Irodov Solutions: Electric Oscillations- 1 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q.94. Due to a certain cause the free electrons in a plane copper plate shifted over a small distance x at right angles to its surface. As a result, a surface charge and a corresponding restoring force emerged, giving rise to so-called plasma oscillations. Find the angular frequency of these oscillations if the free electron concentration in copper is n, = 0.85.1029 m-1.
Ans. I f the electron (charge o f each electron = - e ) are shifted by a smaii distance x, a net + ve charge density (per unit area) is induced on the surface. This will result in an electric field 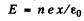 in the direction of x and a restoring force on an electron of
in the direction of x and a restoring force on an electron of
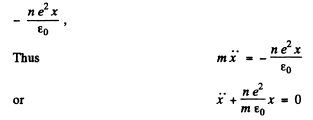
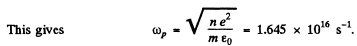
as the plasma frequency for the problem.
Q.95. An oscillating circuit consisting of a capacitor with capacitance C and a coil of inductance L maintains free undamped oscillations with voltage amplitude across the capacitor equal to Vm. For an arbitrary moment of time find the relation between the current I in the circuit and the voltage V across the capacitor. Solve this problem using Ohm's law and then the energy conservation law.
Ans. Since there are no sources of emf in the circuit, Ohm’s 1 law reads
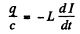
where q = change on the capacitor, 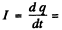 current through the coil. Then
current through the coil. Then
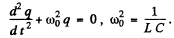
The solution fo this equation is
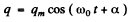
From the problem 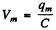 Then
Then
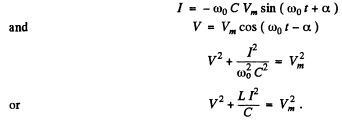
By energy conservation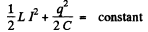
When the P.D. across the capacitor takes its maximum value Vm, the current I must be zero. Thus "constant” 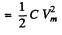
Hence 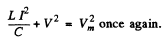
Q.96. An oscillating circuit consists of a capacitor with capacitance C, a coil of inductance L with negligible resistance, and a switch. With the switch disconnected, the capacitor was charged to a voltage Vm, and then at the moment t = 0 the switch was closed. Find:
(a) the current I (t) in the circuit as a function of time;
(b) the emf of self-inductance in the coil at the moments when the electric energy of the capacitor is equal to that of the current in the coil.
Ans. After the switch was closed, the circuit satisfies
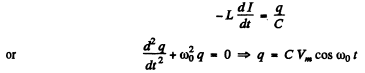
where we have used the fact that when the switch is dosed we must have
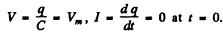
Thus (a)
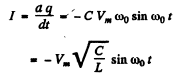
(b) The electrical energy of the capacitor is 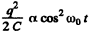 and of the inductor is
and of the inductor is
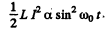
The two are equal when
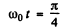
At that instant the emf of the self-inductance is
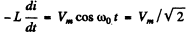
Q.97. In an oscillating circuit consisting of a parallel-plate capacitor and an inductance coil with negligible active resistance the oscillations with energy W are sustained. The capacitor plates were slowly drawn apart to increase the oscillation frequency η-fold. What work was done in the process?
Ans. In the oscillating circuit, let
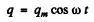
be the change on the condenser where
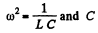 and C is the instantaneous capacity of the condenser (S = area of plates)
and C is the instantaneous capacity of the condenser (S = area of plates)
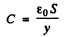
y = distance between the plates. Since the oscillation frequency increases η fold, the quantity
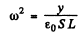
changes η2 fold and so does y i.e. changes from y0 initially to η2y0 finally. Now the P.D.across the condenser is
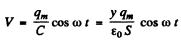
and hence the electric field between the plates is
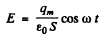
Thus, the chaige on the plate being 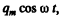 the force on the plate is
the force on the plate is
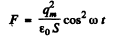
Since this force is always positive and the plate is pulled slowly we can use the average force
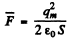
and work done is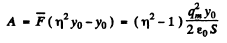
But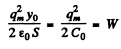 the initial stored energy. Thus.
the initial stored energy. Thus.
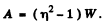
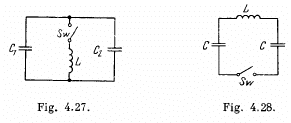
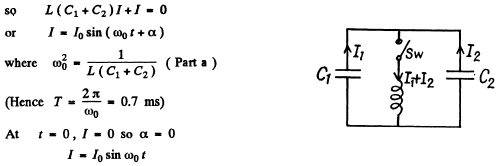
Q.98. In an oscillating circuit shown in Fig. 4.27 the coil inductance is equal to L = 2.5 mH and the capacitor have capacitances C1 2.0 μF and C2 = 3.0 μF. The capacitors were charged to a voltage V = 180 V, and then the switch Sw was closed. Find:
(a) the natural oscillation frequency;
(b) the peak value of the current flowing through the coil.
