Irodov Solutions: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Heat Capacity - 2 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q. 44. Demonstrate that the process in which the work performed by an ideal gas is proportional to the corresponding increment of its internal energy is described by the equation pVn = const, where n is a constant.
Solution. 44. According to the problem : A α U or dA = aU (where a is proportionality constant)
or, 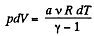 (1)
(1)
From ideal gas law, pV= v R T, on differentiating
pdV + Vdp = v RdT (2)
Thus from (1) and (2)
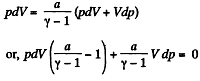
or, 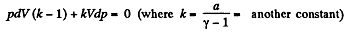
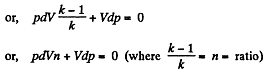
Dividing both the sides by pV
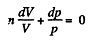
On integrating n In V + In p = In C (where C is constant)
or, 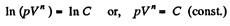
Q. 45. Find the molar heat capacity of an ideal gas in a polytropic process pVn = const if the adiabatic exponent of the gas is equal to γ. At what values of the polytropic constant n will the heat capacity of the gas be negative?
Solution. 45. In the polytropic process work done by the gas
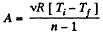
(where Ti and Tf are initial and final temperature of the gas like in adiabatic process)
and 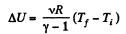
By the first law of thermodynamics Q = ΔU + A
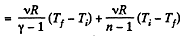
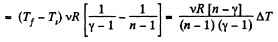
According to definition of molar heat capacity when number of moles v = 1 and ΔT = 1 then Q = Molar heat capacity.
Here, 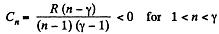
Q. 46. In a certain polytropic process the volume of argon was increased α = 4.0 times. Simultaneously, the pressure decreased β = 8.0 times. Find the molar heat capacity of argon in this process, assuming the gas to be ideal.
Solution. 46. Let the process be polytropic according to the law pVn = constant
Thus, 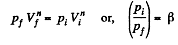
So, 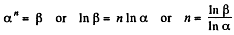
In the polytropic process molar heat capacity is given by
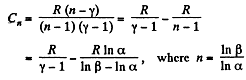
So, 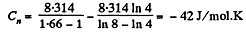
Q. 47. One mole of argon is expanded polytropically, the polytropic constant being n = 1.50. In the process, the gas temperature changes by ΔT = — 26 K. Find:
(a) the amount of heat obtained by the gas;
(b) the work performed by the gas
Solution. 47. (a) Increment of internal energy for ΔT, becomes
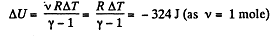
From first law of thermodynamics
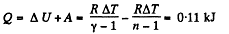
(b) Sought work done, 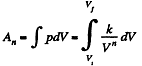
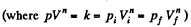
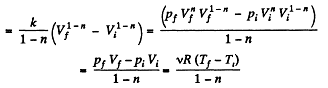
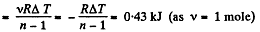
Q. 48. An ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent equals y is expanded according to the law p = αV , where a is a constant. The initial volume of the gas is equal to V0. As a result of expansion the volume increases η times. Find:
(a) the increment of the internal energy of the gas;
(b) the work performed by the gas;
(c) the molar heat capacity of the gas in the process.
Solution. 48. LaW 0f the process is p = α V or pV-1 = α
so the process is polytropic of index n = - 1
As p = αV so, Pi - αV0 and pf = α η V0
(a) Increment of the internal energy is given by
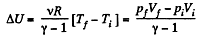
(b) Work done by the gas is given by

(c) Molar heat capacity is given by
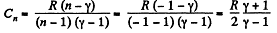
Q. 49. An ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent equals γ is expanded so that the amount of heat transferred to the gas is equal to the decrease of its internal energy. Find:
(a) the molar heat capacity of the gas in this process;
(b) the equation of the process in the variables T, V;
(c) the work performed by one mole of the gas when its volume increases η times if the initial temperature of the gas is T0.
Solution. 49. 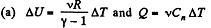
where Cn is the molar heat capacity in the process. It is given that 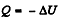
So, 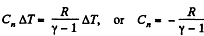
(b) By the first law of thermodynamics, dQ - dU + dA,
or, 
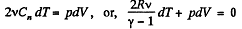
So, 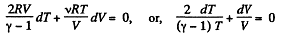
or, 
(c) 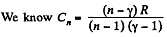
But from part (a), we have 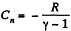
Thus 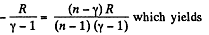
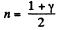
From part (b); we know 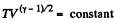
So, 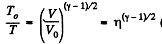 (where T is the final temperature)
(where T is the final temperature)
Work done by the gas for one mole is given by
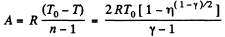
Q. 50. One mole of an ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent equals y undergoes a process in which the gas pressure relates to the temperature as p = aTα, where a and α are constants. Find:
(a) the work performed by the gas if its temperature gets an increment ΔT;
(b) the molar heat capacity of the gas in this process; at what value of α will the heat capacity be negative?
