockwise with a constant angular acceleration β (the initial angular velocity is equal to zero);
(b) with a constant acceleration w (and the zero initial velocity), while the disc rotates counterclockwise with a constant angular velo- city ω.
Ans. Rotating disc moves along the x-axis, in plane motion in x - y plane. Plane motion of a solid can be imagined to be in pure rotation about a point (say 7) at a certain instant known as instantaneous centre of rotation. The instantaneous axis whose positive sense is directed along 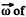 the solid and which passes through the point/, is known as instantaneous axis of rotation.
the solid and which passes through the point/, is known as instantaneous axis of rotation.
Therefore the velocity vector of an aibitrary point (P) of the solid can be represented as :
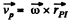 (1)
(1)
On the basis of Eq. (1) for the C. M. (C) of the disc
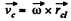 (2)
(2)
According to the problem 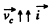 and
and 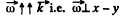 plane, so to satisy the
plane, so to satisy the 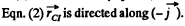 Hence point l is at a distance
Hence point l is at a distance 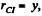 above the centre of the disc along y - axis. Using all these facts in Eq. (2), we get
above the centre of the disc along y - axis. Using all these facts in Eq. (2), we get
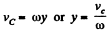 (3)
(3)
(a) From the angular kinematical equation
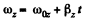
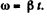 (4)
(4)
On the other hand x = v t, (where x is the x coordinate of the C.M.)
or, t = x/y (5)
From Eqs. (4) and (5), 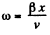
Using this value o f co in Eq. (3) w e get 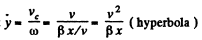
(b) As centre C moves with constant acceleration w, with zero initial velocity
So, 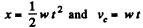
Therefore, 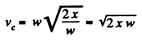
Hence 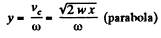
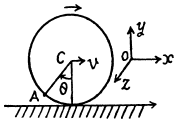
Q. 52. A point A is located on the rim of a wheel of radius R = 0.50 m which rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface with velocity v = 1.00 m/s. Find:
(a) the modulus and the direction of the acceleration vector of the point A;
(b) the total distance s traversed by the point A between the two successive moments at which it touches the surface.
Ans. The plane motion of a solid can be imagined as the combination of translation of the C.M . and rotation about C.M.
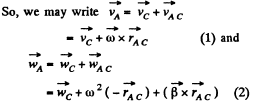
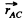 is the position o f vector o f A with respect to C.
is the position o f vector o f A with respect to C.
In the problem 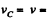 constant, and the rolling is without slipping
constant, and the rolling is without slipping 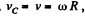
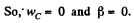 Using these conditions in Eq. (2)
Using these conditions in Eq. (2)
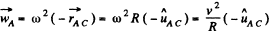
Here, 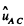 is the unit vector directed along
is the unit vector directed along 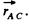
Hence 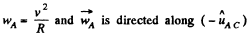 or directed toward the centre of the wheel.
or directed toward the centre of the wheel.
(b) Let the centre o f the wheel m ove toward right (positive jc-axis) then for pure tolling on the rigid horizontal surface, wheel will have to rotate in clockwise sense. If co be the angular velocity o f the wheel then 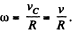
Let the point A touches the horizontal surface at t = 0, further let us locate the point A at t = ty
When it makes θ = ω t at the centre of the wheel.
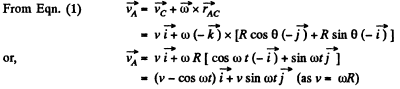
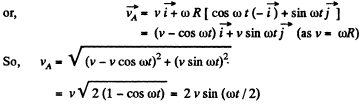
H ence distance covered b y the point A during 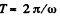
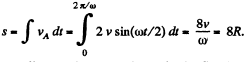
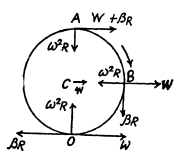
Q. 53. A ball of radius R = 10.0 cm rolls without slipping down an inclined plane so that its centre moves with constant acceleration w = 2.50 cm/s2; t = 2.00 s after the beginning of motion its position corresponds to that shown in Fig. 1.7. Find:
(a) the velocities of the points A, B, and 0;
(b) the accelerations of these points.
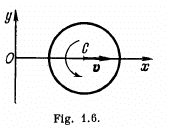
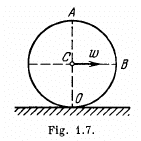
Ans. Let us fix the co-ordinate axis xyz as shown in the fig. As the ball rolls without slipping along the rigid surface so, on the basis o f the solution o f problem Q.52 :
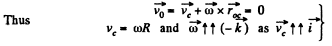
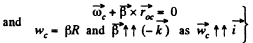
At the position corresponding to that of Fig., in accordance with the problem,
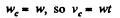
and 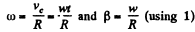
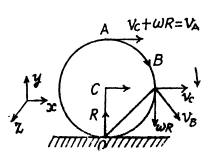
(a) Let us fix the co-ordinate system with the frame attached with the rigid surface as shown in the Fig.
As point O is the instantaneous centre of rotation of the ball at the moment shown in Fig.
so, 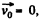
Now, 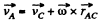
So, 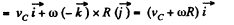
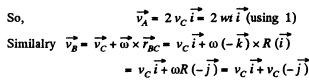
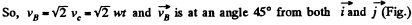
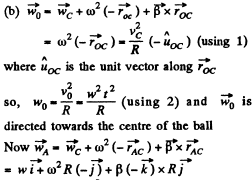

So, 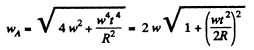
Similarly 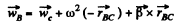
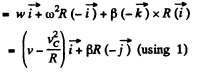
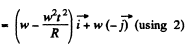
So, 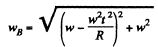
Q. 54. A cylinder rolls without slipping over a horizontal plane. The radius of the cylinder is equal to r. Find the curvature radii of trajectories traced out by the points A and B (see Fig. 1.7).
Ans. Let us draw the kinematical diagram of the rolling cylinder on the basis of the solutioi of problem Q.53.
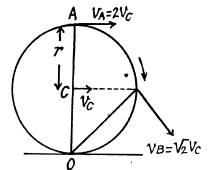
As, an arbitrary point of the cylinder follows a curve, its normal acceleration and radius of curvature are related by the well known equation
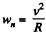
so, for point A, 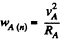
or, 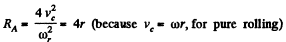
Similarly for point B,
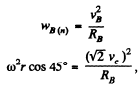
or, 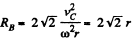
Q. 55. Two solid bodies rotate about stationary mutually perpendicular intersecting axes with constant angular velocities ω1 = 3.0 rad/s and ω2 = 4.0 rad/s. Find the angular velocity and angular acceleration of one body relative to the other.
Ans. The angular velocity is a vector as infinitesimal rotation commute. Then file relative angular velocity of the body 1 with respect to the body 2 is dearly.
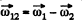
as fo r relative lin ear velocity. The relative acceleration of 1 w.r.t 2 is
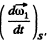
where S ' is a fram e corotating with the second body and S is a space fixed frame with origin coinciding with the point of intersection of the two axes,
but 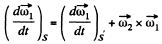
Since S ' rotates with angular velocity 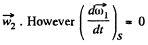 as the first b ody rotates with constant angular velocity in space, thus
as the first b ody rotates with constant angular velocity in space, thus
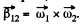
Note that for any vector 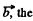 relation in space forced frame (k) and a frame (Jd) rotating with angular velocity
relation in space forced frame (k) and a frame (Jd) rotating with angular velocity 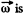
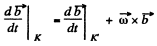
Q. 56. A solid body rotates with angular velocity ω = ati + bt2j, where a = 0.50 rad/s2, b = 0.060 rad/s3, and i and j are the unit vectors of the x and y axes. Find:
(a) the moduli of the angular velocity and the angular acceleration at the moment t = 10.0 s;
(b) the angle between the vectors of the angular velocity and the angular acceleration at that moment.