Ans. The equations of the L - C circuit are
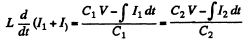
Differentiating again 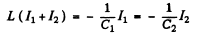
Then
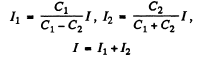
The peak value of the current is 70 and it is related to the voltage V by the first equation
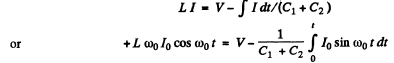
(The P.D. across the inductance is V at t = 0)
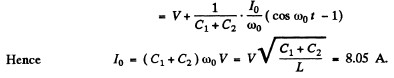
Q.99. An electric circuit shown in Fig. 4.28 has a negligibly small active resistance. The left-hand capacitor was charged to a voltage V0 and then at the moment t = 0 the switch Sw was closed. Find the time dependence of the voltages in left and right capacitors.
Ans. Initially q1 = C V 0 and q2 = 0. After the switch is closed change flows and w e get
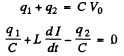
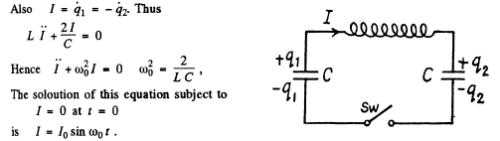
Integrating
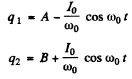
Finally substituting in (1)
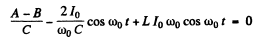
Thus
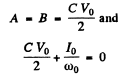
so
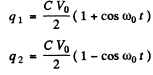
Q.100. An oscillating circuit consists of an inductance coil L and a capacitor with capacitance C. The resistance of the coil and the lead wires is negligible. The coil is placed in a permanent magnetic field so that the total flux passing through all the turns of the coil is equal to φ. At the moment t = 0 the magnetic field was switched off. Assuming the switching off time to be negligible compared to the natural oscillation period of the circuit, find the circuit current as a function of time t.
Ans. The flux in the coil is
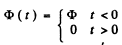
The equation of the current is 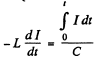 (1)
(1)
This mean that 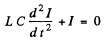

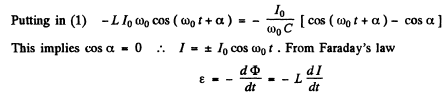
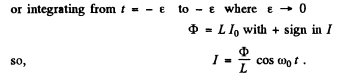
Q.101. The free damped oscillations are maintained in a circuit, such that the voltage across the capacitor varies as 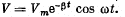 Find the moments of time when the modulus of the voltage across the capacitor reaches
Find the moments of time when the modulus of the voltage across the capacitor reaches
(a) peak values;
(b) maximum (extremum) values.
Ans. Given 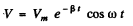
(a) The phrase ‘peak values’ is not clear. The answer is obtained on taking 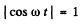
i.e 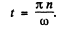
(b) For extrema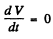
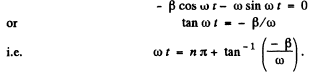
Q.102. A certain oscillating circuit consists of a capacitor with capacitance C, a coil with inductance L and active resistance R, and a switch. When the switch was disconnected, the capacitor was charged; then the switch was closed and oscillations set in. Find the ratio of the voltage across the capacitor to its peak value at the moment immediately after closing the switch.
Ans. The equation of the circuit is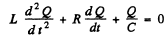
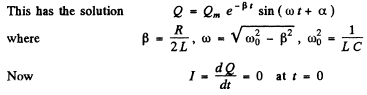
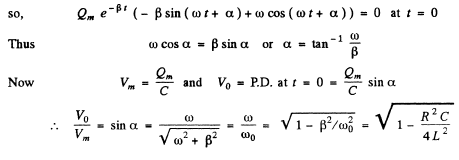
Q.103. A circuit with capacitance C and inductance L generates free damped oscillations with current varying with time as I = = lme-βt sin ωt. Find the voltage across the capacitor as a function of time, and in particular, at the moment t = 0.
