Irodov Solutions: Equation of The Gas State Processes | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Q. 1. A vessel of volume V = 30 l contains ideal gas at the temperature 0°C. After a portion of the gas has been let out, the pressure in the vessel decreased by Δp = 0.78 atm (the temperature remaining constant). Find the mass of the released gas. The gas density under the normal conditions p = 1.3 g/I.
Solution. 1. Let m1 and m2 be the masses of the gas in the vessel before and after the gas is released. Hence mass of the gas released,
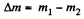
Now from ideal gas equation
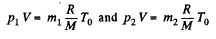
as V and T are same before and after the release of the gas.
so, 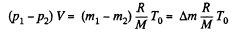
or, 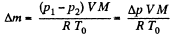 (1)
(1)
We also know 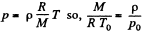 (2)
(2)
(where p0 = standard atmospheric pressure and 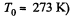
From Eqs. (1) and (2) we get
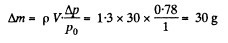
Q. 2. Two identical vessels are connected by a tube with a valve letting the gas pass from one vessel into the other if the pressure difference 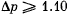 atm. Initially there was a vacuum in one vessel while the other contained ideal gas at a temperature t1 = 27°C and pressure p1 = 1.00 atm. Then both vessels were heated to a temperature t2 =107°C. Up to what value will the pressure in the first vessel (which had vacuum initially) increase?
atm. Initially there was a vacuum in one vessel while the other contained ideal gas at a temperature t1 = 27°C and pressure p1 = 1.00 atm. Then both vessels were heated to a temperature t2 =107°C. Up to what value will the pressure in the first vessel (which had vacuum initially) increase?
Solution. 2. Let m1 be the mass of the gas enclosed.
Then, 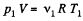
When heated, some gas, passes into the evacuated vessel till pressure difference becomes 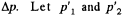 be the pressure on the two sides of the valve. Then
be the pressure on the two sides of the valve. Then 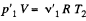 and
and 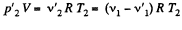
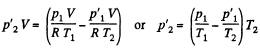
But, 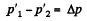
So, 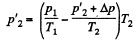
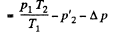
or, 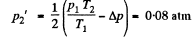
Q. 3. A vessel of volume V = 20 l contains a mixture of hydrogen and helium at a temperature t = 20°C and pressure p = 2.0 atm. The mass of the mixture is equal to m = 5.0 g. Find the ratio of the mass of hydrogen to that of helium in the given mixture.
Solution. 3. Let the mixture contain v1 and v2 moles of H2 and He respectively. If molecular weights of H2 and He are M1 and M2, then respective masses in the mixture are equal to
m1 = v1M1 and m2 = v2M2
Therefore, for the total mass of the mixture we get,
m = m1 + m2 or m = v1 M1 + v2 M2 (1)
Also, if v is the total number of moles of the mixture in the vessels, then we know,
V = V1 + V2 (2)
Solving (1) and (2) for v1 and v2, we get,
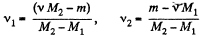
Therefore, we get 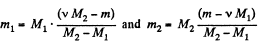
or, 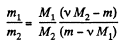
One can also express the above result in terms of the effective molecular weight M of the mixture, defined as,
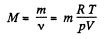
Thus, 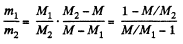
Using the data and table, we get :
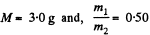
Q. 4. A vessel contains a mixture of nitrogen (m1 = 7.0 g) and carbon dioxide (m2 = 11 g) at a temperature T = 290 K and pressure p0, = 1.0 atm. Find the density of this mixture, assuming the gases to be ideal.
Solution. 4. We know, for the mixture, N2 and CO2 (being regarded as ideal gases, their mixture too behaves like an ideal gas)
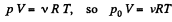
where, v is the total number of moles of the gases (mixture) present and V is the volume of the vessel. If v1 and v2 are number of moles of N2 and CO2 respectively present in the mixture, then
v = v1 + v2
Now number of moles of N2 and CO2 is, by definition, given by
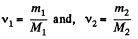
where, m1 is the mass of N2 (Moleculer weight = M1) in the mixture and m2 is the mass of CO2 (Molecular weight = M2) in the mixture.