Solution. 50. Given p = a Tα (for one mole of gas)
So, 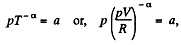
or, 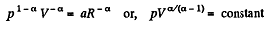
Here polytropic exponent 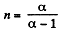
(a) In the poly tropic process for one mole of gas :
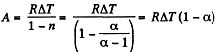
(b) Molar heat capacity is given by
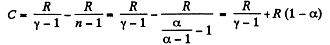
Q. 51. An ideal gas with the adiabatic exponent γ undergoes a process in which its internal energy relates to the volume as U = aVα, where a and α are constants. Find:
(a) the work performed by the gas and the amount of heat to be transferred to this gas to increase its internal energy by ΔU;
(b) the molar heat capacity of the gas in this process.
Solution. 51.
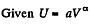
or, 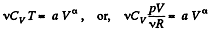
or, 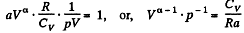
or 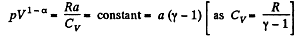
So polytropric index n = 1 - α
(a) Work done by the gas is given by
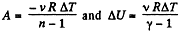
Hence 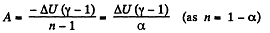
By the first law of thermodynamics, Q = ΔU+A
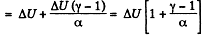
(b) Molar heat capacity is given by
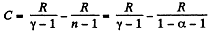
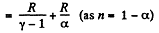
Q. 52. An ideal gas has a molar heat capacity Cv at constant volume. Find the molar heat capacity of this gas as a function of its volume V, if the gas undergoes the following process:
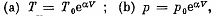
Solution. 52. By the first law .of thermodynamics
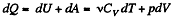
Molar specific heat according to definition
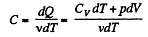
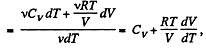
We have 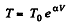
After differentiating, we get 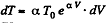
So, 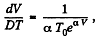
Hence 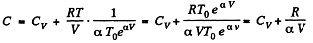
(b) 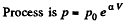
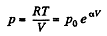
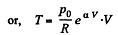
So, 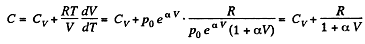
Q. 53. One mole of an ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent equals γ undergoes a process p = p0 + α /V, w here P0 and α are positive constants. Find:
(a) heat capacity of the gas as a function of its volume;
(b) the internal energy increment of the gas, the work performed by it, and the amount of heat transferred to the gas, if its volume increased from V1 to V2.
Solution. 53. Using 2.52
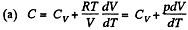 (for one mole of gas)
(for one mole of gas)
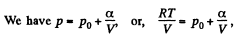
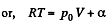
Therefore 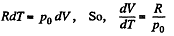
Hence 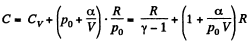

(b) Work done is given by
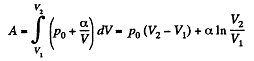
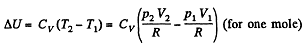
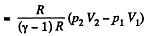
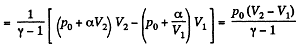
By the first law of thermodynamics Q = ΔU +A
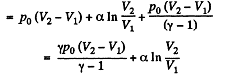
Q. 54. One mole of an ideal gas with heat capacity at constant pressure Cp undergoes the process T = T0 + αV, where T0 and α are constants. Find:
(a) heat capacity of the gas as a function of its volume;
(b) the amount of heat transferred to the gas, if its volume increased from V1 to V2.
Solution. 54. (a) Heat capacity is given by
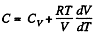 (see solution of 2.52)
(see solution of 2.52)
We have 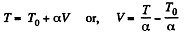
After differentiating, we get, 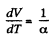
Hence 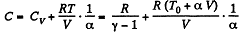
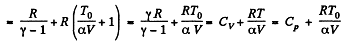
(b) 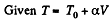
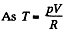 for one mole of gas
for one mole of gas
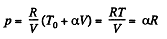
Now 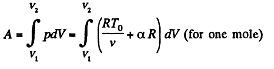
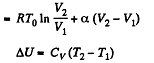
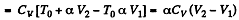
By the first law of thermodynamics Q = ΔU + A
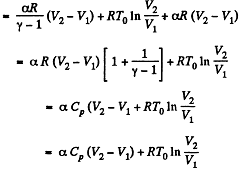
Q. 55. For the case of an ideal gas find the equation of the process (in the variables T, V) in which the molar heat capacity varies as:
(a) C = Cv + αT; (b) C = Cv + βV; (c) C = Cv + ap, where α, β, and a are constants.
Solution. 55. Heat capacity is given by 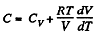
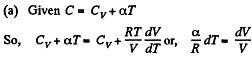
Integrating both sides, we get  is a constant.
is a constant.
Or, 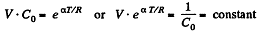
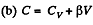
and 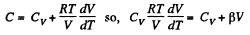
or, 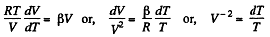
Integrating both sides, we get 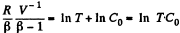
So, 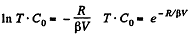
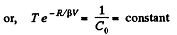
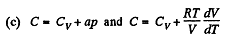
So, 
or 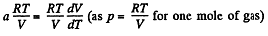
or, 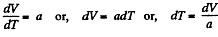
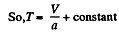 or V - a T = constant
or V - a T = constant
Q. 56. An ideal gas has an adiabatic exponent γ. In some process its molar heat capacity varies as C = α/T, where α is a constant. Find:
(a) the work performed by one mole of the gas during its heating from the temperature T0 to the temperature η times higher;
(b) the equation of the process in the variables p, V.
Solution. 56. (a) By the first law of thermodynamics A = Q - ΔU
or, 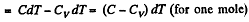
Given 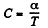
So, 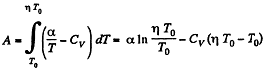
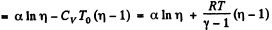
(b) 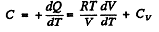
Given 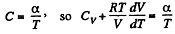
or, 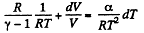
or, 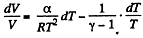
or, 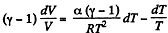
Integrating both sides, we get
or, 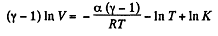
or, 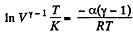
or, 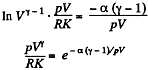
or, 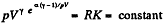
Q. 57. Find the work performed by one mole of a Van der Waals gas during its isothermal expansion from the volume V1 to V2 at a temperature T.
Solution. 57. The work done is
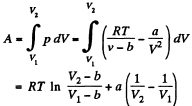
Q. 58. One mole of oxygen is expanded from a volume V1 = 1.00 1 to V2 = 5.0 l at a constant temperature T = 280 K. Calculate:
(a) the increment of the internal energy of the gas:
(b) the amount of the absorbed heat.
The gas is assumed to be a Van der Waals gas.
Solution. 58. (a) The increment in the internal energy is
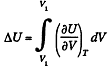
But from second law
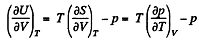
On the other hand 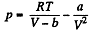
or, 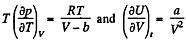
So, 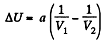
(b) From the first law
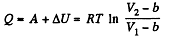
Q. 59. For a Van der Waals gas find:
(a) the equation of the adiabatic curve in the variables T, V;
(b) the difference of the molar heat capacities Cp, — Cv as a function of T and V.
Solution. 59. (a) From the first law for an adiabatic
dQ = dU + pd V = 0
From the previous problem
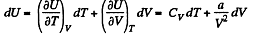
So, 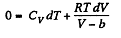
This equation can be integrated if we assume that Cv and b are constant then
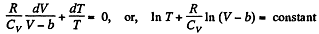
or, 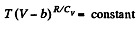
(b) We use
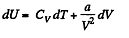
Now, 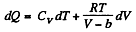
So along constant p, 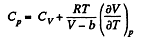
Thus 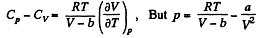
On differentiating, 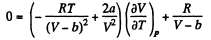
or, 
and 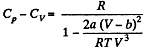
Q. 60. Two thermally insulated vessels are interconnected by a tube equipped with a valve. One vessel of volume V1 = 10 l contains v = 2.5 moles of carbon dioxide. The other vessel of volume V2 = 100 l is evacuated. The valve having been opened, the gas adiabatically expanded. Assuming the gas to obey the Van der Waals equation, find its temperature change accompanying the expansion.
Solution. 60. From the first law
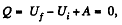 as the vessels are themally insulated.
as the vessels are themally insulated.
As this is free expansion, 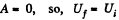
But 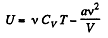
So, 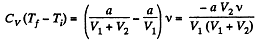
or, 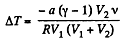
Substitution gives ΔT = - 3 K
Q. 61. What amount of heat has to be transferred to v = 3.0 moles of carbon dioxide to keep its temperature constant while it expands into vacuum from the volume V1 = 5.0 l to V2 = 10 l ? The gas is assumed to be a Van der Waals gas.
Solution. 61. 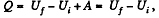 (as A = 0 in free expansion).
(as A = 0 in free expansion).
So at constant temperature.
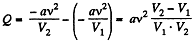
= 0.33 kJ from the given data.
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Heat Capacity - 2 - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is the first law of thermodynamics? |  |
| 2. How is heat capacity defined? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of heat capacity in thermodynamics? |  |
| 4. How is heat capacity different from specific heat capacity? |  |
| 5. Can heat capacity be negative? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|


