Ans. We write
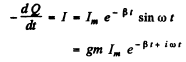 (gm means imaginary part)
(gm means imaginary part)
Then
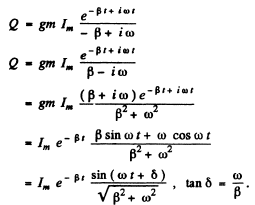
(An arbitrary constant of integration has been put equal to zero.) Thus
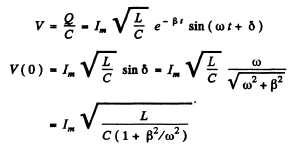
Q.104. An oscillating circuit consists of a capacitor with capacitance C = 4.0 μF and a coil with inductance L = 2.0 mH and active resistance R = 10Ω. Find the ratio of the energy of the coil's magnetic field to that of the capacitor's electric field at the moment when the current has the maximum value.
Ans.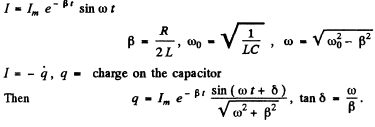
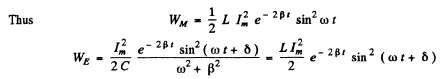
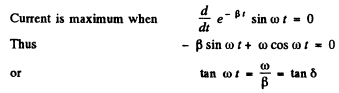
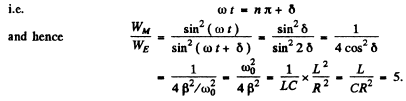
(WM is the magnetic energy of the inductance coil and WE is the electric energy ot t! capacitor.)
Q.105. An oscillating circuit consists of two coils connected in series whose inductances are L1 and L2, active resistances are R1 and R2, and mutual inductance is negligible. These coils are to be replaced by one, keeping the frequency and the quality factor of the circuit constant. Find the inductance and the active resistance of such a coil.
Ans. Clearly
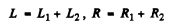
Q.106. How soon does the current amplitude in an oscillating circuit with quality factor Q = 5000 decrease η = 2.0 times if the oscillation frequency is v = 2.2 MHz?
Ans.
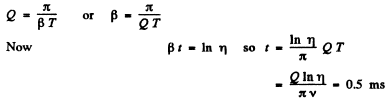
Q.107. An oscillating circuit consists of capacitance C = 10μF, inductance L = 25 mH, and active resistance R 1.0 Ω. How many oscillation periods does it take for the current amplitude to decrease e-fold?
Ans. Current decreases e fold in time
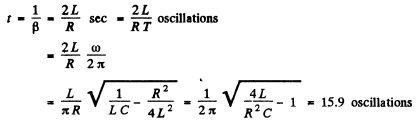
Q.108. How much (in per cent) does the free oscillation frequency ω of a circuit with quality factor Q = 5.0 differ from the natural oscillation frequency ω0 of that circuit?
Ans.
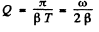
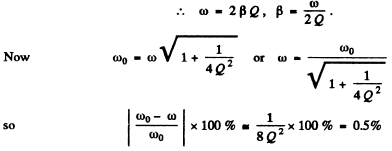
Q.109. In a circuit shown in Fig. 4.29 the battery emf is equal to �� = 2.0 V, its internal resistance is r = 9.0Ω, the capacitance of the capacitor is C = 10μF, the coil inductance is L = 100 mH, and the resistance
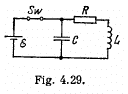
is R = 1.0 Ω. At a certain moment the switch Sw was disconnected. Find the energy of oscillations in the circuit
(a) immediately after the switch was disconnected;
(b) t = 0.30 s after the switch was disconnected.
Ans.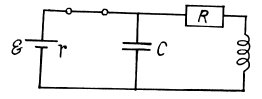
At t = 0 current through the coil 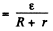
P.D. across the condenser 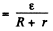
(a) At t - 0, energy stored = W0
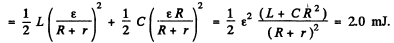
(b) The current and the change stored decrease as e-t R/2L so energy decreases as e-t R/L
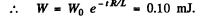
Q.110. Damped oscillations are induced in a circuit whose quality factor is Q = 50 and natural oscillation frequency is vo = 5.5 kHz. How soon will the energy stored in the circuit decrease η = 2.0 times?
Ans.
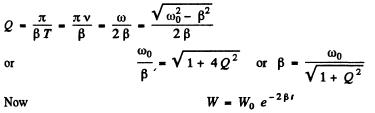
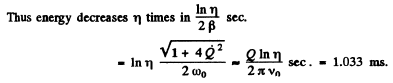
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Electric Oscillations- 1 - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is the equation for the period of an electric oscillation? |  |
| 2. How does the frequency of an electric oscillation change with the change in capacitance? |  |
| 3. Can an electric oscillation occur without the presence of an inductor or a capacitor? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of resonance in electric oscillations? |  |
| 5. How does the damping factor affect the amplitude of an electric oscillation? |  |
