Ans. We have 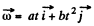 (1)
(1)
So, 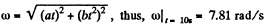
D ifferen tia tin g E q. (1) with respect to time
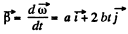 (2)
(2)
So, 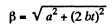
and 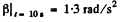
(b) 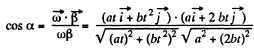
Putting the values of (a) and (b) and ' taking t =10s, we get
α = 17°
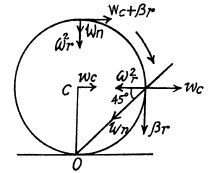
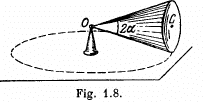
Q. 57. A round cone with half-angle α = 30° and the radius of the base R = 5.0 cm rolls uniformly and without slipping over a horizontal plane as shown in Fig. 1.8. The cone apex is hinged at the point O which is on the same level with the point C, the cone base centre. The velocity of point C is v = 10.0 cm/s. Find the moduli of
(a) the vector of the angular velocity of the cone and the angle it forms with the vertical;
(b) the vector of the angular acceleration of the cone.
Ans. Let the axis of the cone (OC) rotates in an ticlockw ise sense w ith constant angular velocity  and the cone itself about it’s own axis (OC) in clockwise sense with angular velocity
and the cone itself about it’s own axis (OC) in clockwise sense with angular velocity 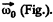 Then the resultant angular velocity of the cone.
Then the resultant angular velocity of the cone.
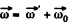 (1)
(1)
As the rolling is pure the magnitudes of the vectors
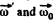 can be easily found from Fig.
can be easily found from Fig.
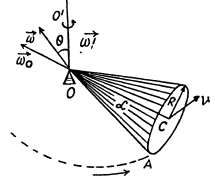
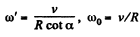 (2)
(2)
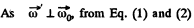
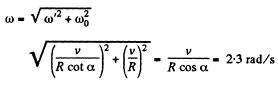
(b) Vector of angular acceleration
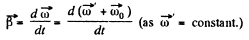
The vector 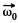 which rotates about the OO' axis with the angular velocity
which rotates about the OO' axis with the angular velocity 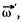 retains i magnitude. This increment in the time interval dt is equal to
retains i magnitude. This increment in the time interval dt is equal to
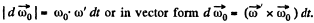
Thus 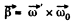
The magnitude of the vector 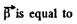
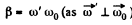
So, 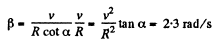
Q. 58. A solid body rotates with a constant angular velocity ω0 = 0.50 rad/s about a horizontal axis AB. At the moment t = 0 the axis AB starts turning about the vertical with a constant angular acceleration β0 = 0.10 rad/s2. Find the angular velocity and angular acceleration of the body after t = 3.5 s.
Ans. The axis AB acquired the angular velocity
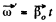 (1)
(1)
Using the facts of the solution of 1.57, the angular velocity of the body
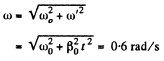
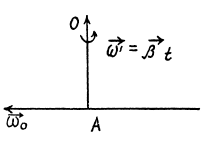
And the angular acceleration.
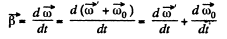
But 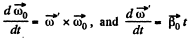
So, 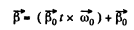
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Kinematics - 3 - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is kinematics in physics? |  |
| 2. What are the three basic equations of motion in kinematics? |  |
| 3. How is average speed different from average velocity in kinematics? |  |
| 4. What is projectile motion in kinematics? |  |
| 5. How is instantaneous velocity different from average velocity in kinematics? |  |
