Therefore density of the mixture is given by
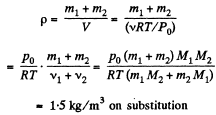
Q. 5. A vessel of volume V = 7.5 1 contains a mixture of ideal gases at a temperature T = 300 K: v1 = 0.10 mole of oxygen, v2 = 0.20 mole of nitrogen, and v3 = 0.30 mole of carbon dioxide. Assuming the gases to be ideal, find:
(a) the pressure of the mixture;
(b) the mean molar mass M of the given mixture which enters its equation of state pV = (m/M) RT, where m is the mass of the mixture.
Solution. 5. (a) The mixture contains v1, v2 and v3 moles of O2 > N2 and CO2 respectively. Then the total number of moles of the mixture
v = v1 + v2 + v3
We know, ideal gas equation for the mixture
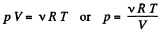
or, 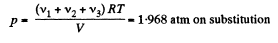
(b ) M ass o f oxygen (O2) present in the mixture : m1 = v1 M1
Mass of nitrogen (N2) present in the mixture : m2 = v2M2
Mass of carbon dioxide (CO2) present in the mixture : m3 = v3M3
So, mass of the mixture
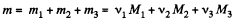
Moleculer mass of the mixture 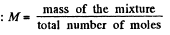
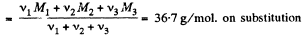
Q. 6. A vertical cylinder closed from both ends is equipped with an easily moving piston dividing the volume into two parts, each containing one mole of air. In equilibrium at T0 = 300 K the volume of the upper part is η = 4.0 times greater than that of the lower part. At what temperature will the ratio of these volumes be equal η' = 3.0?
Solution. 6. Let p1 and p2 be the pressure in the upper and lower part of the cylinder respectively at temperature T0. At the equilibrium position for the piston :
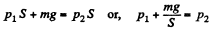 (m is the mass o f the piston.)
(m is the mass o f the piston.)
But 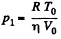 (where V0 is the initial volume of the lower part)
(where V0 is the initial volume of the lower part)
So, 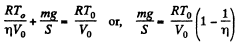 (1)
(1)
Let T be the sought temperature and at this temperature the volume of the lower part becomes V, then according to the problem the volume of the upper part becomes η'V'
Hence, 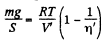 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2).
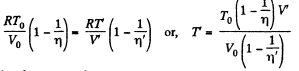
As, the total volume must be constant,
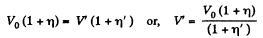
Putting the value of V in Eq. (3), we get
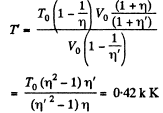
Q. 7. A vessel of volume V is evacuated by means of a piston air pump. One piston stroke captures the volume ΔV. How many strokes are needed to reduce the pressure in the vessel η times? The process is assumed to be isothermal, and the gas ideal.
Solution. 7. Let P1 be the density after the first stroke. The the mass remains constant
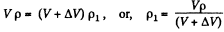
Similarly, if p2 is the density after second stroke
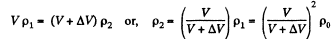
In this way after nth stroke.
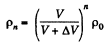
Since pressure α density,
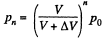 (because temperature is constant)
(because temperature is constant)
It is required by 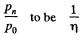
so, 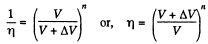
Hence 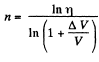
Q. 8. Find the pressure of air in a vessel being evacuated as a function of evacuation time t. The vessel volume is V, the initial pressure is P0. The process is assumed to be isothermal, and the evacuation rate equal to C and independent of pressure.
Note. The evacuation rate is the gas volume being evacuated per unit time, with that volume being measured under the gas pressure attained by that moment.
Solution. 8. From the ideal gas equation 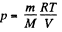
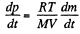 (1)
(1)
In each stroke, volume v of the gas is ejected, where v is given by
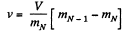
In case of continuous ejection, if (mN-1) corresponds to mass of gas in the vessel at time t, then mN is the mass at time t + Δt, where Δt, is the time in which volume v of the ga
has come out. The rate of evacuation is therefore 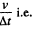
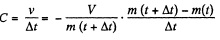
In the lim it Δt - 0, we get
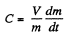 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2)
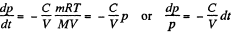
Integrating 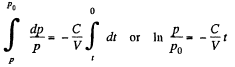
Thus 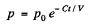
Q. 9. A chamber of volume V = 87 l is evacuated by a pump whose evacuation rate (see Note to the foregoing problem) equals C = 10 1/s. How soon will the pressure in the chamber decrease by η = 1000 times?
Solution. 9. Let p be the instantaneous density, then instantaneous mass = Vp. In a short interval dt the volume is increased by Cdt.
So, 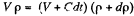
(because mass remains constant in a short interval dt)
so, 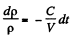
Since pressure α density 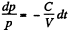
or 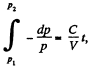
or 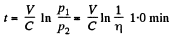
Q. 10. A smooth vertical tube having two different sections is open from both ends and equipped with two pistons of different areas (Fig. 2.1). Each piston slides within a respective tube section. One mole of ideal gas is enclosed between the pistons tied with a non-stretchable thread. The crosssectional area of the upper piston is ΔS = 10 cm2 greater than that of the lower one. The combined mass of the two pistons is equal to m = 5.0 kg. The outside air pressure is P0 = 1.0 atm. By how many kelvins must the gas between the pistons be heated to shift the pistons through l = 5.0 cm?
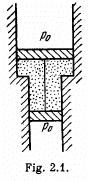
Solution. 10. The physical system consists of one mole of gas confined in the smooth vertical tube. Let m1 and m2 be the masses of upper and lower pistons and S1 and S2 are their respective areas.
For the lower piston
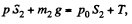
or, 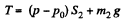 (1)
(1)
Similarly for the upper piston
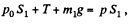
or, 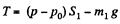 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2)
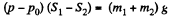
or, 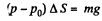
so, 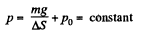
From the gas law, p V = v R T
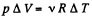 (because p is constant)
(because p is constant)
So, 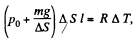
Hence, 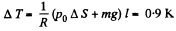
Q. 11. Find the maximum attainable temperature of ideal gas in each of the following processes:
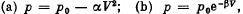
where p0,,α and β are positive constants, and V is the volume of one mole of gas.
Solution. 11. 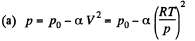
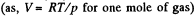
Thus, 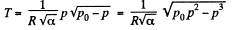 (1)
(1)
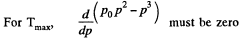
which yields, 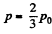 (2)
(2)
Hence, 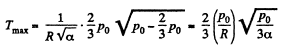
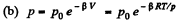
so 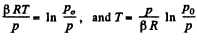 (1)
(1)
For Tmax the condition is 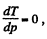 which yields
which yields
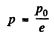
Hence using this value of p in Eq. (1), we get
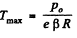
Q. 12. Find the minimum attainable pressure of ideal gas in the process T = T0 + α V2, where T0 and α are positive constants, and V is the volume of one mole of gas. Draw the approximate p vs V plot of this process.
Solution. 12. 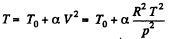
(as, V = RT/p for one mole of gas)
So, 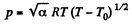 (1)
(1)
For 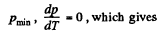
T = 2 T0 (2)
From (1) and (2), we get,
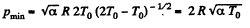
Q. 13. A tall cylindrical vessel with gaseous nitrogen is located in a uniform gravitational field in which the free-fall acceleration is equal to g. The temperature of the nitrogen varies along the height h so that its density is the same throughout the volume. Find the temperature gradient dT/dh.
Solution. 13. Consider a thin layer at a height h and thickness dh. Let p and dp+p be the pressure on the two sides of the layer. The mass of the layer is Sdhp. Equating vertical downward force to the upward force acting on the layer.
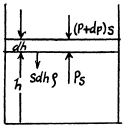
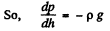 (1)
(1)
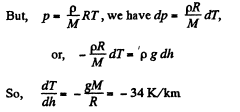
That means, temperature of air drops by 34°C at a height of 1 km above bottom.
Q. 14. Suppose the pressure p and the density p of air are related as p/pn = const regardless of height (n is a constant here). Find the corresponding temperature gradient.
Solution. 14.  (1)
(1)
But, from 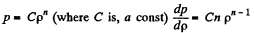 (2)
(2)
We have from gas low 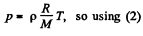
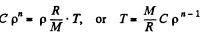
Thus, 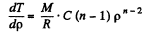
But, 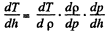
so, 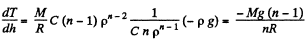
Q. 15. Let us assume that air is under standard conditions close to the Earth's surface. Presuming that the temperature and the molar mass of air are independent of height, find the air pressure at the height 5.0 km over the surface and in a mine at the depth 5.0 km below the surface.
Solution. 15. We have, dp = - p g dh and from gas law 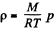
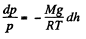
Integrating, we get
or, 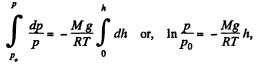
(where p0 is the pressure at the surface of the Earth.)
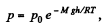
[Under standard condition, 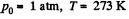
Pressure at a height of 5 atm 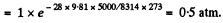
Pressure in a mine at a depth of 5 km 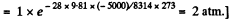
Q. 16. Assuming the temperature and the molar mass of air, as well as the free-fall acceleration, to be independent of the height, find the difference in heights at which the air densities at the temperature 0°C differ
(a) e times; (b) by η = 1.0%.
Solution. 16. We have dp = - pg dh but from gas law 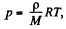
Thus  at const, temperature
at const, temperature
So, 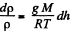
Integrating within limits 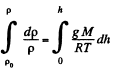
or, 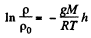
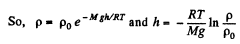
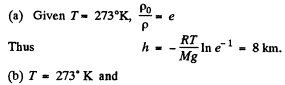
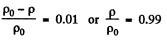
Thus 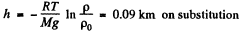
Q. 17. An ideal gas of molar mass M is contained in a tall vertical cylindrical vessel whose base area is S and height h. The temperature of the gas is T, its pressure on the bottom base is P0. Assuming the temperature and the free-fall acceleration g to be independent of the height, find the mass of gas in the vessel.
Solution. 17. From the Barometric formula, we have
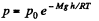
and from gas law
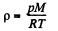
So, at constant temperature from these two Eqs.
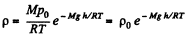 (1)
(1)
Eq. (1) shows that density varies with height in the same manner as pressure. Let us consider the mass element of the gas contained in the coltimn.
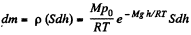
Hence the sought mass,
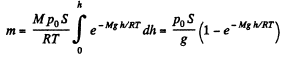
Q. 18. An ideal gas of molar mass M is contained in a very tall vertical cylindrical vessel in the uniform gravitational field in which the free-fall acceleration equals g. Assuming the gas temperature to be the same and equal to T, find the height at which the centre of gravity of the gas is located.
Solution. 18. As the gravitational field is constant the centre of gravity and the centre of mass are same. The location of C.M.
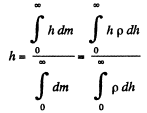
But from Barometric formula and gas law 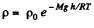
So, 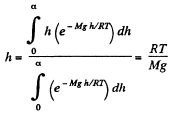
Q. 19. An ideal gas of molar mass /If is located in the uniform gravitational field in which the free-fall acceleration is equal to g. Find the gas pressure as a function of height h, if p = p0 at h = 0, and the temperature varies with height as
(a) T = T0 (1 — ah); (b) T = T0 (1 + ah),
where a is a positive constant.
Solution. 19. (a) We know that the variation of pressure with height of a fluid is given by :
dp = - p g dh
But from gas law 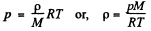
From these two Eqs.
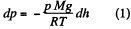
or, 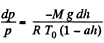
Integrating, 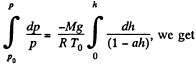
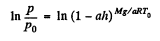
Hence, 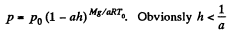
(b) Proceed up to Eq. (1) of part (a), and then put 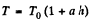 and proceed further in the same fashion to get
and proceed further in the same fashion to get
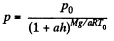
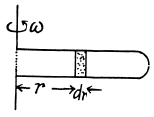
Q. 20. A horizontal cylinder closed from one end is rotated with a constant angular velocity ω about a vertical axis passing through the open end of the cylinder. The outside air pressure is equal to P0, the temperature to T, and the molar mass of air to M. Find the air pressure as a function of the distance r from the rotation axis. The molar mass is assumed to be independent of r.
Solution. 20. Let us consider the mass element of the gas (thin layer) in the cylinder at a distance r from its open end as shown in the figure.
Using Newton’s second law for the element
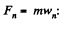
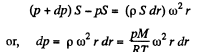
So, 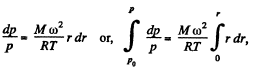
Thus, 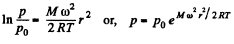
Q. 21. Under what pressure will carbon dioxide have the density p = 500 g/1 at the temperature T = 300 K? Carry out the calculations both for an ideal and for a Van der Waals gas.
Solution. 21. For an ideal gas law
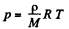
So, 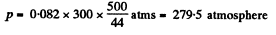
For Vander Waal gas Eq.
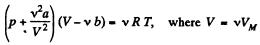
or, 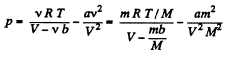
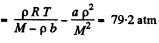
Q. 22. One mole of nitrogen is contained in a vessel of volume V = 1.00 1. Find:
(a) the temperature of the nitrogen at which the pressure can be calculated from an ideal gas law with an error η = 10% (as compared with the pressure calculated from the Van der Waals equation of state);
(b) the gas pressure at this temperature.
Solution. 22. 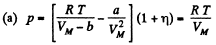
(The pressure is less for a Vander Waal gas than for an ideal gas)
or, 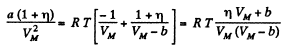
or, 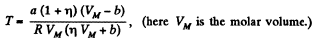
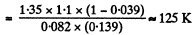
(b) The corresponding pressure is
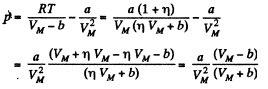
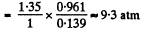
Q. 23. One mole of a certain gas is contained in a vessel of volume V = 0.250 1. At a temperature T1 = 300 K the gas pressure is p1 = 90 atm, and at a temperature T2 = 350 K the pressure is p2 = 110 atm. Find the Van der Waals parameters for this gas.
Solution. 23. 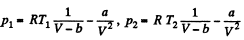
So, 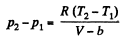
or. 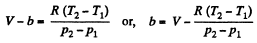
Also, 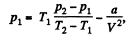
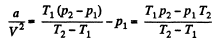
or, 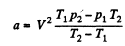
Using T1 = 300 K, p1 = 90 atms, T2 = 350 K, p2 = 110 atm, V = 0.250 litre
a = 1.87 atm. litre2/mole2, b = 0.045 litre/mole
Q. 24. Find the isothermal compressibility x of a Van der Waals gas as a function of volume V at temperature T.
Note. By definition 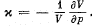
Solution. 24. 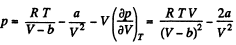
or, 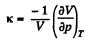
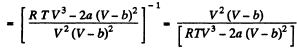
Q. 25. Making use of the result obtained in the foregoing problem, find at what temperature the isothermal compressibility x of a Van der Waals gas is greater than that of an ideal gas. Examine the case when the molar volume is much greater than the parameter b.
Solution. 25. For an ideal gas 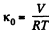
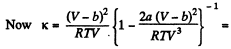
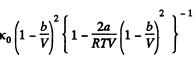

Now 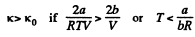
If a, b do not vary much with temperature, then the effect at high temperature is clearly determined by b and its effect is repulsive so compressibility is less.
|
97 videos|379 docs|103 tests
|
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Equation of The Gas State Processes - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the equation of state for an ideal gas? |  |
| 2. How does the equation of state for an ideal gas relate to the gas state processes? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the gas state processes in understanding the behavior of gases? |  |
| 4. How can the equation of state be used to solve problems related to gas state processes? |  |
| 5. Are there any limitations to the ideal gas equation of state? |  |























