JEE Exam > JEE Notes > Additional Study Material for JEE > States of Matter
States of Matter | Additional Study Material for JEE PDF Download
Introduction
- States of the matter are of prime importance to physicists. Everyday elements and compounds form three physical states of matter, however, there are many other states, less common but equally important.
- The liquid-crystal state of certain compounds has the properties of solids as well as liquids and is the basis of electronic displays. More states are obtained when the particles are lighter.
- The electrons in metals and ceramics undergo a change due to which electricity is conducted without dissipation.
Thus matter is classified mainly into three categories depending upon its physical state namely: Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous states.
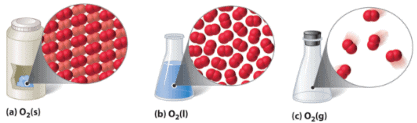
Basic Difference among the Three States of Matter:
- Solids have a definite volume and shape: Definite shape and volume of the solids is result of strong forces of attraction between its constituent particles which keep them together in a fixed position and arrangement.
- Liquids also have a definite volume but no definite volume: They take shape of the container in which they are placed. This is due to the relatively weaker force of attraction among the particles of liquid.
- Gases have neither a definite volume nor a definite shape: They fill the container completely in which they are placed. This is due to the fact that the force of attraction among the particles of liquids is almost zero and they are free to move independently to each other.
 Illustration of Different states of matter
Illustration of Different states of matter
Table: Propeties of Different States of Matter
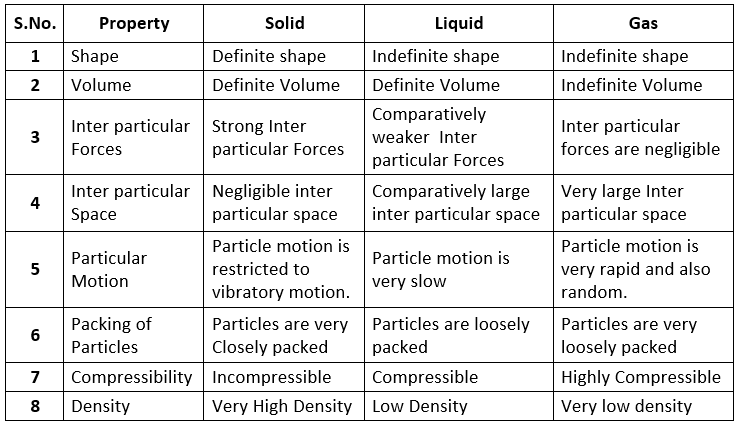
Intermolecular Forces
- Intermolecular forces can be described as the forces of attraction and repulsion existing between the interacting particles of atoms and molecules in a compound.
- The attractive intermolecular forces are called Vander Waals forces which include dispersion forces or London forces, dipole-dipole forces, and dipole-induced dipole forces.
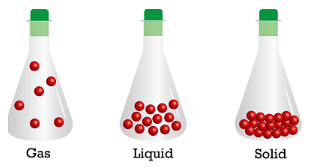
- Intermolecular forces in the case of solids are very strong. The constituent particles are closely packed thereby making the solids incompressible and of high density.
 Intermolecular arrangement in Solids
Intermolecular arrangement in Solids
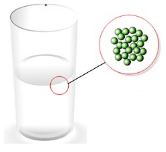
- Intermolecular forces in the case of liquids keep the particles tied to each other but cannot keep them in fixed positions thereby making them easy to flow and have a definite shape.
 Intermolecular arrangement in Liquids
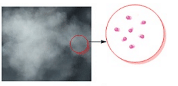
Intermolecular arrangement in Liquids - Intermolecular forces in the case of gases are extremely weak thereby allowing the constituent particles to move freely.
 Intermolecular arrangement in Gases
Intermolecular arrangement in Gases
Melting and Boiling Points
Boiling Point
- The boiling point is the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure of the liquid and the liquid is converted to vapour.
- The boiling point of the liquid depends upon the pressure of the surrounding. When the liquid is at high pressure, it has a higher boiling point than the boiling point at normal atmospheric pressure.
- The boiling point of different liquids is different for a given pressure.
- In 1982, IUPAC defined standard boiling point which is the temperature at which liquid boils under the pressure of 1 bar.
- The boiling point changes with altitude and that’s why when we go to mountain areas i.e. at higher altitudes cooking food takes more time because the pressure decreases and therefore because of this it takes more time in cooking food at hilly areas.
Melting Point
- The temperature at which a solid changes its state to liquid at atmospheric pressure is called the melting point of that liquid.
- This is the point at which both liquid and solid phase exists at equilibrium.
- The melting point of the substance also varies with pressure and is specified at standard pressure.
 View Answer
View AnswerNote:
Another term is freezing point which is just reverse of melting point which is the temperature at which liquid is converted to solid. Technically, you can say that melting point and freezing point are not same because a substance can be super cooled below its freezing point without forming solid.
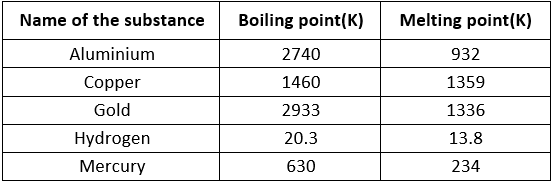
Table: Boiling point and Melting point of Different Substance
The document States of Matter | Additional Study Material for JEE is a part of the JEE Course Additional Study Material for JEE.
All you need of JEE at this link: JEE
|
22 videos|162 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on States of Matter - Additional Study Material for JEE
| 1. What are intermolecular forces? |  |
Ans. Intermolecular forces are the attractive forces that exist between molecules. These forces play a significant role in determining the physical properties of substances such as melting and boiling points.
| 2. How do intermolecular forces affect the melting and boiling points of substances? |  |
Ans. Intermolecular forces determine the strength of attraction between molecules. The stronger the intermolecular forces, the higher the melting and boiling points of a substance. This is because more energy is required to overcome these forces and change the substance from a solid to a liquid or a gas.
| 3. What are the different states of matter? |  |
Ans. The three primary states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. In the solid state, particles are tightly packed and have a fixed shape and volume. In the liquid state, particles are close together but can move past each other, resulting in a definite volume but no fixed shape. In the gas state, particles are far apart and move freely, leading to no fixed shape or volume.
| 4. Why do substances with strong intermolecular forces have higher melting and boiling points? |  |
Ans. Substances with strong intermolecular forces have higher melting and boiling points because the intermolecular forces hold the molecules together more tightly. This requires more energy to break the forces and change the substance from a solid to a liquid or a gas, resulting in higher melting and boiling points.
| 5. How do intermolecular forces impact the properties of substances? |  |
Ans. Intermolecular forces influence various properties of substances, including their boiling and melting points, solubility, viscosity, and surface tension. These forces affect the arrangement and movement of molecules, which in turn determine the macroscopic behavior and characteristics of different substances.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches